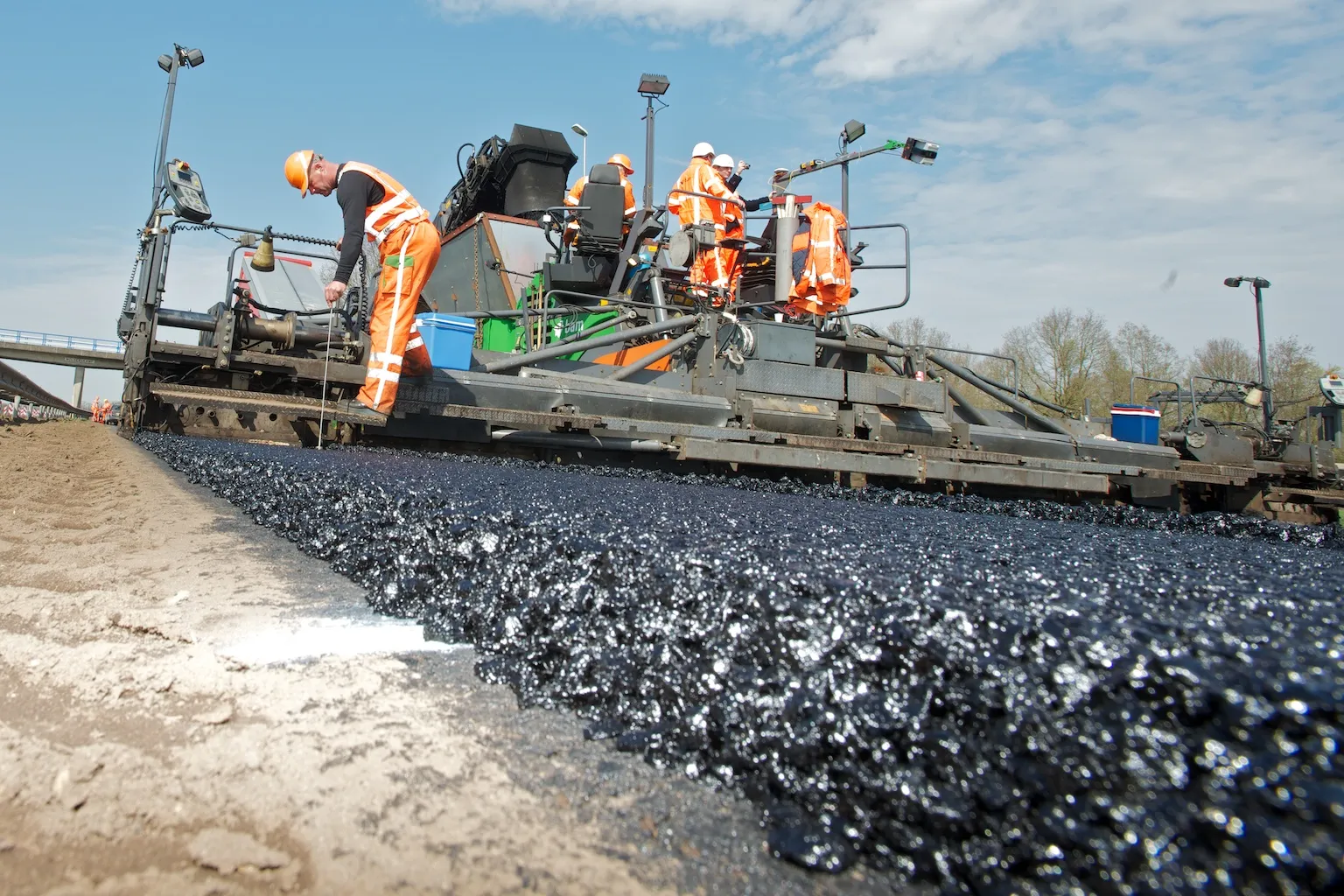
Though reducing production temperatures is an important way to lower the industry’s carbon dioxide emissions, there is a far more obvious – and impactful - way of reducing a highway’s carbon footprint: building roads that last longer.
“The easiest environmental gain is for the contractor to use the right materials and do the right job,” said
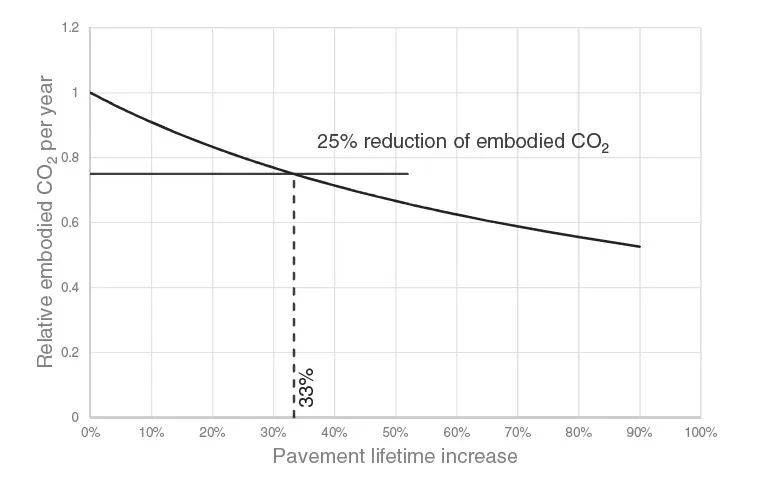
Increasing a pavement’s life by one-third reduces its embodied carbon dioxide by 25%. Doubling its life leads to a halving in embodied carbon, according to Nynas. Even using polymer modified bitumen, which requires more carbon to produce than a standard one, delivers similar carbon savings (see graph).
