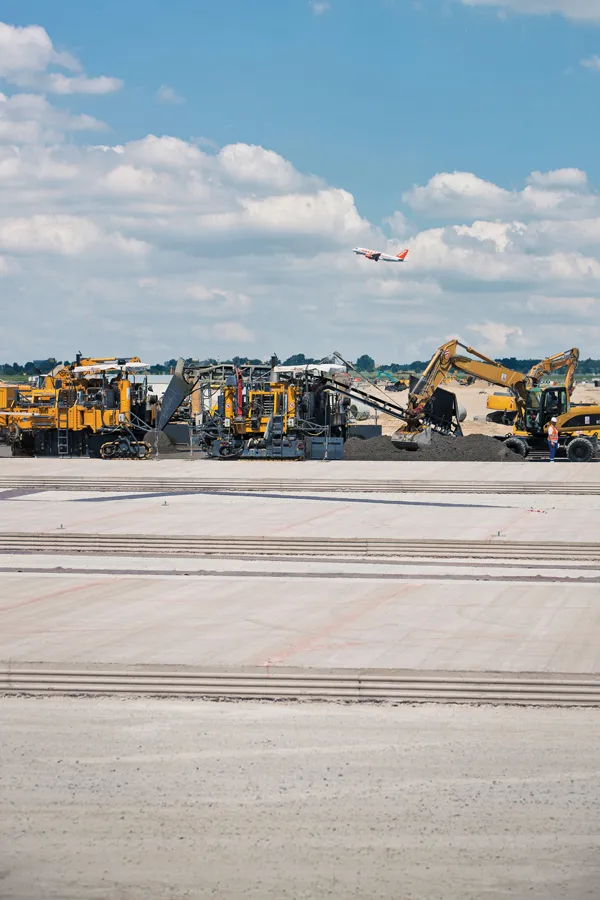
In Lithuania, cold mix asphalt containing recycled asphalt pavement has been installed in a new base course overlay for a section of the A1, the country's most heavily trafficked motorway.
February 17, 2012
Read time: 3 mins

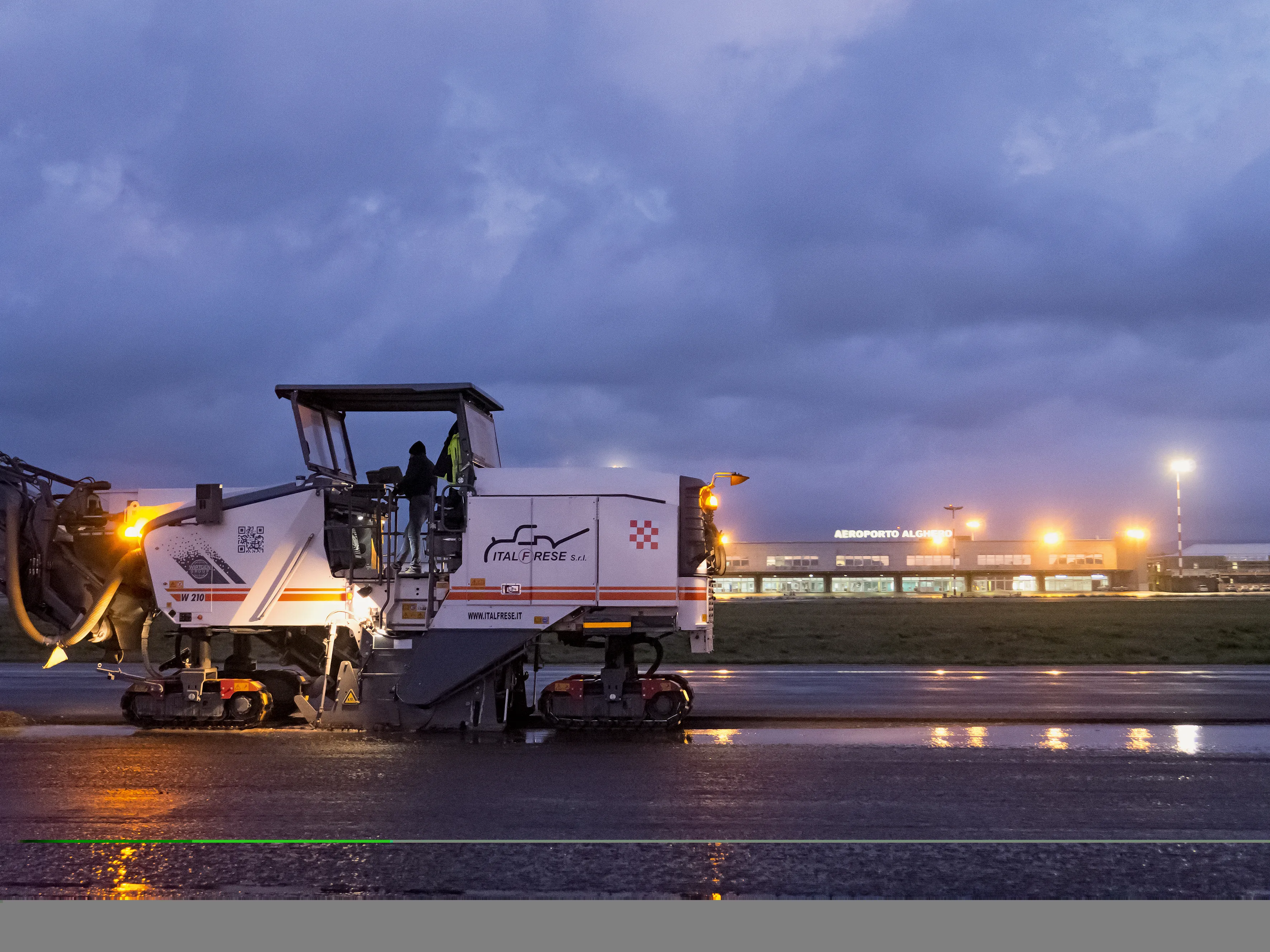
In Lithuania, cold mix asphalt containing recycled asphalt pavement has been installed in a new base course overlay for a section of the A1, the country's most heavily trafficked motorway.
