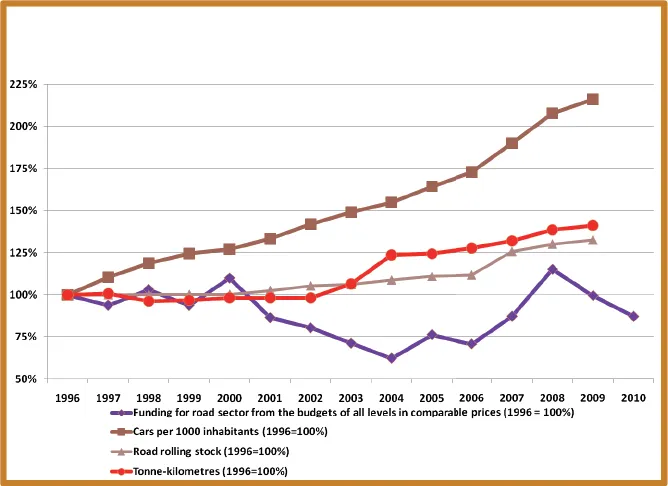
This resulted is government net a windfall of nearly €108 billion, noted the study commissioned by FIA (Federation Internationale de l'Automobile). It also shows that passenger car drivers contributed 71% of road taxes, for a total €205.8 billion of the overall €286.3 billion.
While the revenue from road transport amounted to 2-3% of national gross domestic product (GDP), the expenditure of governments averaged only 0.8% of GDP
In addition to covering the costs that road networks require, road taxes and charges are reinvested in society at large and could also be used to tackle the social costs of road transport.
As the European Commission considers enabling additional charges to fund infrastructure and manage road use, FIA calls for a re-examination of the revenue that is already generated before road users are burdened with new or increased charges on their daily mobility.
Thierry Willemarck, a FIA region president, said European motorists make a significant contribution to public budgets, far beyond the revenue needed to cover the costs of the road network. “This should be acknowledged and their investment used to ensure a safe road network that sufficiently supports the needs of daily commuters.”
Violeta Bulc, European Commissioner for Transport, said more investment is needed. “The European Commission will be carrying out a case study on road taxes and charges,” she said. “We will examine the FIA’s results and build on its conclusions to ensure that road users are fairly charged in a transparent manner.
Our aim is to create a level playing field, which supports interoperability and multimodal use of the transport network."
EU governments make surplus from road taxes, a FIA study finds
European Union governments took in €286.3 billion in road taxes during 2013 but re-invested only €178 billion back into highways, according to a new study.
November 9, 2016
Read time: 2 mins