An innovative solution was put forward to support slip roads on a Dutch motorway. Patrick Smith reports
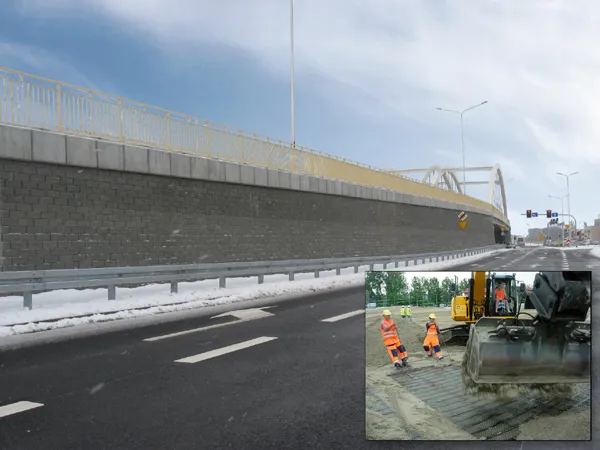
The 2010 opening of the A7 motorway extension on the southern ring road of the city of Sneek, The Netherlands, brings an end to local traffic misery. By using innovative Tensar Geocell Foundation Mattress technology over weak estuarine clay, MNO-Vervat Noord, the main contractor, constructed a key junction and its slip roads in weeks instead of months, with considerable cost savings.
The conversion
April 10, 2012
Read time: 3 mins

An innovative solution was put forward to support slip roads on a Dutch motorway. Patrick Smith reports
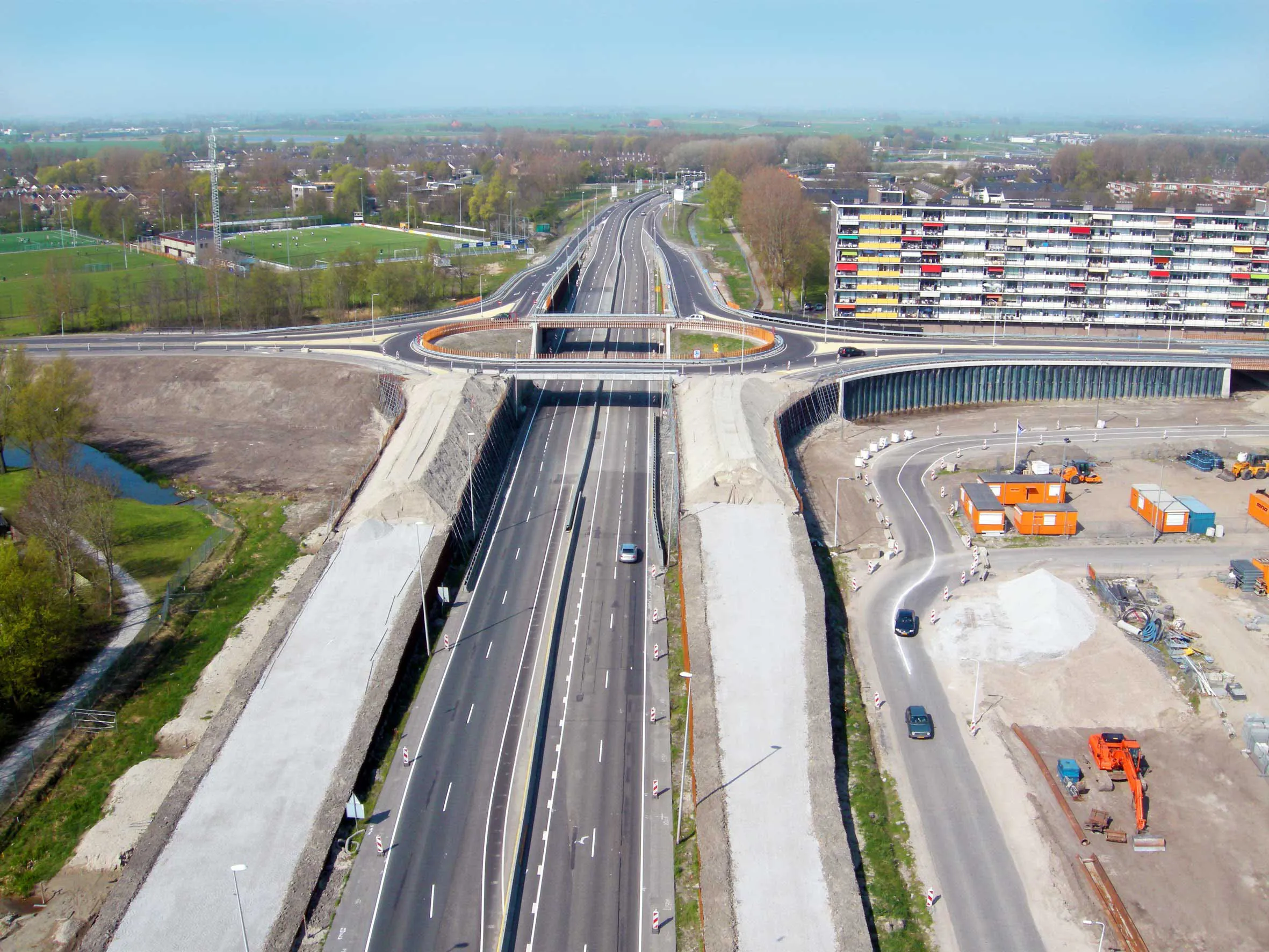
The 2010 opening of the A7 motorway extension on the southern ring road of the city of Sneek, The Netherlands, brings an end to local traffic misery. By using innovative Tensar Geocell Foundation Mattress technology over weak estuarine clay, MNO-Vervat Noord, the main contractor, constructed a key junction and its slip roads in weeks instead of months, with considerable cost savings.The conversion of the ring road around Sneek to a new highway, with replacement of the signal-controlled junctions for client Rijkwaterstraat, the Province of Friesland, City of Sneek, began in 2007, but a problem with the soil was encountered at the Lemmerweg junction in 2009. A 2.5m thick layer of weak peat and soft clay was found below the proposed four slip roads connecting to an overhead roundabout over the A7. In addition, the slip road ramps up to 6m high with a vertical face, and exerting considerable load, meant that site access would have been difficult for heavy construction plant.
"To instigate soil improvement measures over such a large area would have been costly, and the conventional heavy sheet piling techniques would have held the project up by several months. The project budget and schedule would have been under threat," said Theo Huybregts, of
