The Court of Justice of the European Union has said Denmark’s state grant aid to the proposed Fehmarn Belt link is illegal under EU rules.
The court noted that the European Commission approved the Fehmarn project’s financing – total cost likely around the €8.7 billion - in July 2015 without a formal procedure.
Denmark is completely responsible for financing the project that will replace a ferry service. Part of the funds were to come through the European Union and its Connecting Europe Facility for transportation.
Ferry operators Scandlines and Stena Line which provide services between Europe and the Scandinavian peninsula, argued in the European Court that the grant level to be given to whichever company operating the toll structure is based on unrealistically high traffic volume predictions.
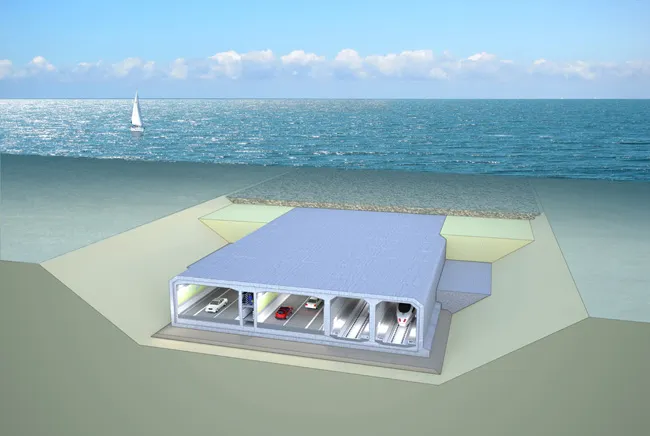
The Fehmarn Belt is a strait between the German island of Fehmarn and the Danish island of Lolland. Ferries connects the islands in the region. Completion of the €8.7 billion project has been set for 2028. However, even before the European Court ruling, the project’s approval process had been bogged down over environmental issues, especially within the German state of Schleswig-Holstein in which the southern end of 18km immersed tunnel will surface.
“We are satisfied with the ruling of the Court of Justice of the European Union. (…) Scandlines is not against a Fehmarn connection established with state aid. State aid may be necessary when completing such large-scale projects,” said Søren Poulsgaard Jensen, chief executive of Scandlines.
“However, we do expect correct procedure, which entails transparency and fair competition. The aid must therefore be accurately and realistically defined, and it must be based on consistent assumptions and safeguarded against abuse. It is decisive for us that the tunnel cannot use the state finances as its sees fit to impose taxpayer-financed price pressure when traffic volumes do not live up to the optimistic prognoses and the ferries appear competitive.”
The arguments are in line with Stena Line’s appeal which questioned the necessity of the aid, the duration of the aid and the undue distortion to the market by allowing the Fehmarn fixed link to dramatically reduce prices.
“In this case State aid has been granted illegally. That’s why we welcome the decision from the court to annul the aid granted by the Commission for the construction of the Fehmarn Belt connection,” said Claes Berglund, director public affairs and sustainability for Stena.
A Rambøll-Arup-TEC consultancy joint venture is engaged in a client consultancy services contract with
A second framework contract, for technical support services to Femern, is being carried out by ÅF-Hansen & Henneberg.







