English national roads authority
The authority believes that the findings of its research could help improve road safety and decrease whole-life pavement costs around the world.
Paid for out of a £1.5 million innovation fund, the project is part of a four-year research program which aims to drive improvements across England’s motorway and A-road network. Application and removal of road markings was identified as one of the most important areas for research.
Often, the shape of old markings can still be seen on a road even after they have been removed. These ‘ghost markings’ can be confusing for drivers and cause problems for autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles. Water-blasting or shot-blasting removal techniques for markings cause damage to the surface of the road, leading to cracks and potholes which reduce the lifetime of the pavement.
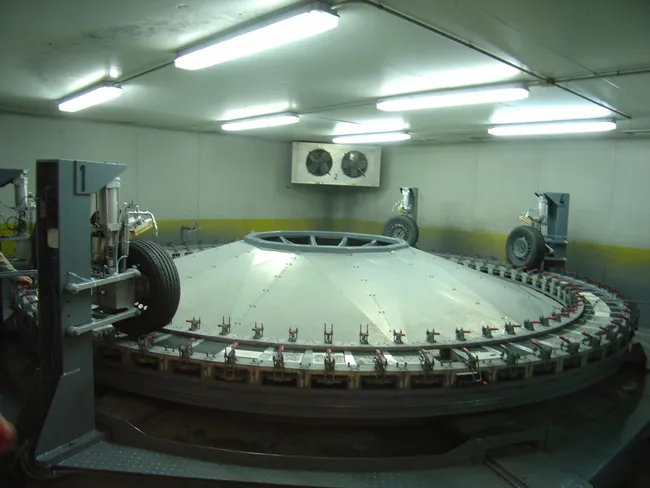
The first phase of the Highways England research saw 36 road marking products from around the world tested at Spain’s AETEC facility in Madrid. “The Spanish facility, as well as being highly respected in the industry and in this field, was able to recreate our road surface,” said Martin Bolt, corporate group leader at Highways England who has been overseeing the research. “Elsewhere the tyres would have been tested on a smooth surface.”
The road marking products, which included thermoplastic, water-based paint, cold plastic and tapes, were tested for skid resistance, dry retroreflectivity, wet retroreflectivity and contrast. A series of images were taken during each testing cycle, including microscopic views.
After 12 months, the products will be removed using five different products. Contractor Kier and specialist road marking supplier Roadcare are working on the research project with Highways England.