Bolivia’s new highway will provide better access into mountain areas – Mauro Nogarin writes
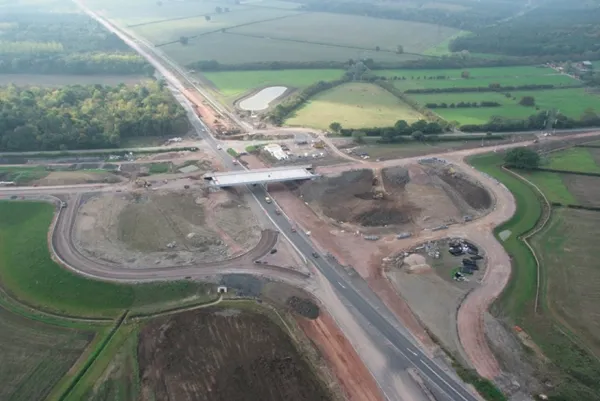
At the beginning of 2015, work began on the construction and paving for the Tupiza - Atocha - Uyuni highway project. The route is located in Bolivia’s Potosí department: it is 189m in length and forms part of the Southwest Basic Road Network (RVF) of Bolivia.
The completion of this important route is requiring funding worth US$150 million, of which 72% is being delivered through loans from the European Investment Bank and the CAF - Latin American development bank, and the remaining 28% comes from the government of the department of Potosí.
This route will increase and diversify the economic development in the southern region of the country, both with tourism at the Salar de Uyuni and with agricultural and mining activity. It is estimated that the travel time will be reduced from 5 hours to two hours and 25 minutes, benefiting the populations of Uyuni, Noel Mariaca, Cerdas, Atocha, Villa Solano, Thola Mayu, Palca Flores, Salo, San Miguel and Tupiza.
According to the project the work is taking 42 months in all, and will open to traffic in June 2018. The majority of the area is located in the highlands, between the Eastern and Western ranges of the Bolivian Andes. The road runs along morphological zones that appear as flat and semi-flat, with undulations and relatively low mountains, where the road mapping is between a flat and wavy topography, as well as straight and winding. The road engineers will use gradients of between 9-10%
In the Atocha and Tupiza Sector, the high mountains range in altitudes from 3,000-5,500m above sea level, with slopes between 15% and 60%, and their lengths of 200-500m. And the average mountains reach elevations from 2,500-5,150m, with slopes of around 10% to more than 60%, with variable lengths between 200 - 500 m.
The main climatic characteristics of the area covered by the project in the municipality of Uyuni are intense cold and little rainfall with an average relative humidity of 33%.
The design of the first 86km of the road consists mostly of long straight sections with few curves, while the vertical geometry features a few smooth slopes. However once the route reaches the town of Atocha, the horizontal geometry suddenly becomes more complex and includes a series of curves.
The next stretch of the road from Atocha to the town of Tupiza measures 103km long and climbs in altitude, with the route featuring with closed curves and drops that reach 10%. Meanwhile the area also features significant slopes as it is a mountainous zone. The road improvements required changes to the alignment and horizontal adjustment to boost safety.
Because of the complex geography and geology of the area, the drainage system designed for the Uyuni to Tupiza stretch of road features both surface and underground systems. The construction of 231 sewers is planned, most of which are in sectors where there are bofedales (high-altitude areas of boggy peat that are common in the Andes, having been expanded by human habitation to increase vegetation) and outcrops of water flows. Three grades of concrete, type "A" (210kg/cm2), type "C" (160kg/cm2) and type "E" (110kg/cm²) are used for these drainage works, with the specific design catering to the volume of water calculated.
The construction company José Cartellone currently has two working areas on the project, with one located in the section between Km23 to Km63 where paving works are being carried out. The second is located in the section between Km77 to Km 90, where excavations are being carried out along with stabilisation of the embankment and alignment. In general the roadway is 7m wide in total and a features a 1m berm with a 50mm asphalt layer that includes the use of PMBs. The design speed of the road is estimated at 80km/h. The structure of the road itself features a sub-base layer of 220mm and with a base layer of 150mm and an asphalt surface 70mm thick.
Along the entire route, seven bridges will be built, with a total length of 351m. However the most important bridges are located at Choroma and Tolonias, with construction starting at the end of 2017. The Choroma Bridge features a design comprising two reinforced concrete supports sitting on deep foundations, while the superstructure has a reinforced concrete slab and a design with three pre-stressed concrete beams that are 35.6m in length. The bridge also consists of two spans and is 71.2m long.
The Tolonias Bridge meanwhile has a similar design with two reinforced concrete supports resting on piles that are 1.2m in diameter. The reinforced concrete slab superstructure has three pre-stressed concrete beams that are also 35.6m in length and with the two spans, the bridge is also 71.2m long.
Bolivia’s new highway
Bolivia’s new highway will provide better access into mountain areas – Mauro Nogarin writes
At the beginning of 2015, work began on the construction and paving for the Tupiza - Atocha - Uyuni highway project. The route is located in Bolivia’s Potosí department: it is 189m in length and forms part of the Southwest Basic Road Network (RVF) of Bolivia.
The completion of this important route is requiring funding worth US$150 million, of which 72% is being delivered through loans from the European Investment
October 10, 2017
Read time: 4 mins