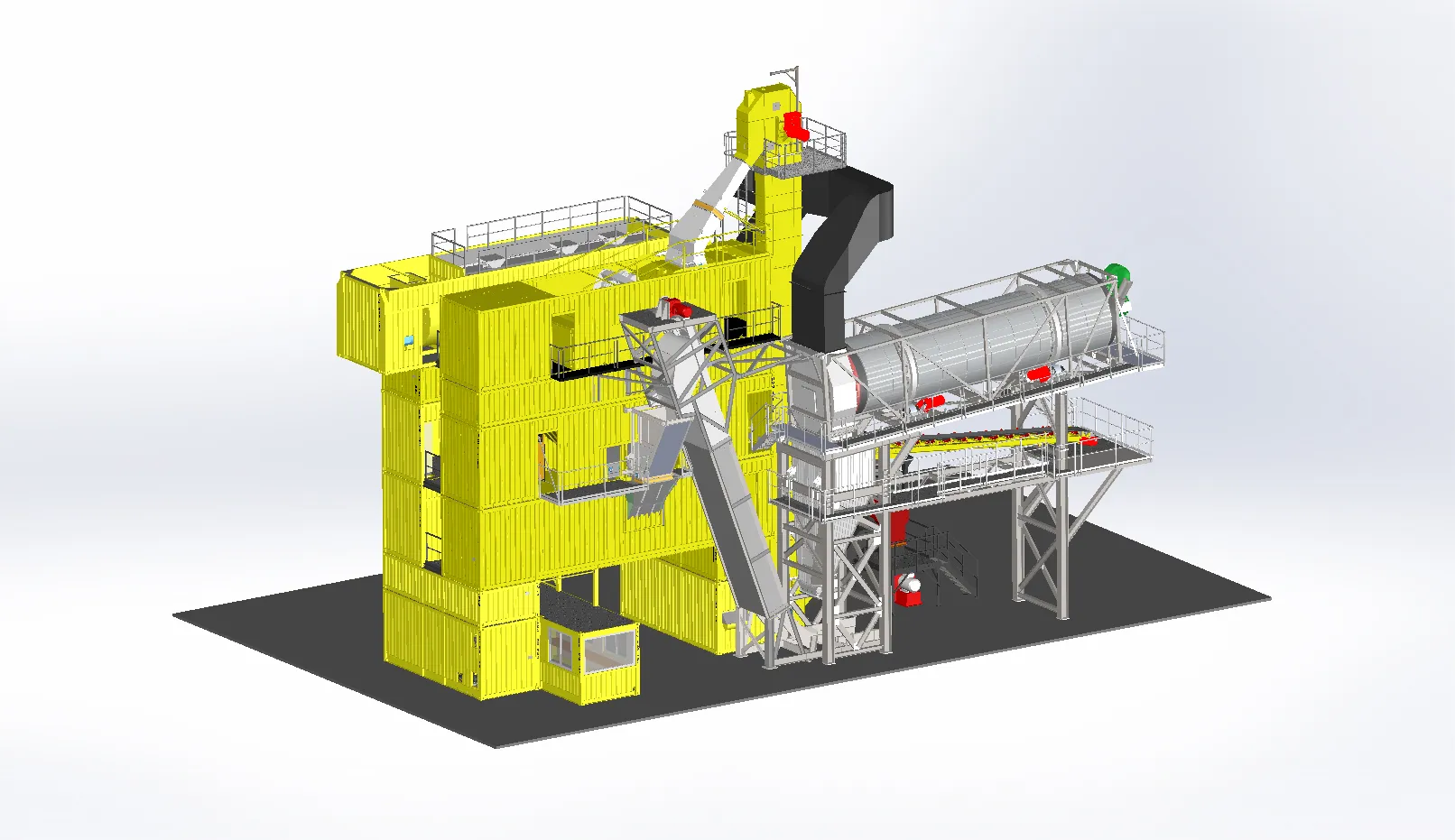
Standards are changing to allow higher percentages of RAP, and batch plant owners want to take advantage of the recycled material. But unsightly steam and dust can escape from the mixer.
The best way to counter this is to meter the amount of RAP being added to a batch system rather than adding it all at once. This is where Astec’s Batch RAP system comes into play.
