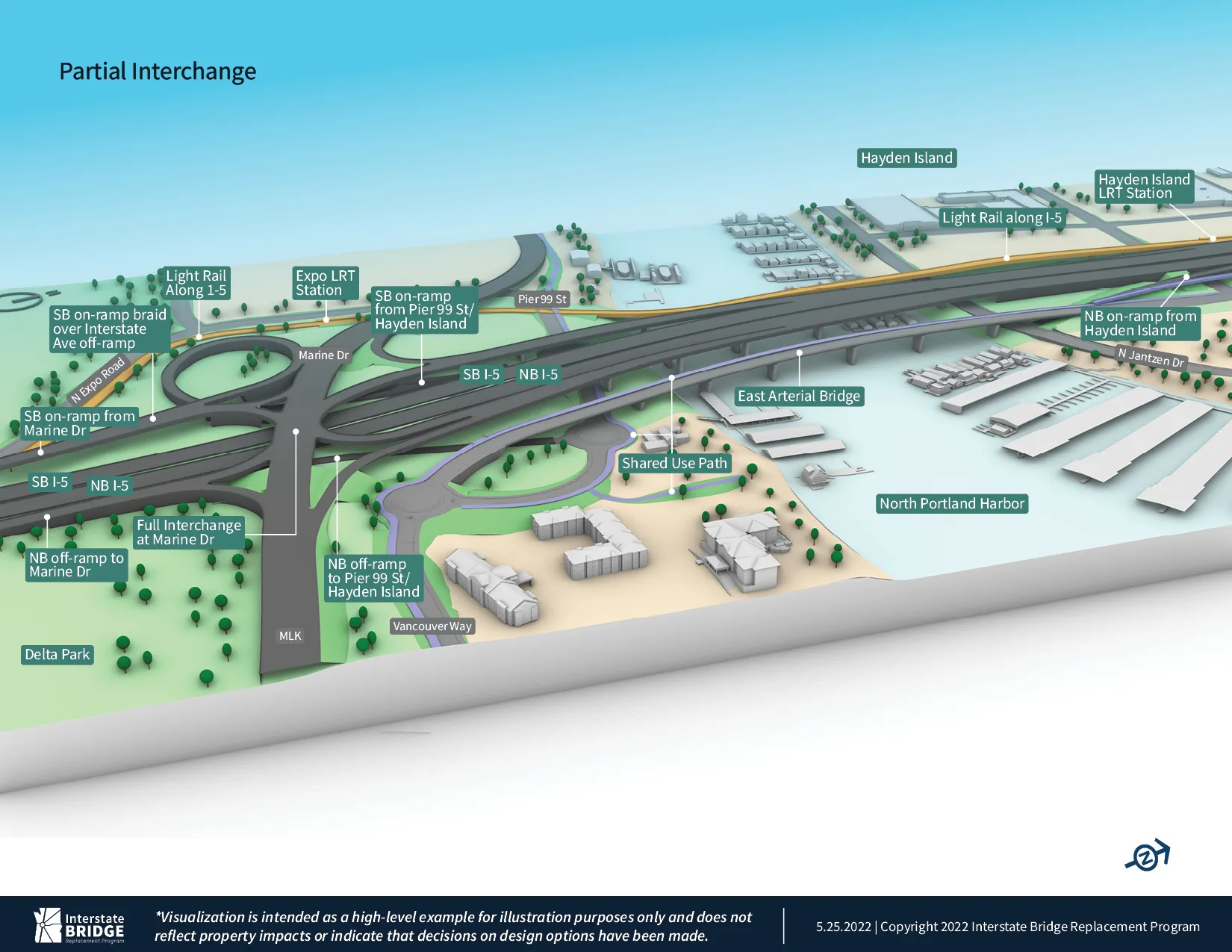
The Vancouver City Council in Washington state has unanimously approved an early draft of the Interstate 5 Bridge plan, according to local media reports.
The new 8-lane Interstate 5 Bridge will have variable-rate tolling, notes the plan called the Modified Locally Preferred Alternative.
The approval is an early step in a long process for the project and the plans are subject to change as the Interstate Bridge Replacement Program seeks more review, paving way for revision. Anne McEnerny-Ogle, mayor of Vancouver, said the approval for a replacement bridge is “from step two to step three of 100 steps, so this is a very exciting time”.
The existing Interstate Bridge is two bridges, side by side. The northbound span is over 100 years old, dating back to 1917. The southbound span opened in 1958.
Vancouver, a city of just under 200,000 in Washington, sits on the north bank of the Columbia River which is the border between Oregon state to the south. Opposite Vancouver is the city of Portland with a population of around 650,000, making it the largest city in Oregon. The I-5 connects Portland with Vancouver and is a major west coast US highway. It extends 2,220km from Washington’s northern border with Canada down to the southern tip of the state of California - the border with Mexico.
According to the Replacement Bridge website, the Interstate Bridge is a critical connection linking Oregon and Washington across the Columbia River as part of a vital regional, national and international trade route.
“With one span now 105 years old, it is at risk for collapse in the event of a major earthquake and no longer satisfies the needs of commerce and travel. Replacing the aging Interstate Bridge with a modern, seismically resilient, multimodal structure that provides improved mobility for people, goods and services is a high priority.”
In January 2021, Oregon and Washington states ear-marked a total of US$50 million for initial Interstate Bridge replacement planning work. A bi-state legislative committee, composed of 16 Oregon and Washington politicians provides additional guidance and oversight for the programme.
More than 138,000 vehicles crossed the Interstate Bridge each weekday in 2018, resulting in 7-10 hours of congestion during peak travel times. Safety is not up to modern standards. The bridges have narrow lanes, no shoulders, poor sight distances on and near the bridge, frequent bridge lifts and substandard ramp merging and diverging contribute to an increase in accidents.
The bridges’ narrow shared-use paths, low railing heights and lack of dedicated pathways on either side of the bridge impede safe travel for pedestrians and cyclists. There are also limited transit options across the bridges and bus services can be unreliable due to traffic congestion or bridge lifts to allow for the passage of ships.
Of particular concern - for an area that is prone to Earthquakes - the bridges’ foundations are set in sandy soil and do not reach bedrock. In a major earthquake, the bridge could be significantly damaged, notes the replacement bridge project’s website.
The Interstate Bridge Replacement Program’s Modified Locally Preferred Alternative announced in May calls for four total lanes: three travel lanes, one auxiliary and two shoulder lanes in each direction.
The preferred alternative presented Thursday also included two shoulder lanes for both the northbound and southbound spans. The shoulder lanes would be available to express buses, as well as emergency vehicles and to help clear accidents.
What has yet to be decided is whether the northbound and southbound spans will be placed side by side or stacked on top of each other. That decision won’t be made until later in the planning process.
The proposed modified locally preferred alternative is being considered by the replacement program’s eight partner agencies — including the city of Vancouver, C-Tran (the Clark County Public Transit Benefit Area Authority, a public transit agency serving Clark County in Washington), the Port of Vancouver and the Southwest Washington Regional Transportation Council.
However, a new bridge is a long way off yet. Based on previous planning activities, the website says, it is estimated that it will take three to five years to complete the planning and federal environmental review process and obtain federal approval before beginning construction. The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) and Federal Transit Administration (FTA) will oversee the federal environmental review process.
It is expected that design will take place in 2024 with construction to start in 2025.
Updates on the IBR program can be found at here.
www.interstatebridge.org.