The consultant engineers, Ingenieursbureau Geologics and Fugro Ingenieursbureau (Regio Noord), worked with the Tensar design team to propose a different approach to the contractor. This comprised installing a load-bearing 1m thick Tensar Geocell Foundation Mattress over a 6,000m2 area of weak clay to stabilise the embankment foundations and to reduce lateral movement. Controlling ground movements was particularly important because the existing ring road, which is located only 1m from the vertical face of the new ramps, had to remain open to normal traffic throughout the construction.
Filled with aggregate, the Tensar Foundation Mattress was installed in 13 working days to provide a stiff layer for the foundations, which allowed access for plant and facilitated drainage from the road construction above. In addition, the Geocell Mattress structure provided the ideal base for Tensartech TR2 steel mesh-faced reinforced soil-retaining walls to the motorway embankments, which were built safely without scaffolding or disturbance to the nearby live traffic.
Meanwhile, the
German company
The company worked with Professor Karl Josef Witt and Mary Noack from Bauhaus University Weimar, Germany, to create the 40cm³ columns.
The geogrid used in the experiment was NAUE's Secugrid, and the four columns were constructed in front of an audience of some 120 at the university.
Crushed gravel of 8-32mm was poured into the formwork with NAUE Secugrid 40/40 Q1 geogrid inserted every 10cm to create three layers of reinforcement.
A forklift placed the vehicle on the columns, and two television crews captured what happened when the forms were removed and Secugrid's ability to absorb such direct forces was put to the test. The reinforced columns held.