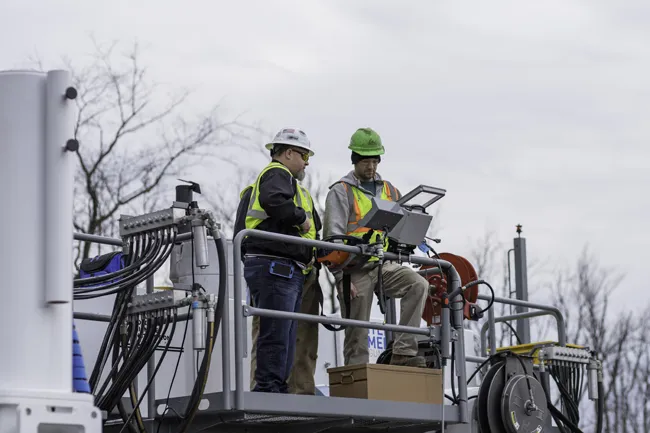
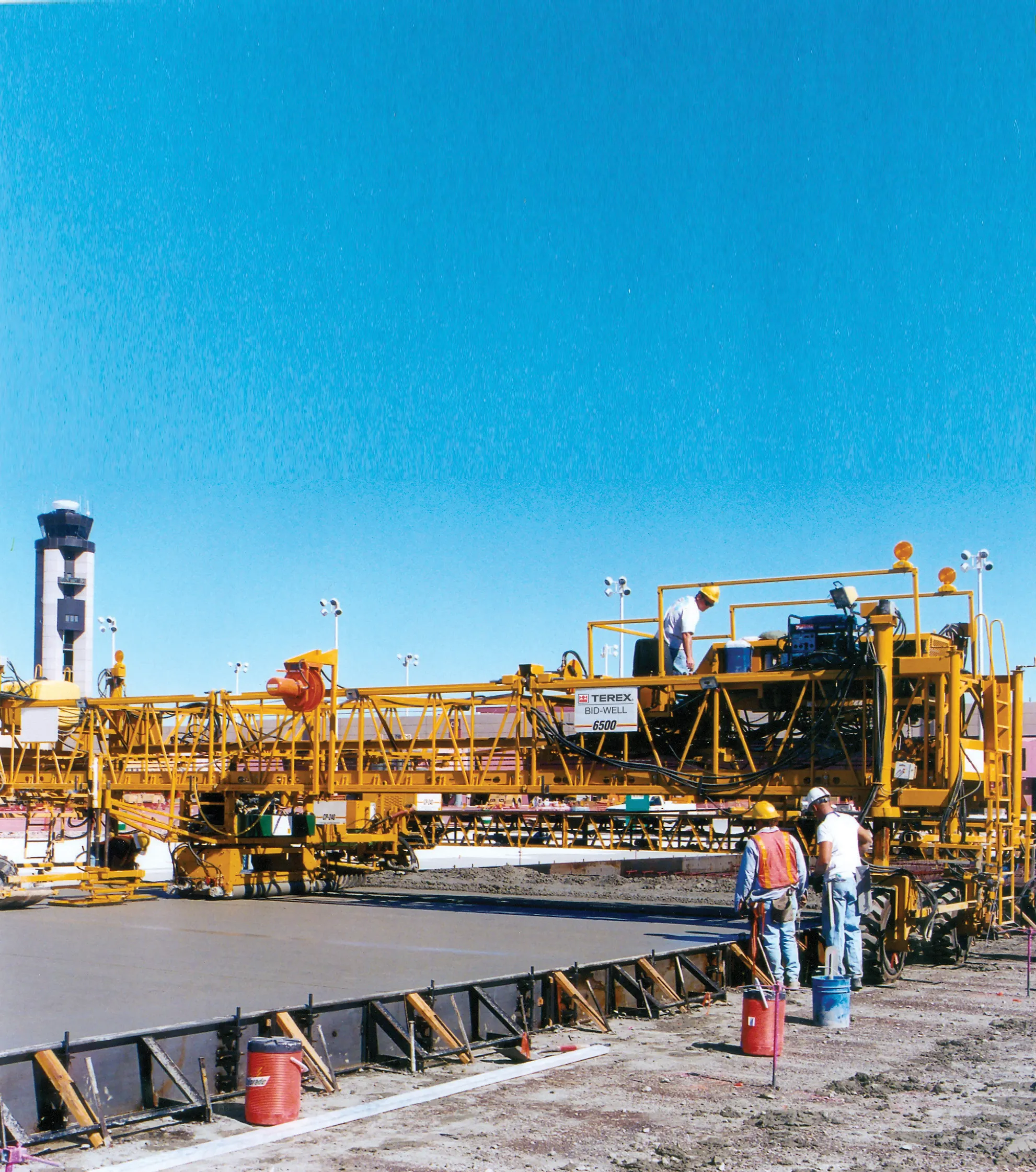
Controlled frequency vibration (CFV) technology has been around since the mid-1990s for concrete pavement applications. The technology has seen a gradual increase in acceptance, particularly in certain applications.
