How do you test an asphalt mix for rutting? In the US, the answer could be any one of several tests, depending on which State you are in: Asphalt Pavement Analyser, Flow Number, Hamburg Wheel Tracking Test, Superpave Shear Test or Triaxial Stress Sweep Test.
But that could all change. The Federal
The development of BMD could lead to the selection of just one test to characterise each of the main failure modes of a road pavement, rather than many tests (see table). These tests would be used in the design of pavement mixes and would mean that the equipment needed for that select group of tests would be in high demand. And with many regions around the world tending to follow US testing standards, the eventual impact could be much bigger. The reason why the FHWA and others think that BMD is needed is that too many pavements are failing even though the mix specification has been met. The ‘balanced’ part of balanced mix design refers to finding a balance between both rutting resistance and cracking resistance.
When the US$150 million Strategic Highway Research Program which produced the Superpave system got underway in the late 1980s, pavements in the US were most likely to fail through rutting. Today’s roads are more likely to fail prematurely due to cracking of various types.
A survey carried out by Oldcastle Materials in 2015 found that in the previous five years the most common forms of distress in pavements were longitudinal cracking (55%), reflective cracking (43%), ravelling (30%), thermal cracking (20%) and slippage (18%).
The reason why mix design needs to change is that the materials going into mixes have changed significantly since the turn of the century. Today we see higher proportions of RAP, various types of polymer modification, warm mix technologies, rejuvenators, fibres.
BMD aims to use performance testing for mix design, rather than relying solely on the volumetric approach. Apparently, this was always the intention of the Superpave system. Low traffic pavements would be designed based on volumetric properties; highways with a moderate amount of traffic would combine volumetric requirements and limited performance tests; high traffic pavements would start with a volumetric approach, developed with an extended set of performance tests.
The reason why the performance testing element never took off is because the tests were not considered practical to be used constantly for mix design. And with the materials being used at the time, the volumetric approach worked just fine.
FHWA acted to hasten the use of BMD in September 2015. Its Expert Task Group on Mixtures and Construction set up a Balanced Mix Design Task Force. The task force agreed on a definition for BMD as ‘an asphalt mix design using performance tests on appropriately conditioned specimens that address multiple modes of distress taking into consideration mix ageing, traffic, climate and location within the pavement structure.’ It also identified three possible approaches to BMD: volumetric design checked with performance tests; using performance tests to modify a volumetric design; and an approach which is totally based on performance tests.
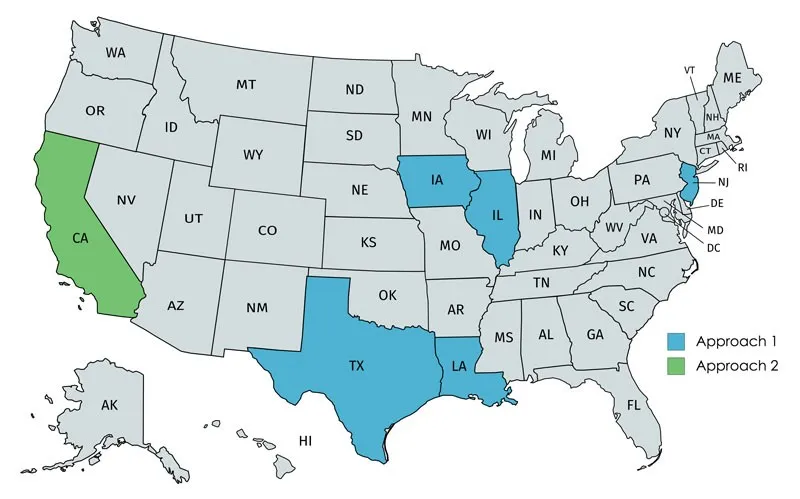
NCAT, the National Center for Asphalt Technology, has researched which States are using the various BMD-type approaches. It found five states using performance tests to check mix design – Illinois, Iowa, Louisiana, New Jersey and Texas – and just one, California - which was using the second approach, modifying mix designs with performance tests. None were using performance testing only, although NCAT reports that several states have carried out or will carry out pilot BMD projects.
According to NCAT, a number of questions have yet to be answered before BMD can progress. One of the fundamental questions is which are the most appropriate tests for each type of failure.
Another challenging area is how to appropriately age specimens for testing that mimics what actually happens on a highway. Rutting and moisture damage tests tend to be carried out on specimens that have been aged for a short amount of time because that type of damage tends to happen soon after a pavement is laid. However, cracking needs longer-aged specimens because cracking occurs later in a pavement’s life.
We may get some answers in May this year, when the results of a one-year, $100,000 project to develop a framework for BMD are expected. The National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP) Project 20-07/Task 406 will present the framework in the form of an AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials) standard.
However, reports suggest that the standard will encompass ‘a wider variety of testing procedures and criteria’. Whether all 50 states can agree on just a handful of tests remains to be seen.