The all-important bitumen emulsion binder, Nymuls RX, was produced locally under licence from bitumen specialistThe A1 is Lithuania's main cross-country route, linking the capital Vilnius in the east, westwards to Kaunas and then Klaipeda by the Baltic Sea. Maximum traffic density along the 300km long, dual four-lane highway is 40,000 vehicles/day.
It is towards Klaipeda that a 3.4km stretch of the motorway's eastbound carriageway was giving particular trouble. Built in the mid-1980s this portion of road had an experimental 200mm thick base course of fly ash stabilised gravel, mixed to meet the then prevailing Soviet standards. But 25 years on, the bitumen bound layers above the base course displayed extensive reflected cracking.
"Over time, the base course has developed considerable strength, becoming a semi-rigid pavement rather than the flexible one it was supposed to be," says deputy director of the Lithuanian Road Administration (LRA) Petras Tekorius.
Weather-induced movement caused the rigid material to crack, with a detrimental effect on the asphalt above.
"We had two problems in reinstating the carriageway: what to do with the base course, and how to rebuild the pavement in the best way." The original base course had considerable residual bearing capacity, despite the cracks. "So we decided to leave the original base course in situ, but to cap it first with a 120mm thick unbound layer of crushed stone to form an anti-cracking and levelling medium, and then a new 200mm base course of cold recycled asphalt," says Tekorius.
This would introduce to the carriageway sufficient elasticity, according to LRA's head of Roads Division Zigmantas Perveneckas. As to the choice of recycled cold mix asphalt, this seemed the natural thing to do.
"We are doing our utmost to implement sustainable technologies in the roads industry," he says.
The LRA has used cold mix recycling on a number of road projects since the early 2000s, prompted by European bitumen specialist Nynas. Although the roads involved were of a lesser nature than the A1, their successful refurbishment has bred sufficient confidence for a more substantial challenge to be undertaken. Certainly, the A1 is the big one, in terms of cold recycling.
Roads civil engineering contractor responsible for the A1 recycling is
"Our investment is paying off: we have had to build the market for cold mix recycled asphalt but now the contracts are coming through," says the company's deputy director Alvydas Peldzius, who pays tribute to the assistance given by Nynas in providing technological guidance and training.
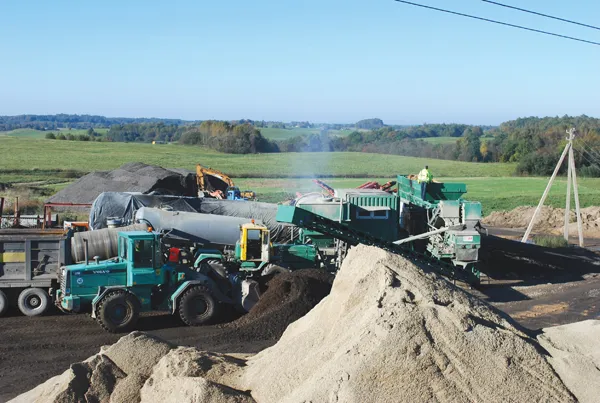
The A1 section under repair first had its three existing asphalt layers milled off and the planings graded and stockpiled at a temporary mixing plant set up 2km from the site. Crushed stone was placed on the original base course, to form the stress absorbing layer. Then production of the cold mix for the new base course began, using the reclaimed asphalt; an amount of virgin aggregate to make up the required volume; fillers and the Nymuls RX bitumen emulsion, to create the base course.
After this material had been placed, in two layers each of 100mm, amounting to 30,000tonnes, an 80mm thick hot asphalt concrete binder course was added, followed by a 40mm stone mastic asphalt surface course.
The direct cost saving of the recycled solution over conventional construction was around 20%, much more when sustainability and environmental benefits are added.