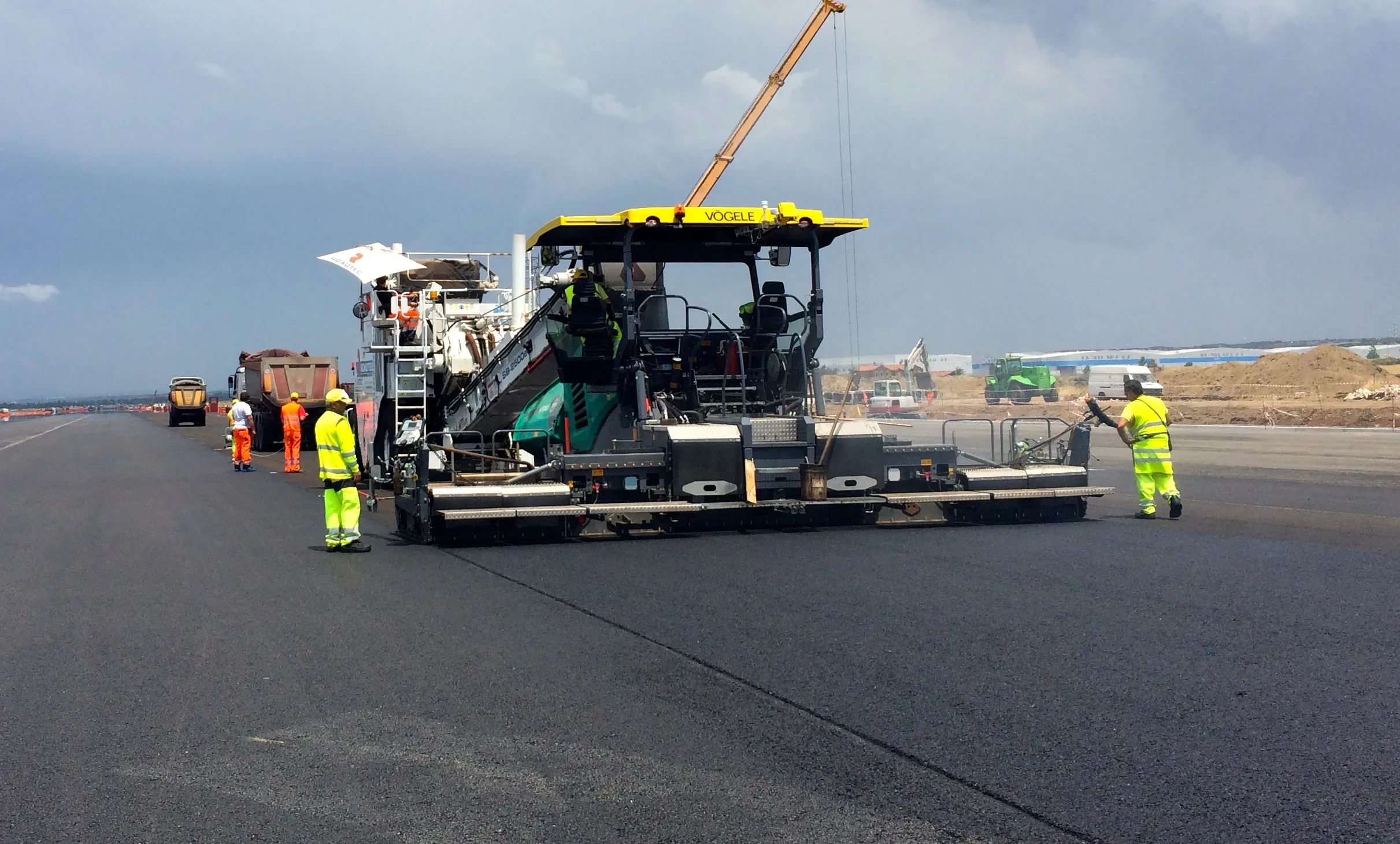
An asphalt paving trial at Rome Airport tested mat quality with and without the use of MTVs
Rome’s airport Fiumicino or the Leonardo da Vinci Airport of Rome is one of Europe’s busiest airports and lies 25.6km southwest of the city, a 30-minute train ride away. Handling just over 38.5 million passengers in 2014, the airport’s three runways carry heavy traffic, so much so that the runway 16L/34R recently required resurfacing. The 3,902m long by 60m wide runway had to be milled and repaved, with local contractor Pavimental winning the contract. The company is considered the leader in asphalt production in Italy.
Before full paving production began on the project, Pavimental wanted to test whether a
The Fiumicino 16L/34R runway project was less than five minutes away from the asphalt plant so the contractor was initially doubtful that MTVs could offer benefits.
The contractor used its
For the three tests conducted, Pavimental had
Pavimental used the PAVE-IR Scan system to show the overall quality achieved by each paving method. One was paving with the help of the Roadtec SB-2500e/ex Shuttle Buggy MTV. Another was with HMA trucked from the production plant and loaded into the paver.
The determining factor in the research test was to measure the level of thermal segregation occurring in the asphalt mat behind each paving method. In the past, extensive testing resulted in Stroup-Gardiner and Brown establishing in 2000 a classification of thermal segregation and its related consequences. In the classification system, when temperature differences are below 10ºC segregation is considered nonexistent, between 10ºC and 16ºC it is low, between 17ºC and 21ºC medium and it is considered high when over 21ºC.
The higher the measured temperature, the more likely the paved surface will experience fatigue and be less durable. What all the tests point out is that temperature deviations will make pavement less durable and will increase maintenance costs.
For the Rome international airport test, a lift was laid by each method. The testing occurred over a six-day period with test mats laid by each method.
MOBA used infrared scanning to examine the level of thermal segregation. The results concluded that the finished pavement quality from each paving method show a temperature change of <8ºC when using the Roadtec Shuttle Buggy and temperatures varied from between 20ºC and 25ºC when trucked HMA was loaded directly into the paver.
The collected data shows that when the Roadtec Shuttle Buggy is used the maximum thermal segregation detected is 8ºC, so the results indicate NULL segregation, while when the PowerFeeder or direct truck-to-paver methods are used the temperature differentials can be more than 20ºC at any given time. The trucked-in methods will have durability that is expected to be about half of what can be achieved through the Roadtec Shuttle Buggy, which remixes the HMA and provides continuous paving.
Pavimental found the results useful. The initial thinking was that with the HMA production source so close to the jobsite, there would be no need for a material transfer vehicle. However the results of the thermal segregation tests suggest otherwise.