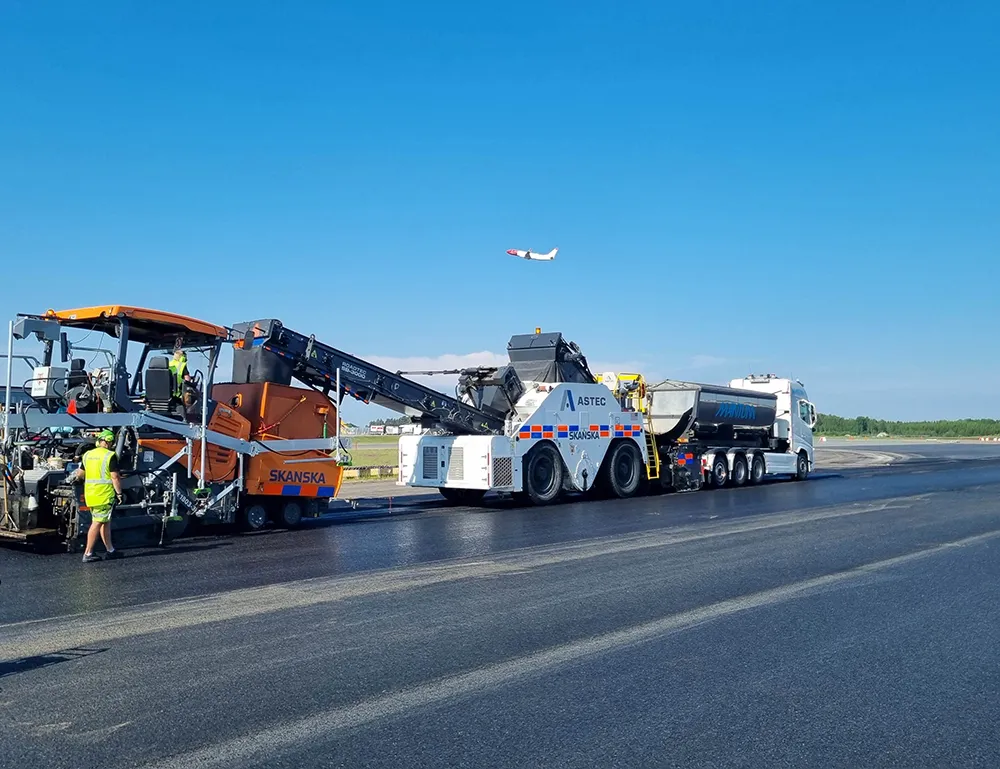
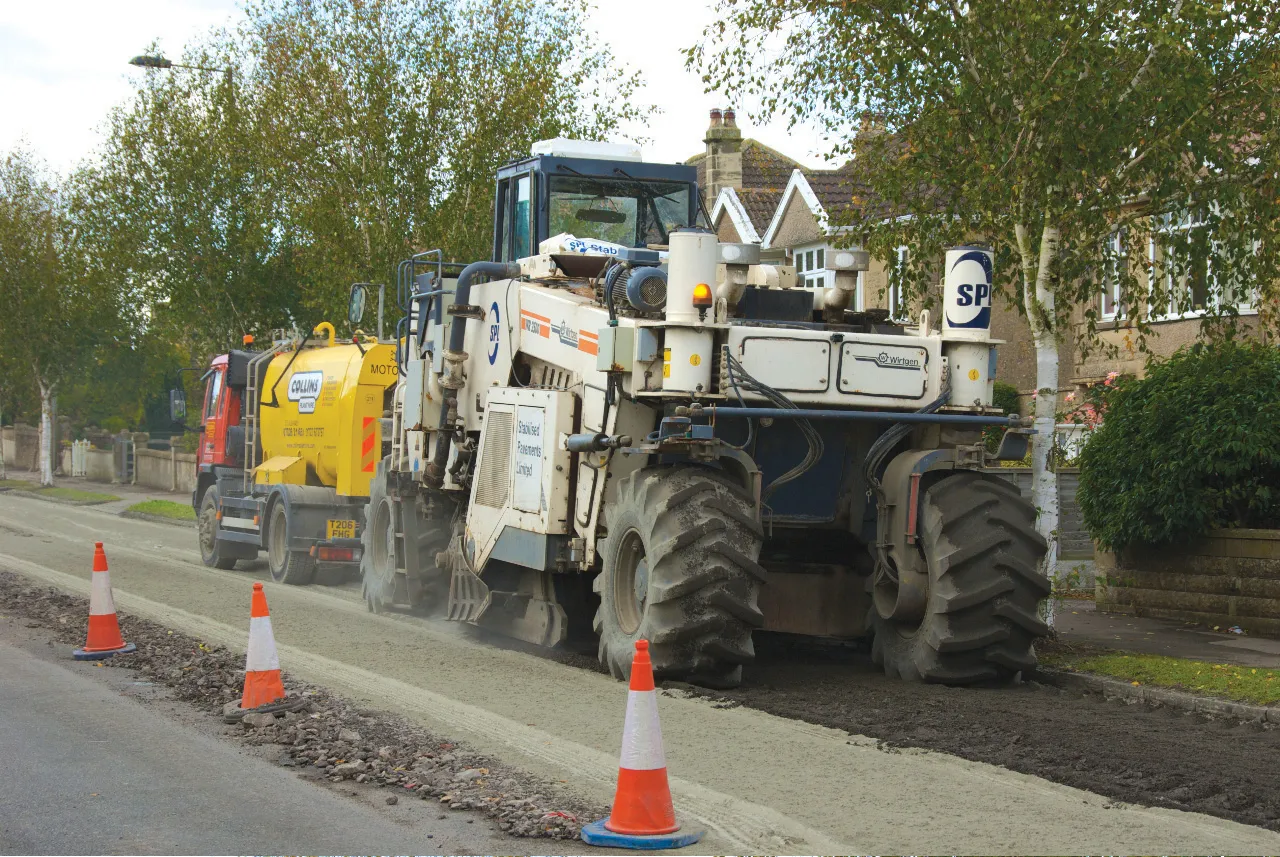
Increases in mobility and loads to which roadways are subjected has led, over the past decade, to new technologies for increasing the life of highly stressed pavements.
Alongside traditional layers in asphalt concrete with normal or modified binders, there are new technologies which make it possible to produce high performance bituminous layers through the use of polyfunctional polymeric systems (PPSs).
These systems are multifunctional compounds formed of fibers and polymers joined in a single pellet.
Resulting from several years of research by
Polyfunctional Polymeric Systems (PPSs) are made from a compound of fibers of differing nature, plastomeric or elastomeric polymers, paraffinic compounds, liquid components and other additives (depending on the type and purpose of the PPS). They are manufactured in pellets to reduce dosing problems.
Each type of fiber selected for the compound has a specific behavior.
Traditional fibers serve to thicken and stabilise the mastic - filler plus bitumen. They are usually made from micro-fibers of cellulose origin.
Multipurpose fibers consist of various types of cellulose, mineral and synthetic micro-fibers. In addition to the functions of traditional fibers, they have a structuring effect that ensures greater resistance to fatigue and complex modulus.
PPSs act simultaneously on several properties, causing a physical and chemical modification in bituminous mixtures. In particular, they acting on the characteristics of the bitumen, for example penetration, softening point and viscosity, and create a micro-structural reinforcement of the bitumen film.
Another feature is the method of use. Pellets are used in the production phase of asphalt concrete, allowing the modification of the mixture directly inside the mixer.
