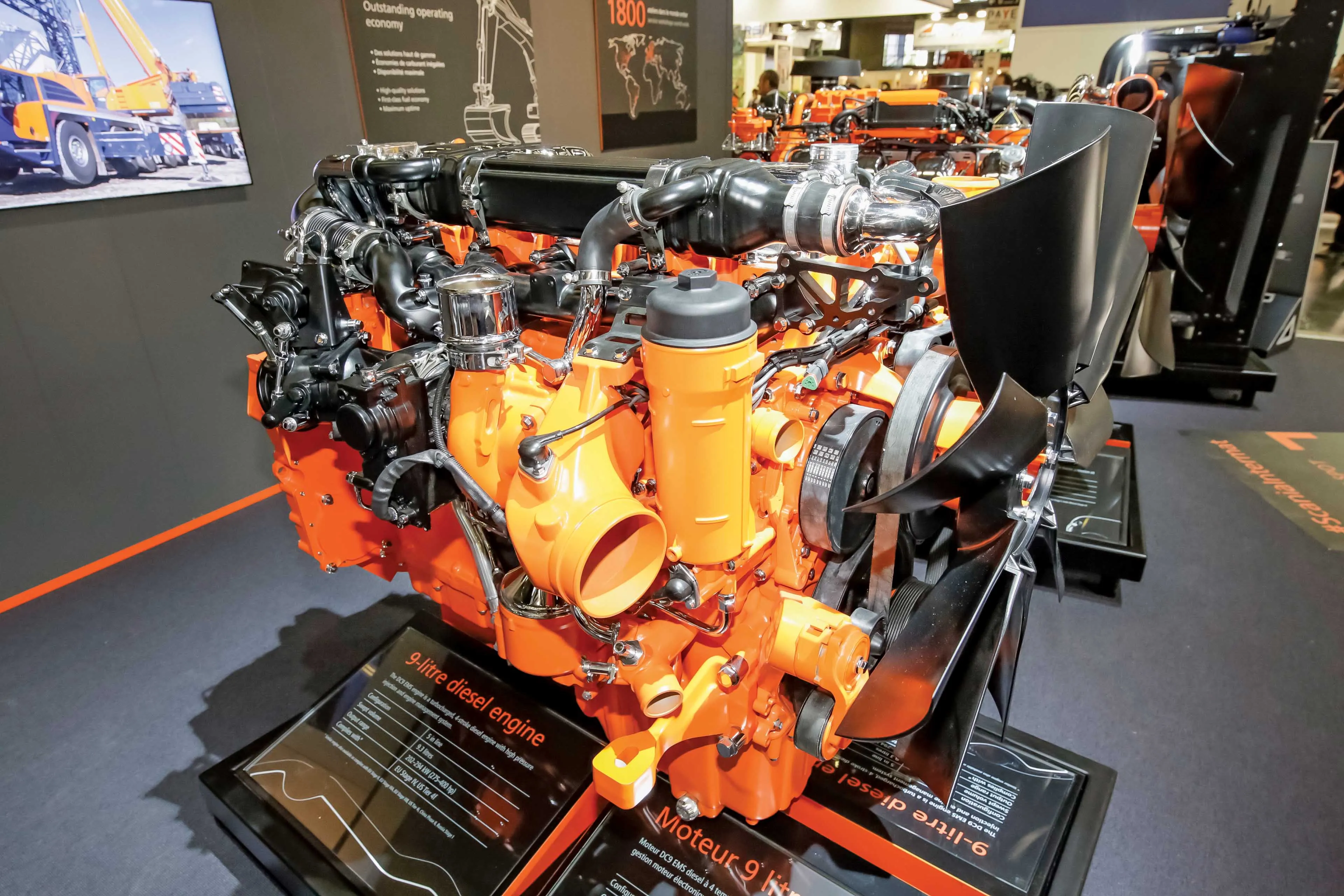
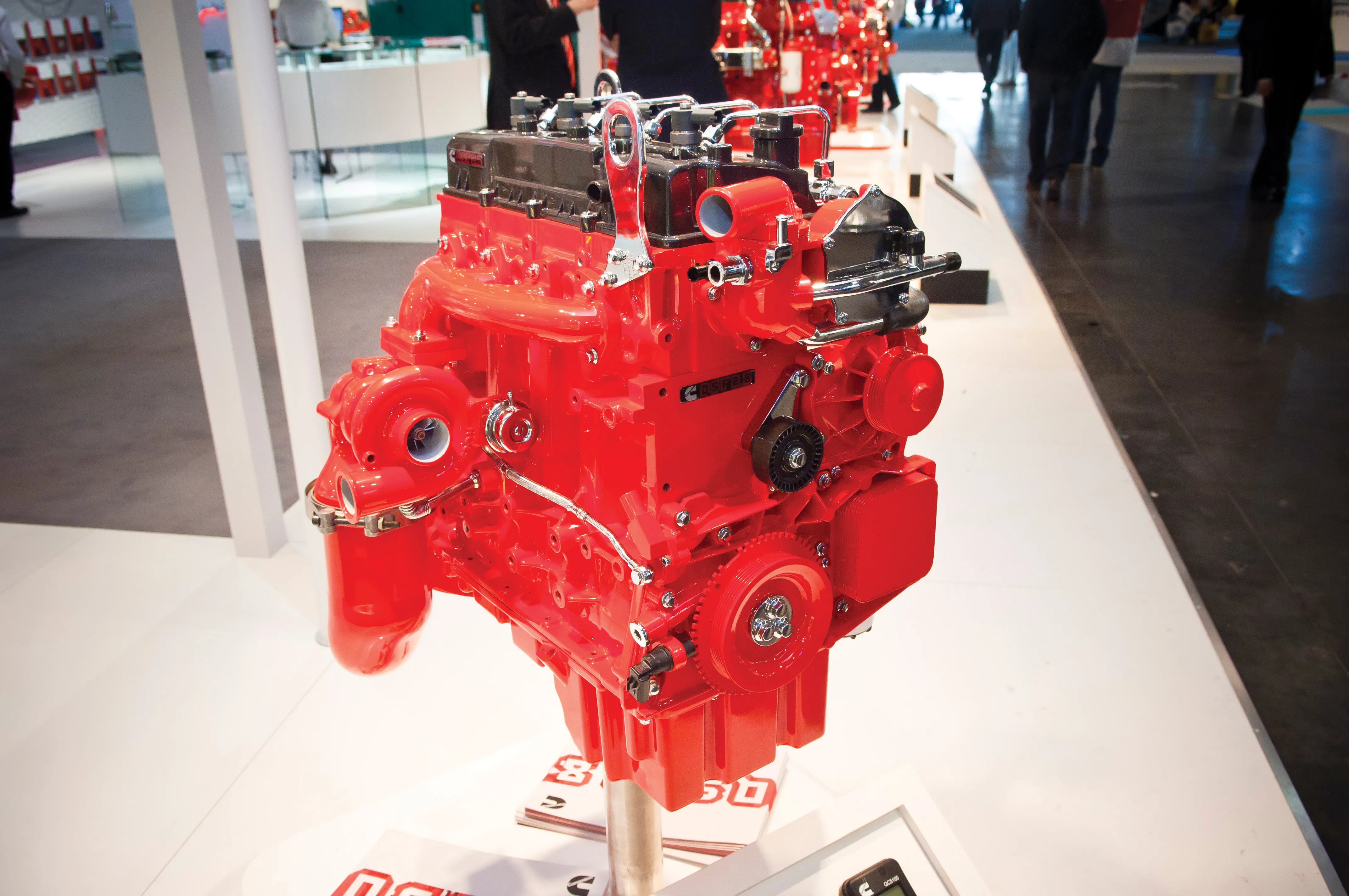
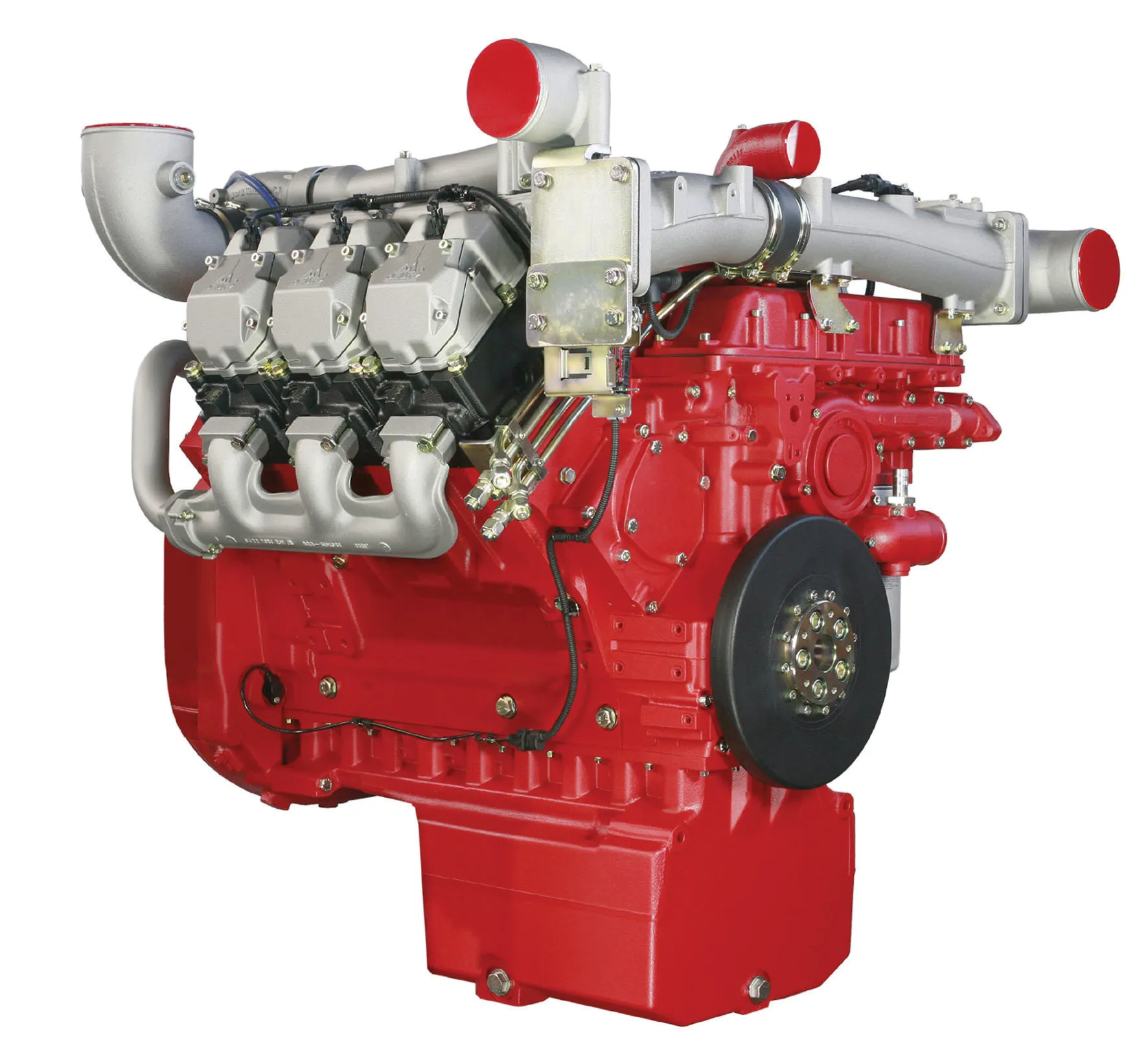
With the introduction of Stage V/Tier 5 emissions regulations set for 2019-2020, depending on engine power output,
For 2019, FPT’s Hi-eSCR system will integrate the diesel particulate filter (DPF) into the SCR unit. The particulate filter will replace part of the existing SCR catalyst, resulting in no additional space requirement for the OEM.
“We need to introduce a product of the same size, to avoid costly investment on the equipment manufacturer’s part,” said brand manager Douwe Hilarius.
FPT has also introduced its smallest engine for the off-highway sector, the R22. This three-cylinder, 2.2-litre engine complies with Stage IIIB/Tier 4 Final emissions standards and is available with 600 hour service intervals. The engine uses FPT’s space-saving Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) and Partial Flow Filter (PFF) in a single maintenance-free converter.
FPT Industrial ready for Stage V standard
With the introduction of Stage V/Tier 5 emissions regulations set for 2019-2020, depending on engine power output, FPT Industrial says that it will build upon its SCR-only strategy, remaining one of the few manufacturers not adopting Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) to meet the standard. The Italian firm’s Hi-eSCR after-treatment system, already in use on Stage IV/Tier 4 Final engines, maximises in-engine combustion technology without using EGR. This saves weight, cost and space for the equipment manufacture
January 6, 2017
Read time: 2 mins