The pavement industry needs to come up with novel solutions in order to meet the twin challenges of climate change and squeezed budgets. This was the message from Kraton Polymers market
development manager Rombout Hartemink when he addressed FIRM13. Hartemink illustrated the properties of“If you have such a transformational product,” he continued, “you can achieve dramatically different costs in certain applications.” HiMA contains 7.5% SBS polymer, but unlike bitumen normally modified with this quantity of polymer, is not stiff and unworkable.
Hartemink’s presentation of HiMA applications around the world included the case of a US cul-de-sac, damaged by heavy garbage trucks. Microsurfacing using standard emulsion and aggregates had failed, so that the solution being used was the expensive one of a 25mm ‘mill and fill’ layer of hot asphalt which came in at around $14.4/m2 ($12.00/yd2, see Fig.2).
By using HiMA microsurfacing, this cost was cut to under a third of the hot mix option, costing around $4.2/m2 ($3.60/yd2, see Fig.2). “I used this example because it tells us that we can consider microsurfacing applications for roads where we might normally not think about them,” said Hartemink.
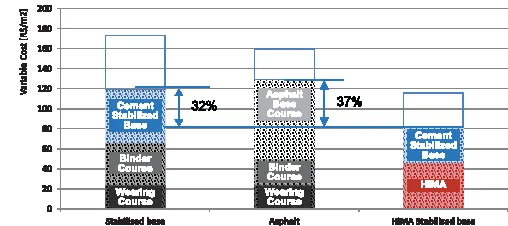
Brazil also supplied an example of a ‘dramatically different’ solution. Standard road construction in Brazil sees the binder course and wearing course laid over a cement stabilised base, rather than the European construction of base course, binder course and wearing course.
By using a thinner but better HiMA layer over a reduced cement stabilised base layer, the road depth has been reduced by 37% compared to traditional Brazilian road construction. This equates to cost savings of 32% and 37% respectively (see Fig.1) while improving the resistance to reflective cracking from the base.
“This shows a different design based on a thinner but better asphalt layer and a dramatically reduced amount of cement-stabilised base leading to a dramatic cost reduction,” said Hartemink.
Although uptake of innovative technologies in Europe can be limited by the specification and approval processes under traditional forms of contract, there are still opportunities in cases where the contractor has an ongoing responsibility for maintenance – as is the case for the concessionaire contracts in Brazil.
"With toll roads in France, and now that we see more term contracts in European countries such as the UK, people are interested in innovative solutions, they want to listen and talk," said Hartemink.
Honeywell Titan's additive extends paving season
A trial section of road in Alaska is being used to showcase two of the benefits that Honeywell’s new bitumen additive, Honeywell Titan, can bring to paving. First it can extend paving seasons: the trial took place in October, with temperatures that fell to -10°C during one night; and second, it raised the performance grade (BG) of the bitumen to create a stiffer road for the heavy traffic it experiences, which should extend the road’s life.
Honeywell Titan is a low weight, ethylene-based polyolefin added at the asphalt plant. It comes in a powder form, has a low molecular weight and a melting point of 115°-140°C. In terms of cost, Wood said that Honeywell Titan is competitive with other modifiers in the industry. “We believe if you look at the cost in use, Honeywell Titan will be cost-effective.”








