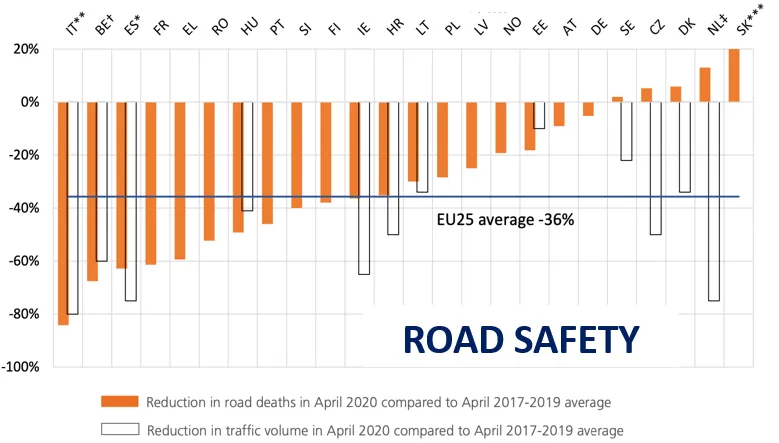
Researchers at the National Centre for Asphalt Technology* (NCAT) and the National Concrete Pavement Technology Center in the US have carried out an extensive study into the albedo of asphalt and concrete pavements. Results of the study, which was commissioned by the Federal Highways Administration, were published in December.
The albedo of a pavements is its ability to reflect solar energy, measured on a scale of 1 to 10. Albedo, which the researchers found changes over time, impacts on the thermal behaviour and the performance of pavements.
“Both concrete and asphalt pavements are influenced by the temperature of the materials in them,” says Mike Heitzman, assistant director and senior research engineer at NCAT and one of the principal investigators for the research. “The less energy that is reflected, the more is absorbed by the pavement, the temperature changes and the pavement can behave differently. With asphalt pavements, the warmer they get, the softer they become.”
The research suggests that albedo can impact on pavement performance by a factor of between 10-15%. So, for instance, an asphalt pavement might experience 10% more cracking or rucking, according to Heitzman.
Researchers took readings in seven locations in different states, chosen to reflect a range of aggregates and climates. At each location, measurements were made for five asphalt roads and five concrete roads. “In the past, studies have been fairly limited to local areas,” explains Heitzman. “By having seven locations around the country, we had a great variety of aggregates to work with. That came to be very important for the asphalt pavements in particular.”
The aim of the research was to produce thermal models linked to albedo changes which could be plugged into design software. Findings were quite conclusive for aggregate pavements but less so for concrete. “With asphalt we were able to demonstrate that the coarse aggregate in the mix played a key role in the albedo of the pavement,” notes Heitzman. One reason for this could be that in warmer, southern US states, black mould tends to grow on the concrete surface, darkening it, he explains.
Further research is required before the impact of albedo could become part of pavement design and testing, he says. It might also be more efficient to look at other factors which play a bigger role in performance enhancement and deterioration. “There are another 10 or 20 variables that influence performance that may be more relevant.”
More information is available on the NCAT website.
*The National Center for Asphalt Technology was set up in 1986 as a partnership between Auburn University and the National Asphalt Pavement Association (NAPA) Research and Education Foundation to provide practical research and development to meet the needs of maintaining US highway infrastructure. NCAT works with state highway agencies, the Federal Highway Administration and the highway construction industry to develop and evaluate new products, design technologies and construction methods that quickly lead to pavement improvements.