Ferocious daytime temperatures can provide a tough challenge to construction firms working in desert conditions in Egypt's south. Despite the high daytime temperatures however, Egyptian contractor Orascom has managed to complete an airport project on budget and ahead of schedule, while meeting the client's tight specifications. The firm has just completed the project to revamp Suhag Airport in the south of the country. This airport now features a new runway, taxiways and aircraft hard standing, as well as n
April 13, 2012
Read time: 3 mins

Ferocious daytime temperatures can provide a tough challenge to construction firms working in desert conditions in Egypt's south.
Despite the high daytime temperatures however, Egyptian contractor
In all Orascom says it paved around 34km of roads at the site, including the perimeter road around the airport. The runway itself measures 3km long by 70m wide while there are three taxiways of 400m each and two concrete aircraft parking aprons measuring 37,900m2 for military aircraft and 40,000m2 for civil aircraft.
The runway features three layers of asphalt, a wearing course, binder course and base course. Under this are two layers of compacted soil and aggregates, built to tight specifications to meet Egyptian requirements and regulations. The aircraft parking areas are made of high quality concrete and were laid in two layers, each 150mm thick and with a 700mm structure of earth and aggregate underneath. After laying the concrete was cut with slots every 5m and these were then filled with sealant.
In all nine
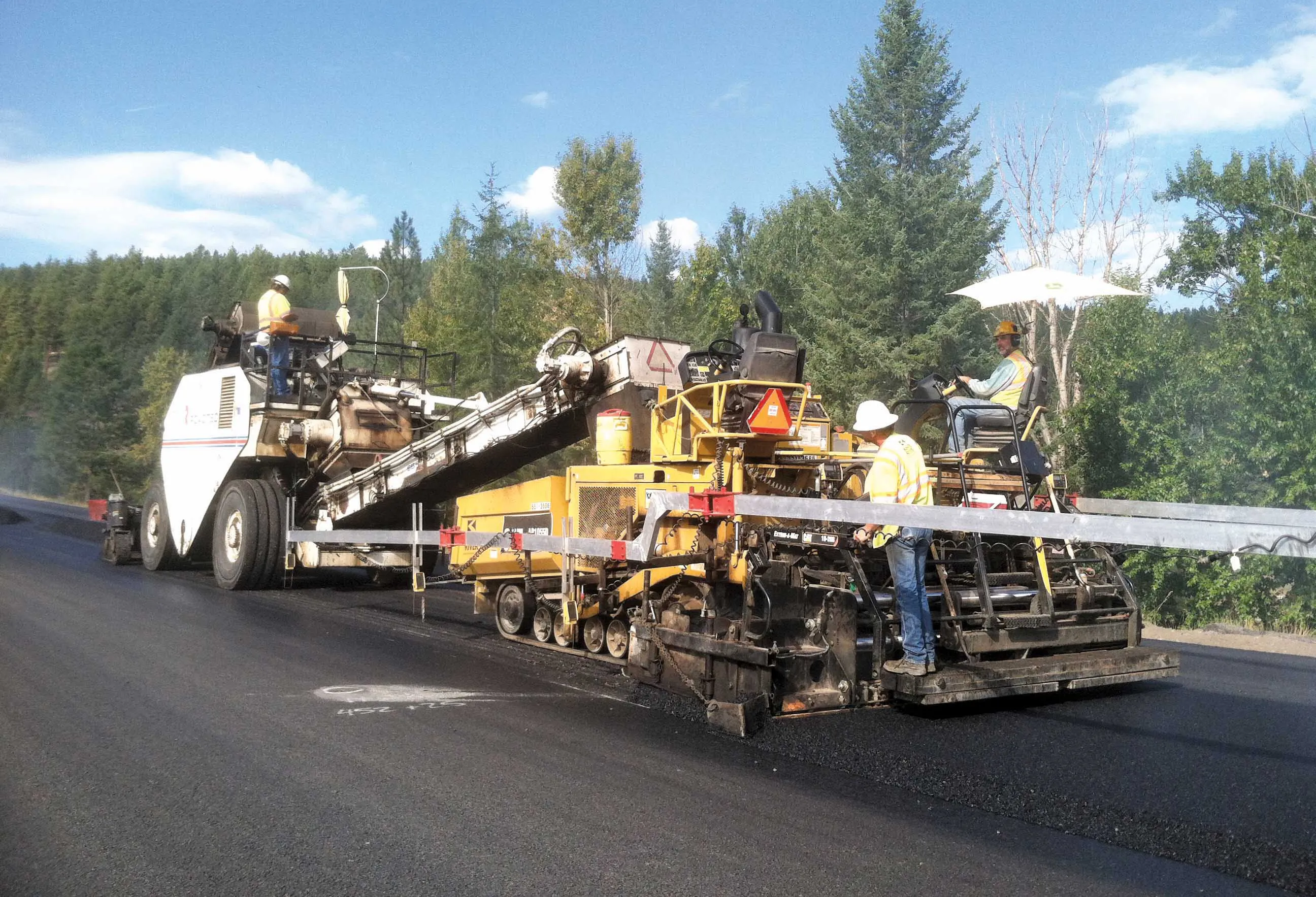
In addition, 14 single drum soil rollers and twin drum asphalt rollers of various makes were used for compaction of the earth and asphalt surfaces. A
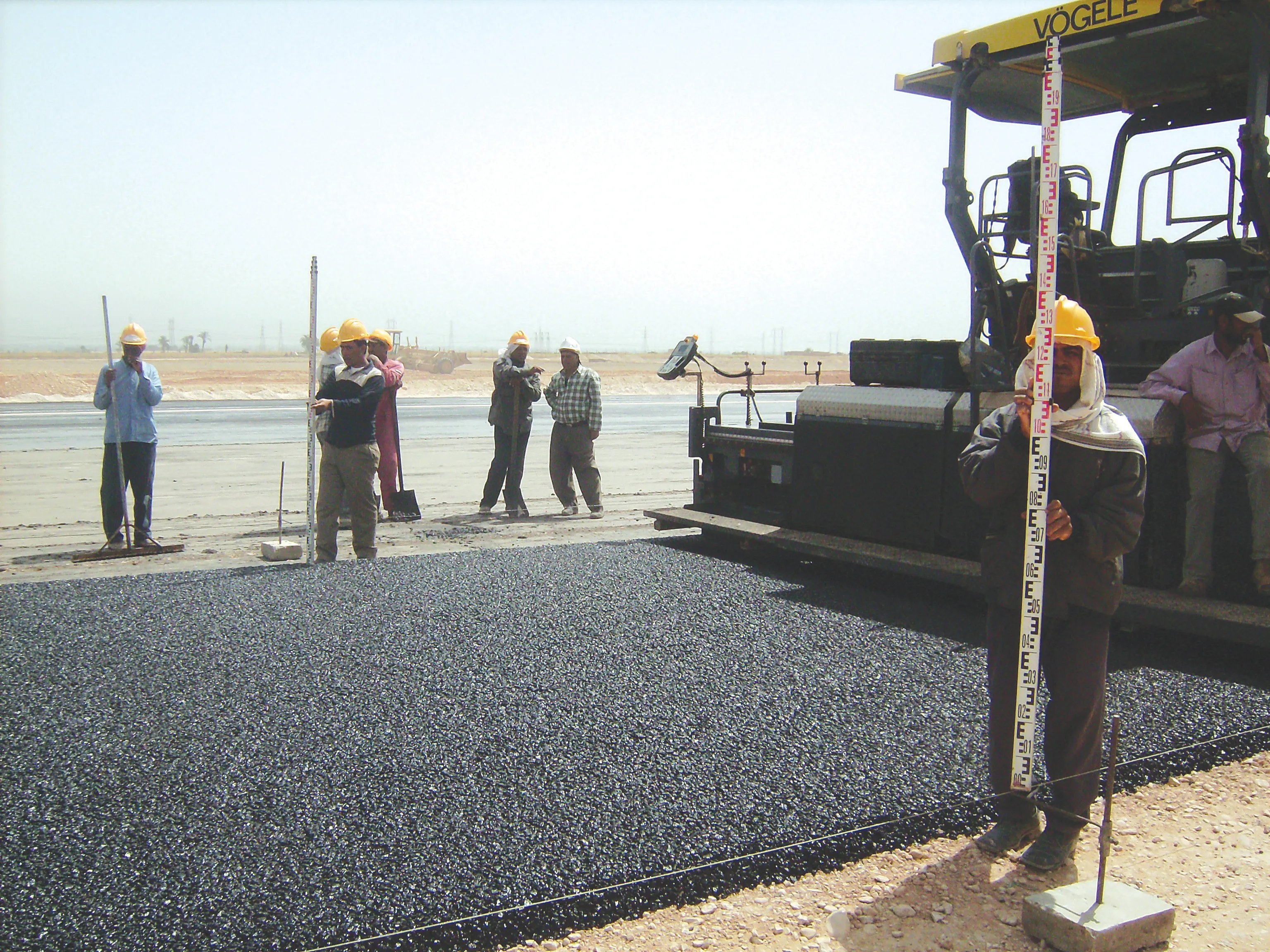
Because the asphalt and concrete paving work had to be carried out to high specifications, total stations were used to monitor progress throughout and a tolerance of +/- 2mm was allowed on the concrete surface for instance. The concrete paving job was only carried out at night to save the crew from working with the material during the fierce daytime temperatures that can hit peaks of 45ºC.
Orascom had to build five concrete culverts along the length of the runway as well as two for each of the taxiways although these are all for electrical cabling rather than drainage, as rainfall in these desert conditions is a rare event. The new airport is now open to traffic and also benefits from a brand new control tower and terminal building, as well as other new facilities.