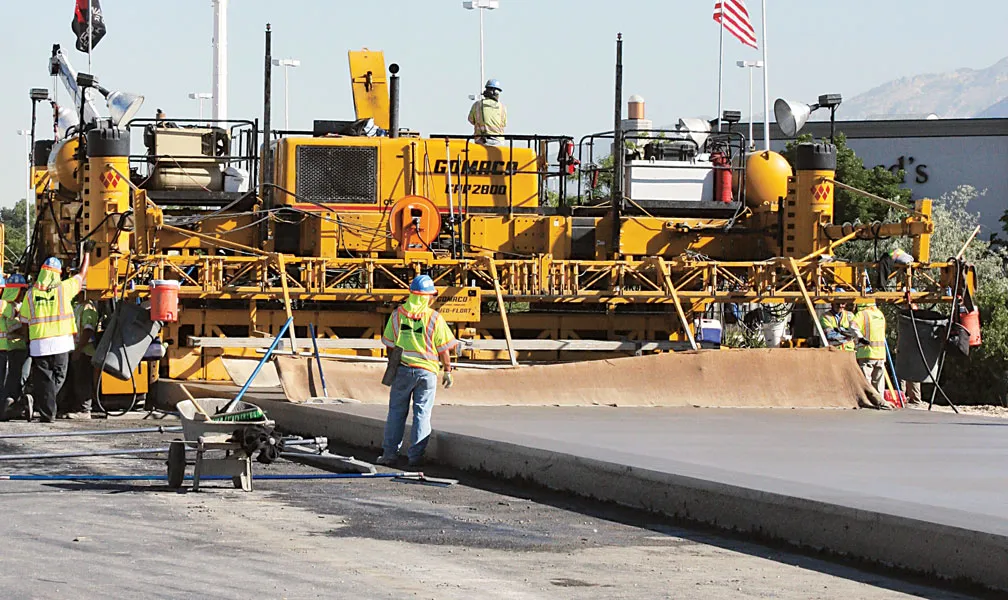
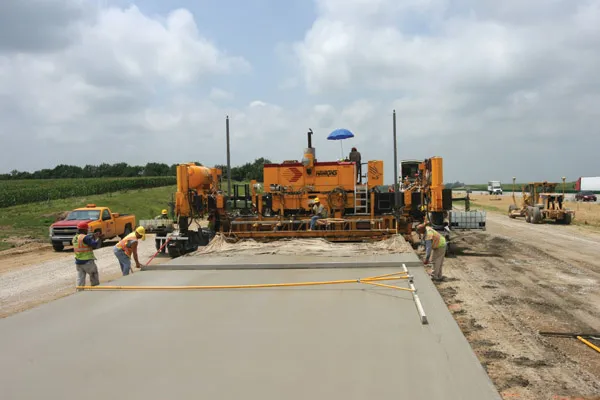
Machine control technologies were pioneered in the concrete paving sector with systems having been used for over 10 years. Leica Geosystems was the first of the machine control technology suppliers to offer these systems on concrete slipforming machines and has developed a strong position in this segment. However the company met resistance from some quarters in the construction market and specialist Karl Soar said that some contractors were very reluctant to give up using conventional stringlines. He said,
July 1, 2013
Read time: 4 mins

Machine control technologies were pioneered in the concrete paving sector with systems having been used for over 10 years. Leica Geosystems was the first of the machine control technology suppliers to offer these systems on concrete slipforming machines and has developed a strong position in this segment. However the company met resistance from some quarters in the construction market and specialist Karl Soar said that some contractors were very reluctant to give up using conventional stringlines. He said, “We provide tools so they can stay in the comfort zone.”
The introduction of machine control systems to paving has changed the way operations work, as well as the duties of those on-site and for example, Soar said that the surveyor has now become a data manager as this is effectively a quality management operation. Machine control systems have brought benefits and Soar said, “It’s all about performance contracts these days.”He added that squeezed time schedules place pressure on either finish or completion times, which is why the machine control technologies are important for achieving the necessary smoothness within project deadlines.
Most recently
In addition,
The software calculates the optimum course on the basis of the measured points, creating a virtual stringline and data is saved on a USB stick for use on the machine. The paver then follows the file on the stick, moves to the start point and then follows the files created. The system bases its calculations on the actual job site measurements and does not require construction drawings and is said to be less costly than conventional 3D technology.