“The trouble with running RAP in a batch plant is that if you just dump the RAP in fast, you have serious problems with steam,” according t
August 24, 2016
Read time: 3 mins

Standards are changing to allow higher percentages of RAP, and batch plant owners want to take advantage of the recycled material. But unsightly steam and dust can escape from the mixer.
The best way to counter this is to meter the amount of RAP being added to a batch system rather than adding it all at once. This is where1250 Astec’s Batch RAP system comes into play.
“The trouble with running RAP in a batch plant is that if you just dump the RAP in fast, you have serious problems with steam,” according to engineer Mike Varner, director of thermal systems and research for US-based Astec. “Water expands 1,700 times when it changes to steam and when that occurs over a few seconds, you create a huge amount of steam.”
Greg Renegar, chief engineer at Astec, says the plant’s exhaust system has no way to accommodate that steam. “The baghouse can’t handle the amount of steam produced when water and RAP are dropped in.”
According to Varner, the addition of 25% RAP to a 2.76tonne batch is the equivalent of adding 5%, or approximately 34kg, of moisture.
“That 34kg of moisture turns into almost 60m3 of steam,” says Varner. “A baghouse fan cannot suck hard enough to keep up with the steam. Dust and steam will come out of every crack at the top of the plant.”
By using the Batch RAP system rather than “dumping in” the RAP in a five-second time frame, recycled material is dribbled in at a rate of 1% of RAP per second.
With the variable speed for the feeder belt, which introduces RAP directly into the pug mill, the introduction of RAP is at a more reasonable level. Controlling the speed and rate that RAP is fed into super-heated virgin material means steam that comes off the RAP as it hits the superheated mix can be eliminated or contained and controlled.
Varner said more companies are running RAP to remain competitive with continuous-mix plants. The Batch RAP system enables plant owners to use RAP on an old batch plant, which originally wasn’t set up for RAP use. The computer monitoring system hooks into the existing computer controls.
In the north-eastern US, Varner says that RAP is available from milling several miles of roads, and older plants in that region of the country need additional RAP facilities. Also, continuous plants can run 30-40% of RAP, while batch plants typically don’t run RAP well.
“The whole intent of the Batch RAP system is to make the introduction of RAP as continuous as possible for a batch plant,” says Varner. “That means less strain on the exhaust system and makes the batch plant more like a continuous plant in respect to RAP.”
The best way to counter this is to meter the amount of RAP being added to a batch system rather than adding it all at once. This is where
“The trouble with running RAP in a batch plant is that if you just dump the RAP in fast, you have serious problems with steam,” according to engineer Mike Varner, director of thermal systems and research for US-based Astec. “Water expands 1,700 times when it changes to steam and when that occurs over a few seconds, you create a huge amount of steam.”
Greg Renegar, chief engineer at Astec, says the plant’s exhaust system has no way to accommodate that steam. “The baghouse can’t handle the amount of steam produced when water and RAP are dropped in.”
According to Varner, the addition of 25% RAP to a 2.76tonne batch is the equivalent of adding 5%, or approximately 34kg, of moisture.
“That 34kg of moisture turns into almost 60m3 of steam,” says Varner. “A baghouse fan cannot suck hard enough to keep up with the steam. Dust and steam will come out of every crack at the top of the plant.”
By using the Batch RAP system rather than “dumping in” the RAP in a five-second time frame, recycled material is dribbled in at a rate of 1% of RAP per second.
With the variable speed for the feeder belt, which introduces RAP directly into the pug mill, the introduction of RAP is at a more reasonable level. Controlling the speed and rate that RAP is fed into super-heated virgin material means steam that comes off the RAP as it hits the superheated mix can be eliminated or contained and controlled.
Varner said more companies are running RAP to remain competitive with continuous-mix plants. The Batch RAP system enables plant owners to use RAP on an old batch plant, which originally wasn’t set up for RAP use. The computer monitoring system hooks into the existing computer controls.
In the north-eastern US, Varner says that RAP is available from milling several miles of roads, and older plants in that region of the country need additional RAP facilities. Also, continuous plants can run 30-40% of RAP, while batch plants typically don’t run RAP well.
“The whole intent of the Batch RAP system is to make the introduction of RAP as continuous as possible for a batch plant,” says Varner. “That means less strain on the exhaust system and makes the batch plant more like a continuous plant in respect to RAP.”