The European Commission has published proposals setting strict limits on exhaust emissions for off-highway machinery. This proposal has major implications for the construction machinery sector and would make the EU exhaust emissions limits the strictest in the world. There has been a call for swift reading of the regulation in Parliament and Council. This long-anticipated proposal for a revision of the directive 97/68/EC, covers exhaust emissions reduction for engines installed in non-road mobile machinery.
October 3, 2014
Read time: 3 mins
The 2465 European Commission has published proposals setting strict limits on exhaust emissions for off-highway machinery. This proposal has major implications for the construction machinery sector and would make the EU exhaust emissions limits the strictest in the world. There has been a call for swift reading of the regulation in Parliament and Council. This long-anticipated proposal for a revision of the directive 97/68/EC, covers exhaust emissions reduction for engines installed in non-road mobile machinery. In the construction equipment sector, the regulation applies to a wide variety of machines, from hand-held equipment to the largest mining machine. The key elements of the regulation for the sector are that it has been set with introductory dates of 2019 to 2020 and brings limit values that will reduce emissions to extremely low levels. Furthermore, there will be an unprecedented rate of introduction across the entire power range of equipment, irrespective of combustion cycle and fuel. “We welcome that highly-essential requirements are met, such as a predictable introduction pace and emission limits that acknowledge the vast technological progress made in the industry”, announced Eric Lepine, president of CECE (the 1181 European Committee for Construction Equipment) and managing director of 178 Caterpillar France. “But the proposal certainly needs further studying and refining, in particular with regard to further provisions for replacement engines and the concerns of niche equipment manufacturers.”
Lepine emphasized that the construction equipment industry is working hard to provide its customers with machines offering the highest productivity and lowest environmental impact. However, delivering the next generation of machines to the market in time will remain a complex challenge. “Product cycles are long and product diversity is huge, putting a tremendous strain on development time,” said Lepine. The sector calls on the European Parliament and Council to facilitate a swift reading of the proposal, in order to secure sufficient lead-time ahead of the legislation entering into force.
CECE points out that European manufacturers of construction equipment, many of them niche producers or SMEs, already produce the cleanest and safest machinery in the world. They need economy of scale to stay competitive in a global environment and maintain profitable manufacturing sites in Europe. “The global market for highly-regulated products is in comparative terms quite small. Europe cannot afford to deviate too much from requirements in other ambitious nations in this field”, said Lepine. “We urge the EU to maintain alignment in standards and limits with other regions, notably with the US, and actively promote worldwide alignment.”
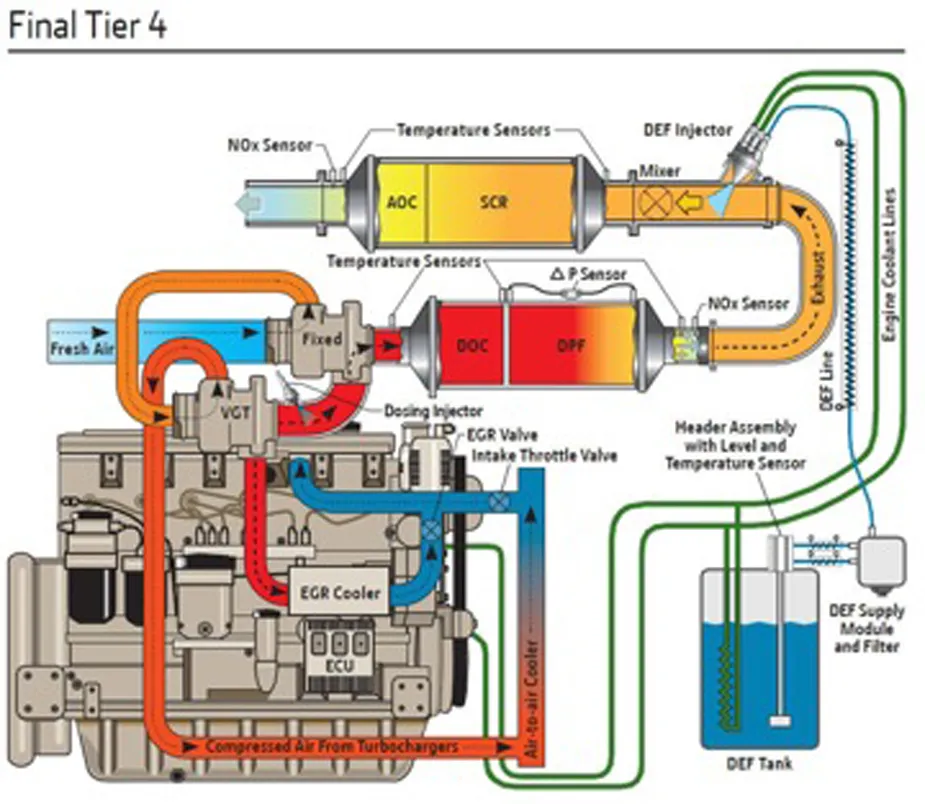
The revision of the directive 97/68/EC fits into a regulatory process that started in the early 1990s and that saw several revisions since. Stakeholders have been closely involved in the directive’s review process, providing the legislator with essential technical background and data. The most recent changes have come into force only this very year, with the introduction of stage IV, already reducing the mass of NOx and particulates from new engines by more than 95% compared to 15 years ago. The next stage will bring more equipment into scope, reduce the mass of emissions further, and will additionally target the number of small particles emitted. This is expected to result in increased use of diesel particle filters (DPFs) on engine exhausts.
Lepine emphasized that the construction equipment industry is working hard to provide its customers with machines offering the highest productivity and lowest environmental impact. However, delivering the next generation of machines to the market in time will remain a complex challenge. “Product cycles are long and product diversity is huge, putting a tremendous strain on development time,” said Lepine. The sector calls on the European Parliament and Council to facilitate a swift reading of the proposal, in order to secure sufficient lead-time ahead of the legislation entering into force.
CECE points out that European manufacturers of construction equipment, many of them niche producers or SMEs, already produce the cleanest and safest machinery in the world. They need economy of scale to stay competitive in a global environment and maintain profitable manufacturing sites in Europe. “The global market for highly-regulated products is in comparative terms quite small. Europe cannot afford to deviate too much from requirements in other ambitious nations in this field”, said Lepine. “We urge the EU to maintain alignment in standards and limits with other regions, notably with the US, and actively promote worldwide alignment.”
The revision of the directive 97/68/EC fits into a regulatory process that started in the early 1990s and that saw several revisions since. Stakeholders have been closely involved in the directive’s review process, providing the legislator with essential technical background and data. The most recent changes have come into force only this very year, with the introduction of stage IV, already reducing the mass of NOx and particulates from new engines by more than 95% compared to 15 years ago. The next stage will bring more equipment into scope, reduce the mass of emissions further, and will additionally target the number of small particles emitted. This is expected to result in increased use of diesel particle filters (DPFs) on engine exhausts.