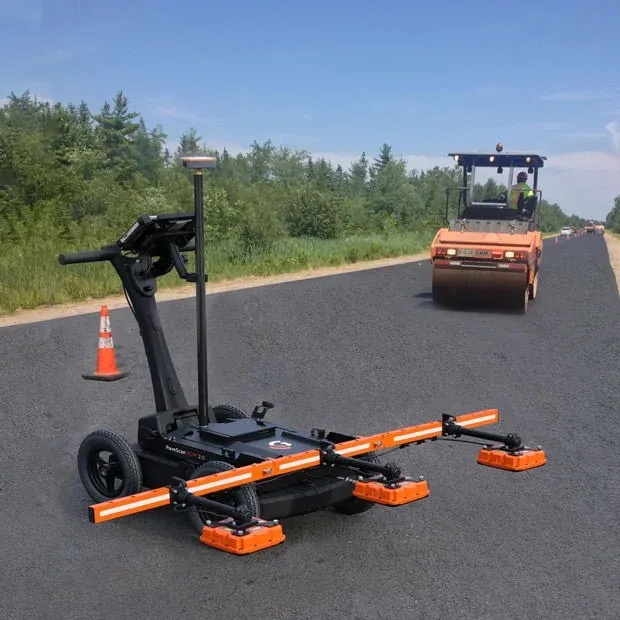
GSSI, a manufacturer of ground penetrating radar (GPR) equipment, says that from technician to engineer, the PaveScan RDM 2.0 testing system is easy to operate.
The PaveScan RDM 2.0 is a second-generation asphalt density assessment tool ideal for non-destructive asphalt compaction testing, quality assurance/quality control of new pavements and determining pavement non-conformity.
By uncovering inconsistencies that occur during the paving process, including poor uniformity and significant variations in density, PaveScan RDM 2.0 helps to avoid premature failures like road raveling, cracking, and deterioration along joints.
Thanks to seamless GPS integration, real-time onscreen data output and export options, this system is ideal for government transportation agencies and paving contractors alike. The pavement density measurement technology used in PaveScan RDM 2.0 is an accepted American Association of State and Highway Transportation Officials (AASHTO) specification, PP 98-19.
The complete PaveScan RDM 2.0 system includes a rugged deployment cart and an integrated concentrator box that accommodates up to three sensors. It includes housing for cable management and hot-swappable, dual batteries.
The new sensor design was built specifically for the extremes of the asphalt paving environment and features a green laser to aid location accuracy. Also available is a system upgrade kit to expand to three sensors for better pavement coverage.
Additional GPS options and mounting pole provide high precision location information and work seamlessly with the PaveScan interface.