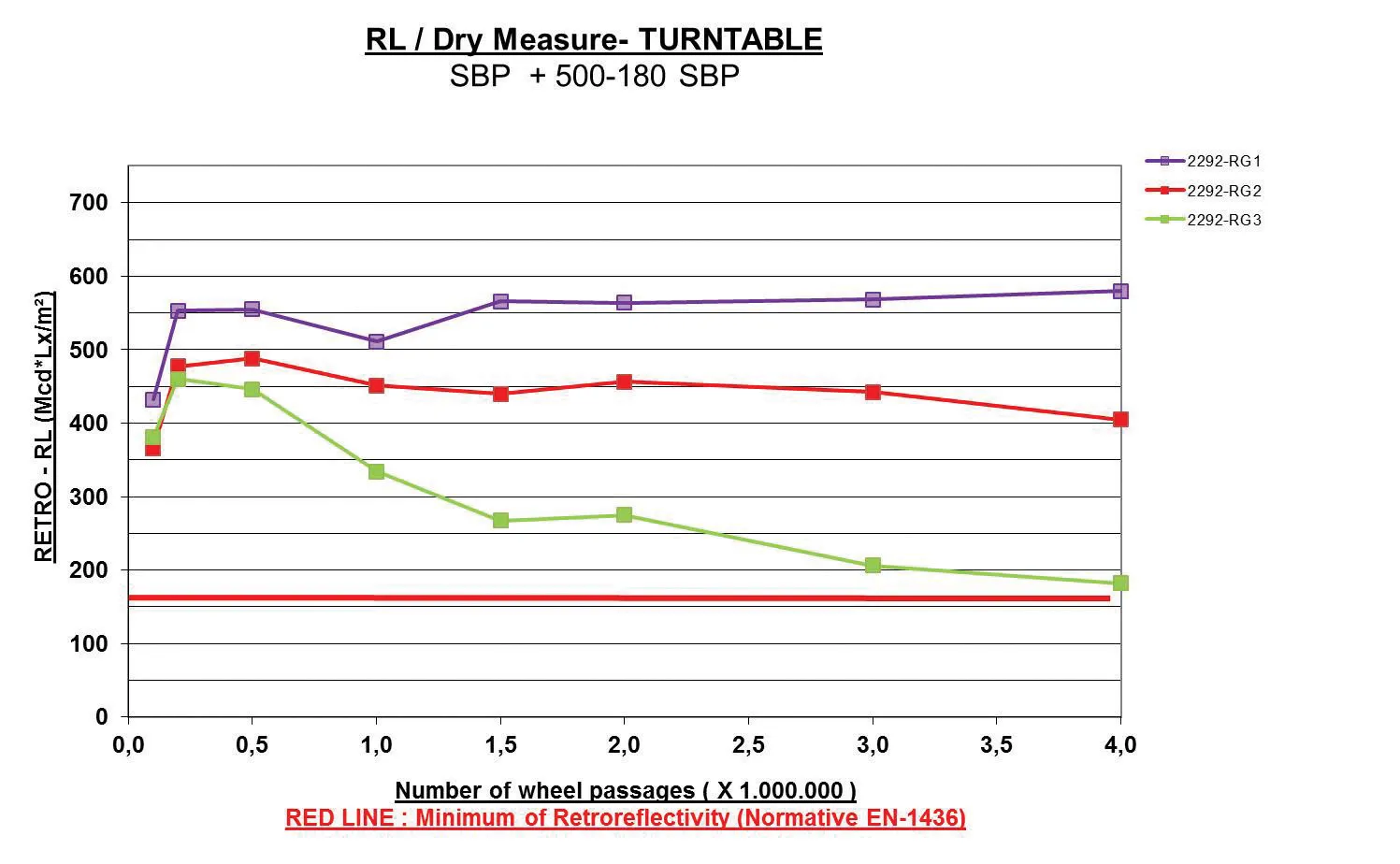
Extra fuel is burnt due to a number of pavement properties that impact on how the road surface and the vehicle interact. Friction is one of these – the higher the friction, the more fuel is burnt – and this is most relevant for cars.For trucks, deflection is more relevant; the weight of the vehicle causes the pavement to deflect and then fuel is required to push the vehicle up over the ‘bump’.
The MIT study, conducted by postdoctoral researcher Hessam Azarijafari, research scientist Jeremy Gregory, and principal research scientist in the Materials Research Laboratory Randolph Kirchain, concentrated on the deflection-induced effect.
Their argument is that while car traffic is likely to decrease, freight will increase. While this may not necessarily be true, it is likely that cars will be powered by renewable electricity at an earlier stage than trucks due to challenges around battery technology.
The researchers used data from 30 national databases to plug into their study and modelling. The climate of each state was also taken into consideration. In cold climates, such as Colorado, the roughness-induced excess fuel consumption is far more significant than deflection-based excess consumption – between six and 10 times more.
However, in warmer states deflection-induced consumption is three times that of friction-based consumption for asphalt pavements, although equal for concrete ones.
The study looked at ways of increasing pavement stiffness, or E modulus, such as adding fibres or carbon nanotubes or adjusting the mix design by changing the grading or type of aggregate and the properties of the binder. The analysis considered increasing the E modulus, by resurfacing at a rate of 10% of roads a year, to be equal to that of the 95th percentile of roads recorded in the Long-Term Pavement Performance (LTTP) database.
The researchers conclude that “the reduction in emissions from pavement use can be achieved with no changes in either 12 technology or manufacturing practices or the use of novel construction materials”. However, an increase in stiffness can have an adverse impact on other performance criteria such as cracking, something that is not considered in the report. There are many contributing and conflicting characteristics that impact on the whole life carbon impact of a road, not least the number of times it must be maintained.
Research and trials by the Danish Road Directorate which saw test sections paved from 2012, looked at reducing the frictional element of fuel wastage by changing the composition of the road surface to provide a low rolling resistance.
However, although the surfaces could deliver a fuel saving of around 6%, the test sections started ravelling within two years. Following more research, a new type of low rolling resistance asphalt is now under trial in Denmark, with a section laid in 2018.