For the 0- to 37mm (1.5”) slump pavement mix designs, many contractors were experiencing material separation due to speeds over 8,000vibrations/minute (VPM). With the wide variability of concrete materials, moisture levels, batching uniformity, chemical incompatibilities, and slump loss rates, vibrator speeds needed to be highly controlled and predictable.
As a result, CFVs have become standard in the US construction sector. Concrete surfaces used in pedestrian ways, roads, and runways are now generally restricted to using CFVs for placement purposes. There are various manufacturers of hydraulic paving vibrators and the firms have developed an array of products that are similar in dynamics.
These paving vibrators feature sensors that tell the machine operator what speeds are being generated. With accurate speed control systems, the contractors learned to set the vibrator speed to deliver the desired results. From this learning curve, individual agencies have set vibrator speed ranges as specification for pavement mixes. Over a period of years in the US, CFVs have now become the standard for use in concrete pavement construction.
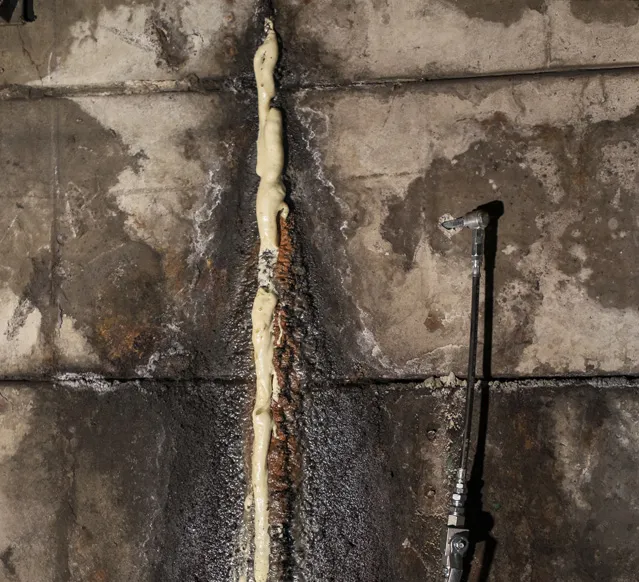
There are some important principles to be employed, with the data that is collected from vibrator speed logs being examined against the core samples from the pavement. This ensures that the effect of the vibration energy on the concrete can be properly evaluated. Higher vibrator speeds can cause surface problems from material separation. Those issues include permeability, poor aggregate arrangement, inconsistent surfaces and a greater susceptibility to freeze/thaw damage, resulting in a need for early repairs.
Improved CFV products have emerged in recent times as the technology has evolved. For decades, the success of CFVs did not grow proportionately to the growth in low-viscosity pumpable concrete for commercial applications.
However, the gap between commercial mix design and vibration technology is starting to close with the introduction of several CFV products in the industry. Progress has been attributed to better testing methodology, vibrator speed specifications, and more widespread training. Increased use of CFV technology shows that controlled vibration helps to minimise blemishes in concrete.
There are shortcomings with such equipment. When mixes feature a low-viscosity with large amounts of available water, uncontrolled frequency vibrators force water to the form faces, resulting in blemishes. But when vibrator speeds are controlled for low-viscosity concrete, blemishes are controlled.
Understandably, the use of CFV technology is on the rise, given the improved results these units can deliver. Industry studies have highlighted the separation issues that result when available water present in commercial mixes ends up as surface blemishes on form faces. And when a concrete structure is intended to display any architectural value in addition to its structural properties (such as for a bridge), patching and self-consolidating concrete have been viable options.
However a more simple answer to these over-vibration issues has been to control and lower the speeds so that these become more compatible with low-viscosity pumpable mixes. For modern projects, compatible vibrator speeds are applied to test samples during the pre-construction phase.
As contractors tackle the material, pumping, and batching variability issues, they are beginning to resolve surface issues by increasing the use of CFV technology, the quality of work delivered is generally improving.
In other words, controlled frequency vibration is here to stay.
*Paul Jaworski, Minnich Manufacturing Research and Development