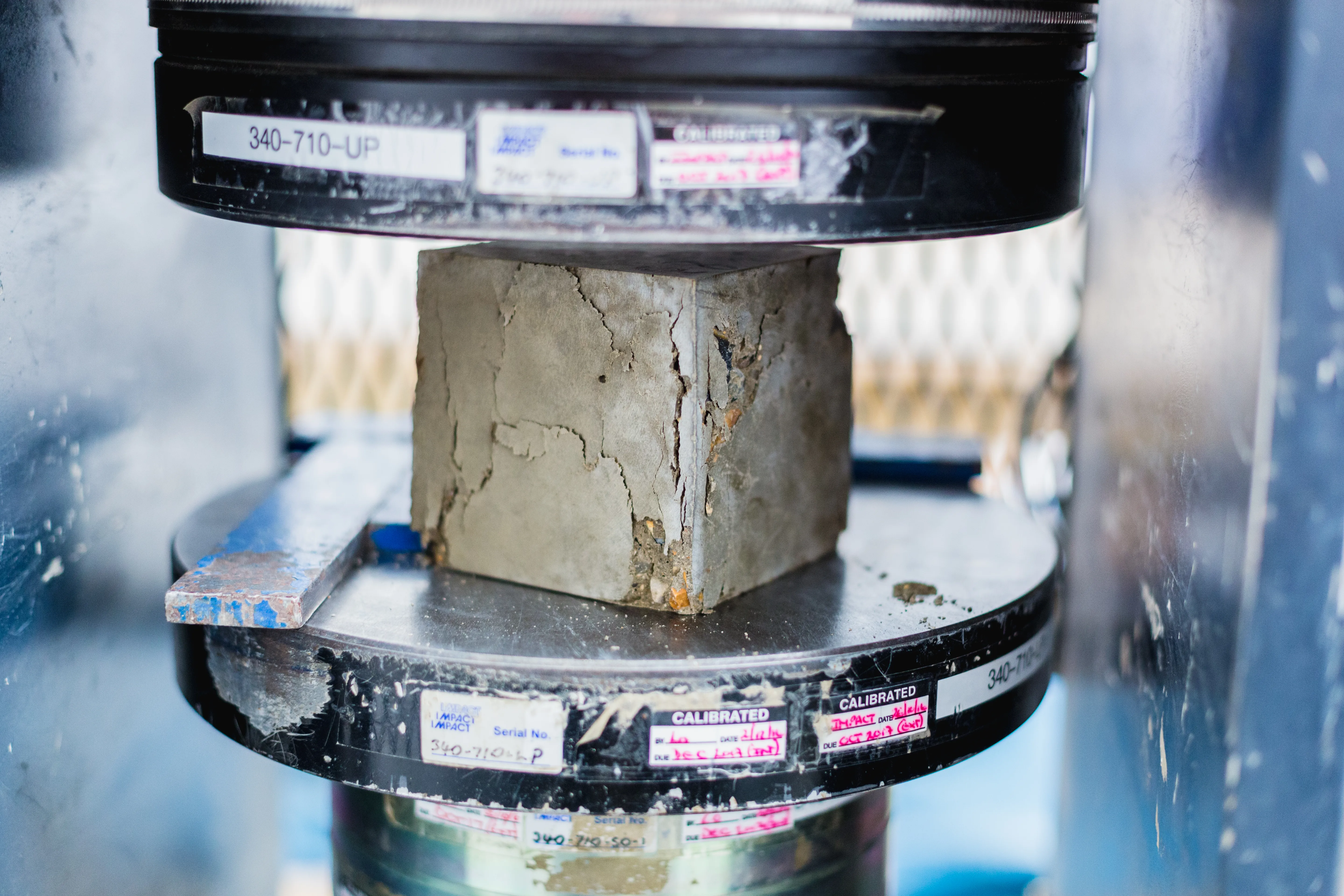
However, ensuring that the bitumen in a mix is right for the job is not as easy as it used to be. The rheology of bitumen has changed over the last decade, so that although a bitumen may meet the parameters defined and measured by traditional, empirical tests, its long-term behaviour may not be as good as expected.
To try and better predict long-term performance, US researchers have developed new parameters ΔTc - or Delta Tc – and the Glover-Rowe parameter to help express long-term durability and cracking behaviour. Though more widely used in the US, where ΔTc was first referenced in 2011, there is little wider awareness of these parameters in Europe, other than among researchers.
“Some of the major asphalt contractors are now picking up on it,” said Dennis Day, technical support manager for Nynas Bitumen in the UK. “On the client side, I suspect they are not aware of it. We need to raise awareness of the new rheological characterisation of bitumen which is the only way to ensure you have good quality bitumens.”
The composition of bitumen has changed as refining processes have been updated. Advanced refining technology means that more high-value products can be extracted from a barrel of crude oil, leaving different products at the bottom of the barrel which are often blended with other products to create a bitumen that meets the standard property tests.
“Most refineries focus on producing fuel, with bitumen being only being a fraction of the total throughput,” adds Robertus. “These refineries generally maximise their economy by being flexible on the crude oil used as refinery feed. Consequently, the bitumen produced comes from a range of different oils which contributes to variations in product quality.”
According to Robertus, Nynas as a specialist bitumen producer has a different approach: “Most of Nynas’ bitumen is produced by straight run vacuum distillation from a limited number of crude oils. This brings consistency in the quality of the product.”
Nynas would like to further the industry’s understanding of parameters such as ΔTc, by analysing existing pavements. “We would like to look at certain sites that have done particularly well, or particularly poorly to analyse what has happened. We would take a sample and extract the bitumen to see how it looks in terms of the Delta Tc and the rheology,” said Robertus.
This would help increase our understanding of how the qualities of bitumen contribute to pavement lives – and carbon reduction.