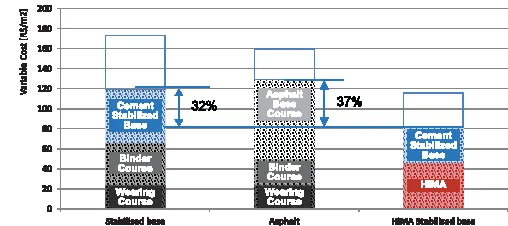
This technology is extremely versatile and can be used even in poorly served geographically areas. It has also, in the past year, been particularly successful in various pavements, especially in Italy where it has been used for high modulus binder, draining and wearing layers. It has also combined with other types of additives with the function of uniting the advantages of warm mix to those related to the use of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP).
In particular, they are being widely used in split mastic asphalt (SMA) and in highly modified wearing courses. These bituminous mixtures, in addition to having a granulometric grading as reference, require high percentages of bitumen and high performance levels achieved through the use of polymers.
On the other hand, the use of fibers - mostly composed of cellulose - is necessary to prevent the percolation of the bitumen, in addition to having a stabilising and structuring effect. In particular, this technology has also been used for the construction of the A53 (Pavia-Bereguardo) motorway in Italy. This project involved the expansion of the area around the city of Bereguardo, at the A7 Milano-Genova motorway, improving the western ring road of Pavia, for about 9.5km. Work includes the modification of the road due to heavy traffic. Completion is scheduled for mid-2016.
More specifically, the new project includes both the expansion of the existing pavement and the construction of the roadway’s pavement structure:
- Mix stabilised in situ with recycled materials, polypropylene fibrillated fiber-reinforced;
- Base binder, high modulus with PPS (BBHM) = 9 cm;
- High-modulus wear layer with PPS (UHM) = 9 cm.