A variety of innovative solutions are now available for increasing sustainability in asphalt production. Considering the entire road construction process from material acquisition and asphalt production to building the roads, companies can save up to 54% CO2 with these technologies. This is based on an annual production of 100,000tonnes asphalt and with the use of 60% of recycled materials in the feed as well as the use of carbon-neutral fuel.
The latest solutions include the reuse of asphalt, the correct storage of virgin mineral and recycling material, the use of temperature-reduced asphalt, the electrification of bitumen tanks and the use of renewable energies such as future fuels.
The 2015 Paris Climate Accords require greenhouse emissions to be halved by 2030 and eliminated completely by 2050. Despite being a relatively small sector, the asphalt industry can contribute because asphalt production offers potential for reducing emissions such as CO2 and Ctot (total carbon).
One of the control instruments for owners of mixing plants is the taxation of emitted CO2 and emissions trading, the costs of which will increase worldwide in the years to come. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions from asphalt plants will deliver cost savings.
The material removed by milling the asphalt during road resurfacing is also cheaper than virgin mineral from a quarry. In addition to this, reclaimed asphalt already contains bitumen, which is also reused and delivers further savings.
Different cold and hot recycling feed systems are available, including the firm’s hot-gas generator. This allows up to 100% recycling material to be added, with low emissions. The company’s patented REVOC system is a supplement for existing asphalt mixing plants equipped with one or more recycling systems and reduces the total carbon concentrations in the exhaust gas.
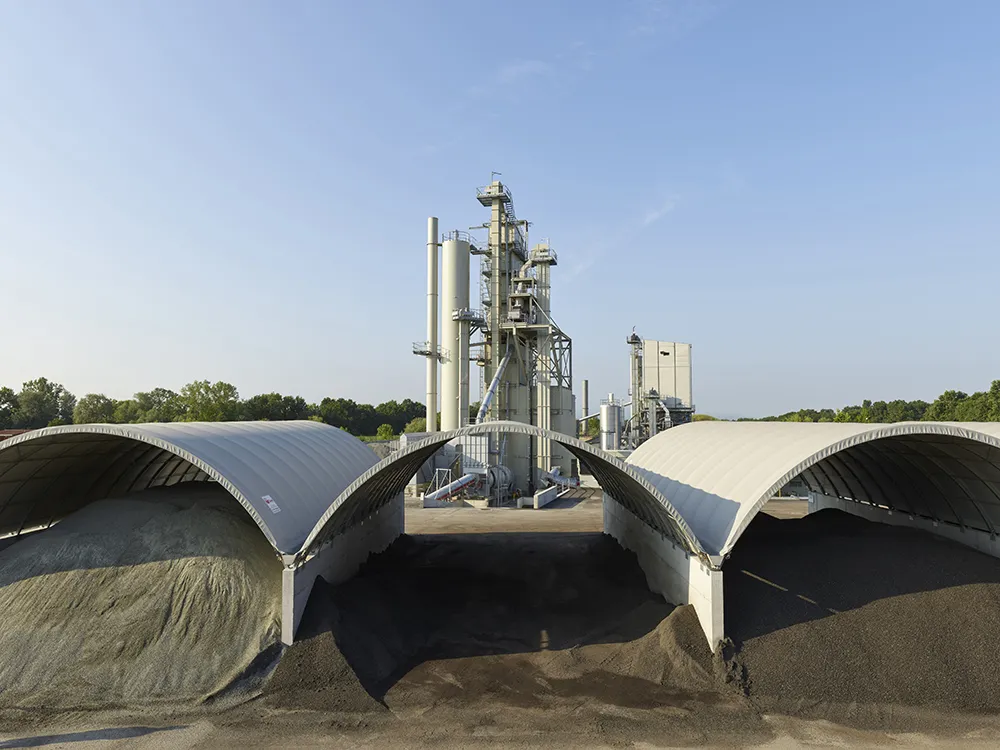
Keeping the stored virgin mineral and recycling material as dry as possible is an important factor for energy-efficient mixing and can further reduce CO2 emissions. Just 1% more moisture in the starting material corresponds to a litre of additional heating oil (or equivalent fuel) for each tonne of asphalt mix. This is one reason why the German TA-Luft regulation now requires covered storage of materials.

