Researchers in Australia say they have shown that single-use disposable face masks could be used successfully in recycled concrete aggregate for road paving.
The new road-making material is a mix of shredded used face masks and processed building rubble developed at RMIT University. The mixture meets civil engineering safety standards, according to a press release from the institute. RMIT University, formerly the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology and Melbourne Technical College, is a public research university in Melbourne, Australia. It has been rated as the top art and design university in Australia.
Analysis shows the face masks help to add stiffness and strength to the final product which is designed for use is base layers of roads and pavements.
The researchers’ study will appear in the weekly journal Science of the Total Environment, published by Elsevier. According to the publication’s website, “Science of the Total Environment is an international multi-disciplinary journal for publication of novel, hypothesis-driven and high-impact research on the total environment, which interfaces the atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere and anthroposphere”.
“This initial study looked at the feasibility of recycling single-use face masks into roads and we were thrilled to find it not only works, but also delivers real engineering benefits,” said Mohammad Saberian, lead author of a report on the study. “We hope this opens the door for further research, to work through ways of managing health and safety risks at scale and investigate whether other types of PPE [personal protective equipment] would also be suitable for recycling.”
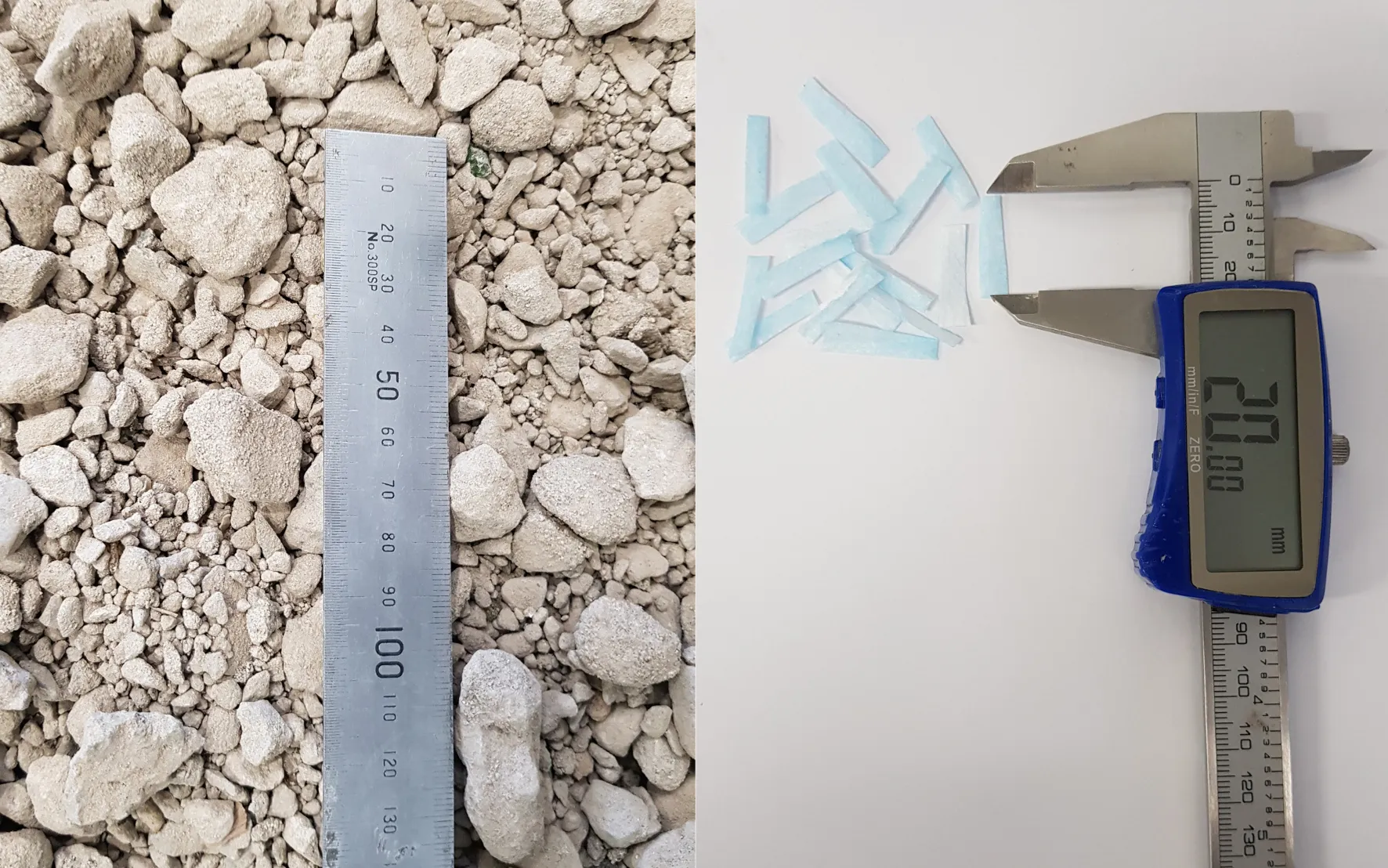
In Australia alone, about 3.15 million tonnes of recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) is added to stockpiles each year rather than being reused. The experimental study was conducted with a small amount of unused surgical face masks. It identified an optimal mixture – 1% shredded face masks to 99% RCA – that delivers on strength while maintaining good cohesion between the two materials.
The mixture performs well when tested for stress, acid and water resistance, as well as strength, deformation and dynamic properties, meeting all the relevant civil engineering specifications, noted the press release.
According to the study’s abstract, “for the first time”, a series of experiments, including modified compaction, unconfined compression strength and resilient modulus tests, were conducted on the blends of different percentages of the shredded face mask (SFM) added to the RCA for road base and sub-base applications. The experimental results show that RCA mixed with three different percentages - 1%, 2% and 3% - of SFM satisfied the stiffness and strength requirements for pavements base/sub-base.
The introduction of the shredded face mask not only increased the strength and stiffness but improved the ductility and flexibility of RCA/SFM blends. The inclusion of 1% SFM to RCA resulted in the highest values of unconfined compressive strength (216 kPa) and the highest resilient modulus (314.35 MP).
However, beyond 2%, increasing the amount of SFM led to a decrease in strength and stiffness.
A free download pdf is available now ahead of official publication later this year and some alterations may be made before then.
M. Saberian, J. Li, S. Kilmartin-Lynch, et al., Repurposing of COVID-19 single-use face masks for pavements base/sub-base, with co-authors RMIT Indigenous Pre-Doctoral Research Fellow Shannon Kilmartin-Lynch and Research Assistant Mahdi Boroujeni, is published in Science of the Total Environment (DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145527).
In related work, the RMIT researchers said that they have also investigated the use of shredded disposable face masks as an aggregate material for making concrete, with promising preliminary findings.