Modified epoxy chip seal is one of three technologies under investigation in the 18-month Climate Resilient Sustainable Road Pavement Surfacing (CRISPS) programme; the others are modified epoxy asphalt surfaces and fibre mastic asphalt. The programme is being led by the University of Birmingham in the UK, in collaboration with the University of Auckland, the Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) and the International Road Federation (IRF).
New Zealand and the Netherlands have been interested in using epoxy bitumen since the early 2000s, when they worked on a research programme together, explained David Alabaster, principal pavement engineer at New Zealand transport agency Waka Kotahi, at a seminar in December 2021, hosted by the IRF. Engineers observed that the material had been installed on bridge decks and was still intact 40 years later.
“There have been bridge decks that have survived for 40 years so there’s a track record of durability in these materials,” said Alabaster.
Those initial studies showed that epoxy bitumen had several advantages over a standard binder: it proved to be more resistant to rutting; to low temperature crack initiation; and to surface abrasion from tyre action, even after oxidation. Oxidation is a major problem in New Zealand, said Alabaster.
Epoxy bitumen is a two-part system which has to be used relatively quickly after mixing. Part A is epoxy resin and Part B is a curing agent which is mixed into the bitumen.
Having perfected the manufacture of epoxy bitumen mixes, New Zealand began trialling its use for porous asphalt. Its standard material, though safe and quiet, was only lasting between seven and eight years and costing between NZ$20 and NZ$30/m2 to replace.
“Testing suggested we could get to a 40-year life with the way we were doing it for an extra NZ$6/m2 which is a tiny amount for the increase in performance,” said Alabaster.
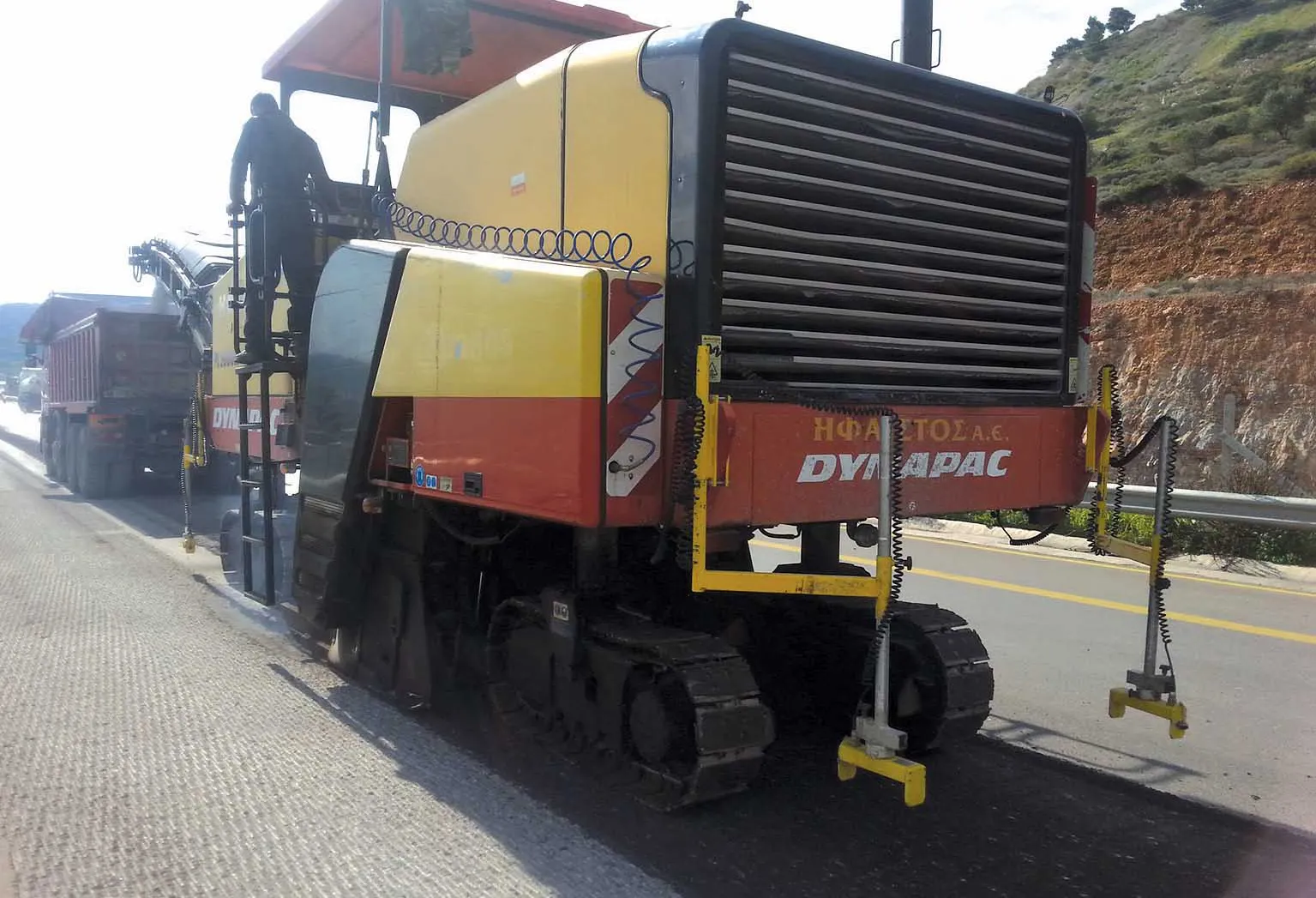
From 2016, normal production of the epoxy bitumen began, with 25% epoxy. New Zealand has laid over 100,000m2 on all the busiest highways, and the country’s first home-manufactured bitumen blend has been approved. Having come on a fact-finding mission to New Zealand, Netherlands contractor Duravermeer laid the first epoxy modified material on a ringroad in Boekel in 2021.
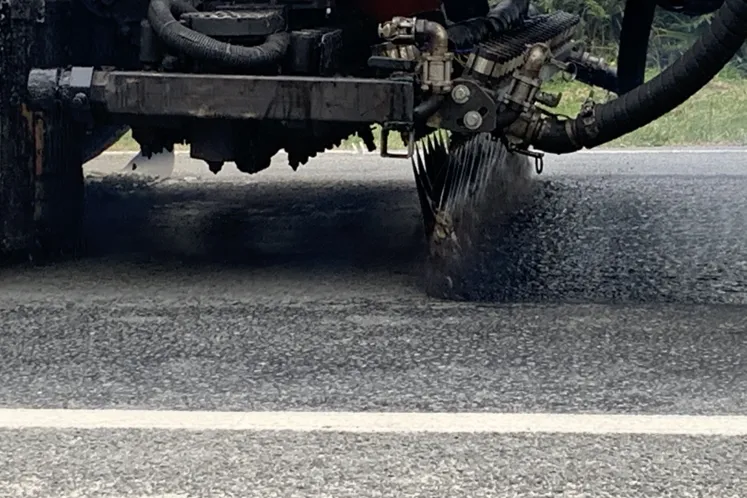
New Zealand then began looking at modified epoxy chips seals to tackle the problem of flushing, where binder rises out of the surface leading to a decrease in skid resistance and sometimes damage to the surface. After initial hand trials, researchers built a modified spray bar with two sets of nozzles, one for the part A and the other for the Part B.
To date, New Zealand has laid the modified epoxy chip seal on two trial sites which have been performing significantly better than standard materials in terms of texture loss. The next step is the trials in Ethiopia.