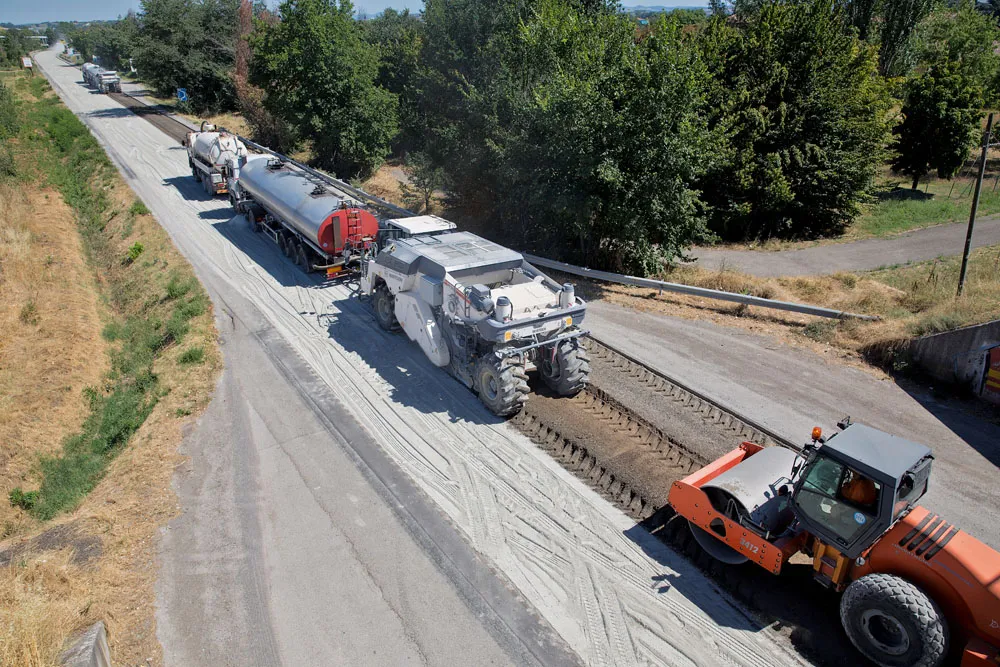
The drying and heating processes for virgin mineral and recycling material are energy-intensive in asphalt production. Fuel and emissions can be saved by the use of reduced-temperature asphalt: mixes with a final temperature of around 120°C. This can deliver a 30% fuel saving compared to conventional mixes, which usually require a temperature of around 160°C. The savings potential for energy and CO2 is greater: 18,000kWh and 6,000kg CO2 are saved during the production of 2,000tonnes of asphalt/day.
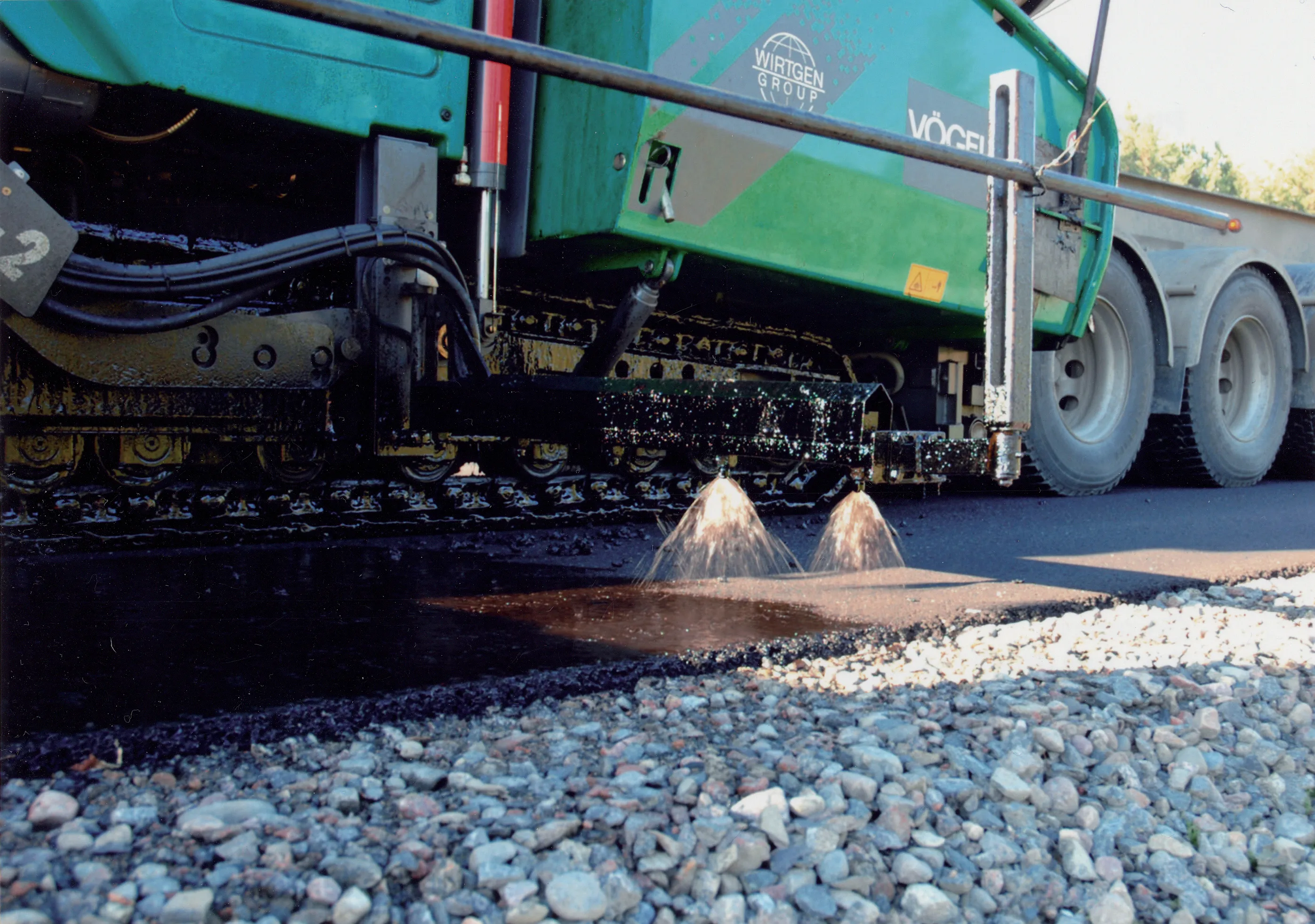
High-quality asphalt mixing plants can produce high-quality reduced-temperature asphalt in a reliable process. One important technology for this is a foam bitumen module, available as a retrofit solution. Foam bitumen requires water for producing reduced-temperature asphalt, which is already available at an asphalt plant anyway. Mixing hot bitumen with water multiplies the volume, which is why this process is also referred to as foaming bitumen. The released surface energy ensures that the binder moistens the mineral during the mixing process even at low temperatures, temporarily allowing workability comparable to hot asphalt.
The hot bitumen tanks are available with one or multiple chambers and can also be equipped with an agitator or a mixing nozzle and can be heated electrically to eliminate local emissions for CO2-neutral storage. In addition, electrically heated tanks are not regulated by environmental authorities and there are no restrictions.
More sustainability in asphalt production means moving away from fossil fuels such as coal and oil. The company already offers the EVO JET burners, which can use future fuels made from renewable raw materials with a neutral CO2 balance. They include biomass to liquid fuels (BtL) and wood dust. Even the complex process of burning wood dust results in a smooth flame pattern – the prerequisite for reliable operation of the plant.
The new burner technology can also be used for modern fossil, gaseous fuels such as liquid gas or natural gas. Changing from coal dust to natural gas or liquid gas already halves CO2 emissions.
In addition to this, the firm’s development engineers continue to work on the use of other fuel types and using hydrogen, could be one option for the future.