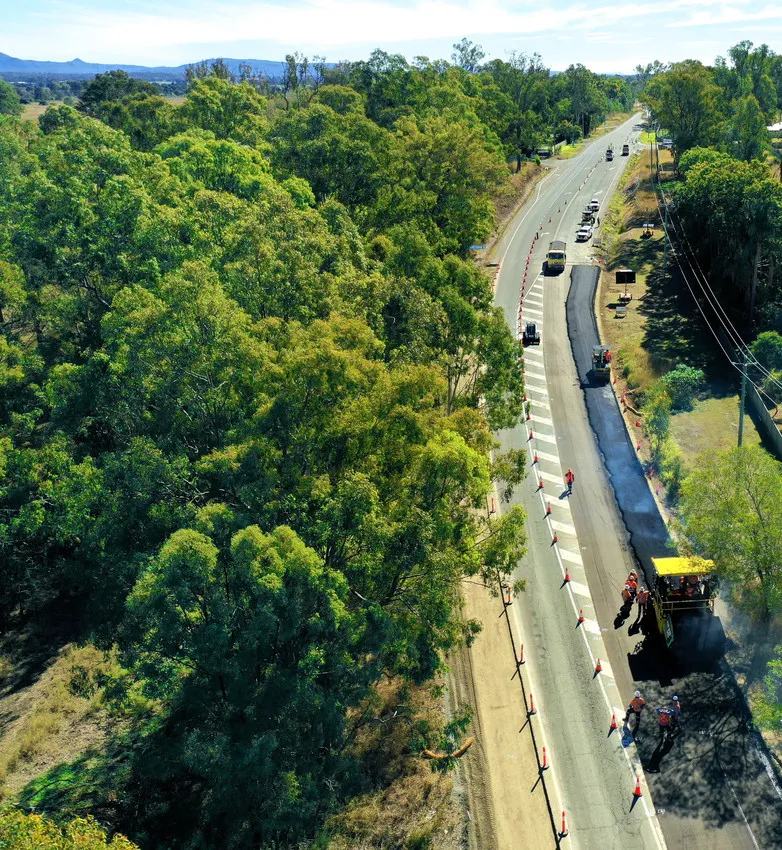
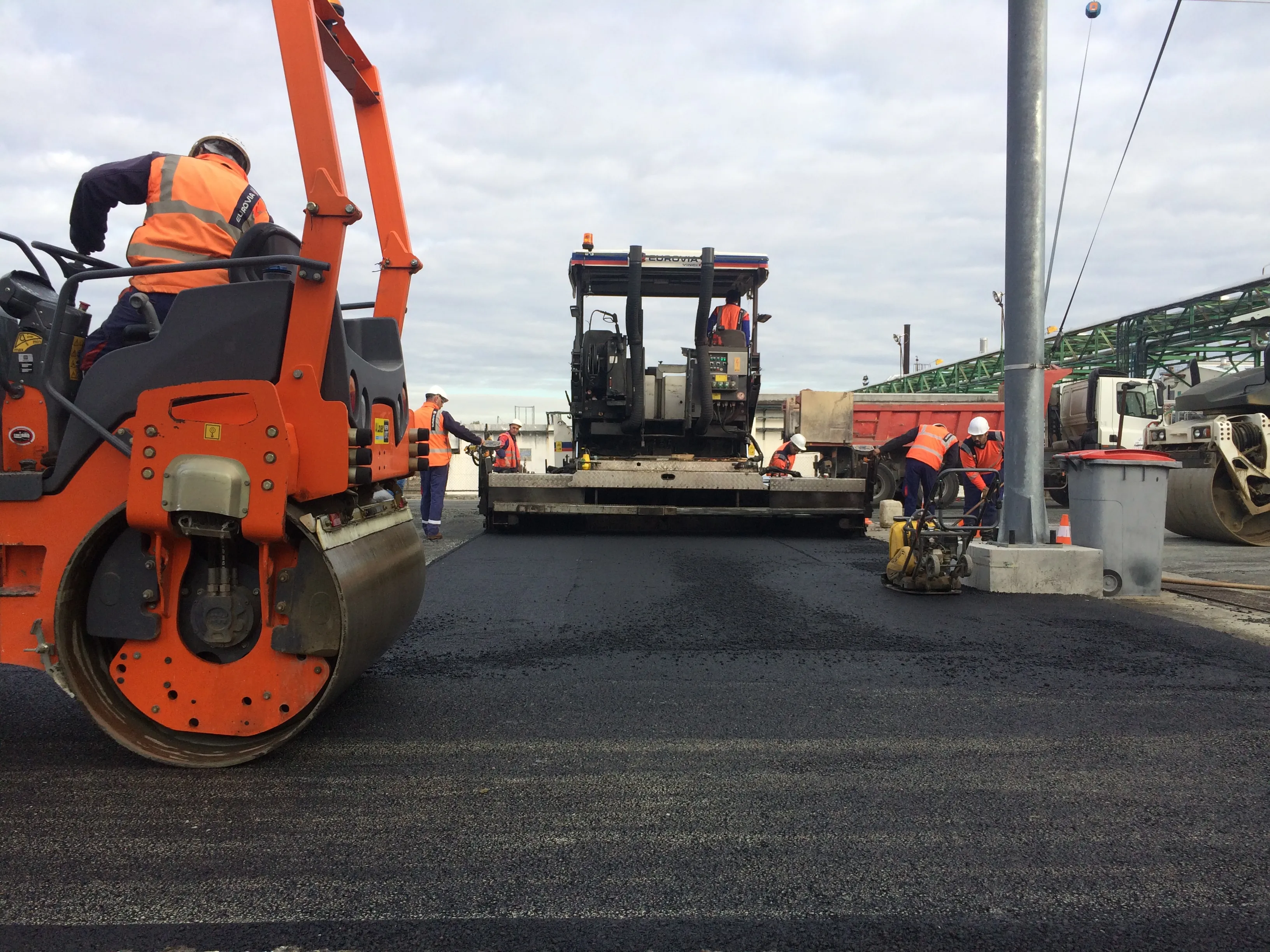
The CarbonBind Project, from Puma Energy Bitumen, has won the Australian Flexible Pavement Association’s (AFPA) National Innovation Award.
Earlier this year, CarbonBind – a bio-based asphalt and sprayed seal binder – also won AFPA’s regional awards in Australia’s Victoria and New South Wales states.
Puma, based in Switzerland, said CarbonBind is a blend of bitumen with a sustainably-grown plant-based component that maintains at least equal quality and technical performance with normal asphalt. The company said it is an alternative to conventional products and “significantly reduces the overall carbon footprint of bitumen and the asphalt products that contain it”.
CarbonBind captures carbon from the atmosphere and stores it permanently in a road’s pavement. There are different grades available, but in atypical application, for every tonne of CarbonBind used 150kg of CO2 is sequestered into the road or pavement forever.
Puma says that the carbon footprint reductions were externally verified by means of a robust life-cycle assessment and documented in environmental product declarations. The biogenic material is sustainably source, in a process certified under the International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC) system.
"[The award] recognises our commitment to create a sustainable future for the bitumen and asphalt industry through rigorous R&D,” said Phil Chirnside, Puma Energy General Manager Australia. “We are committed to reducing the carbon intensity of our bitumen products, developing novel and sustainable bitumen products with low-temperature asphalt additives and bio-based alternatives to fossil-derived bitumen. CarbonBind is probably the most exciting bridge between legacy technology and the low carbon, high-performing binders of the future."
CarbonBind is one of a range of Puma Energy Bitumen products available to help customers reduce their carbon footprint. The range also includes Olexocrumb; waste tyres are used to create crumbed rubber-modified bitumen. The process not only reduces harmful tyre waste but also provides bitumen that is longer lasting and better for roads.
In 2022, Puma Energy Bitumen invested in production facilities to help meet rising demand for waste rubber modified binders and other speciality products.
Puma Energy – a mid- and downstream oil company - is incorporated in Singapore and has corporate headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland. The business is 96% majority-owned by Singapore-based French company Trafigura and has around 3,500 employees worldwide working in all its divisions including fuels, aviation fuels, lubricants and what the company calls future energies, not only bitumen. Its operations span 40 countries across five continents and encompass the supply, storage, refining, distribution and retail of a range of petroleum products.