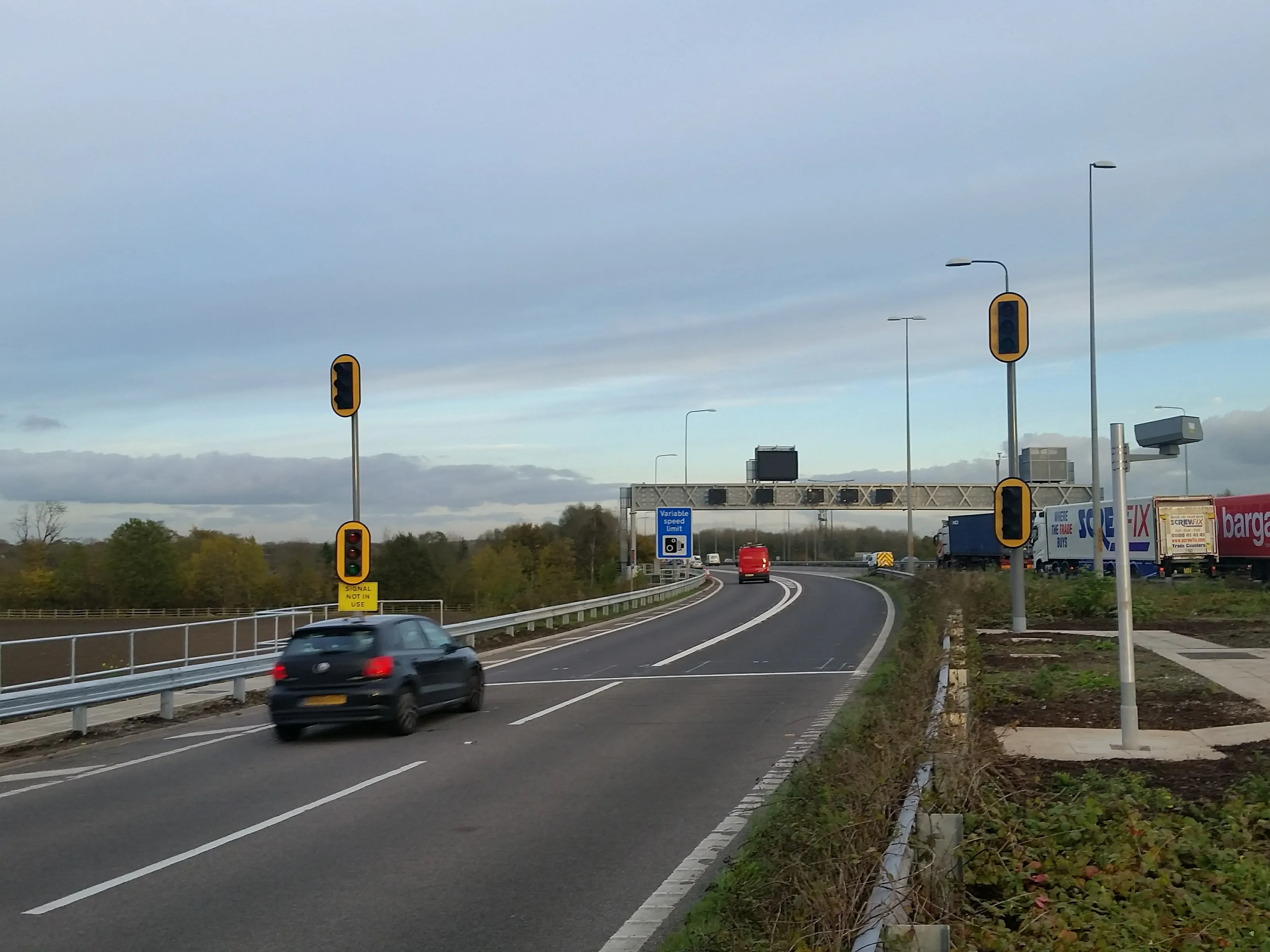
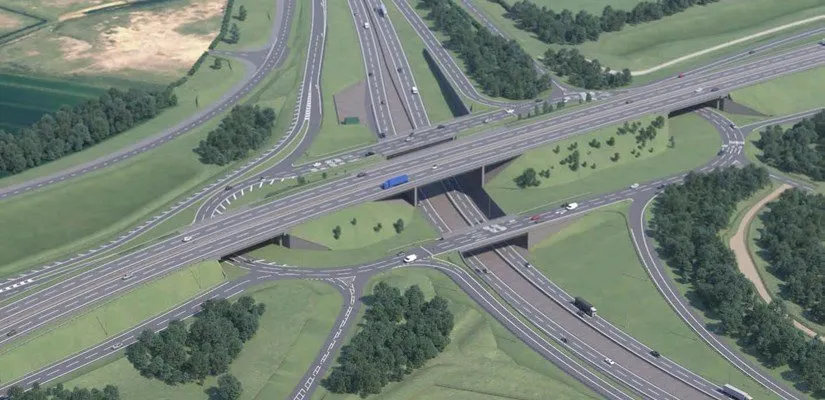
Large volumes of eastbound traffic on the M62 can cause weaving problems, leading to congestion between junctions 10 and 11. This problem is exacerbated by traffic joining the motorway from the M6 northbound and southbound link roads. This merging traffic causes flow breakdown on the M62 through the Croft Interchange, which in turn causes queues to form along the motorway to junction 9.
The M2M scheme combines the use of two standard technologies in an innovative way. Variable mandatory speed limits on the M62 and metering using traffic signals between the M6 to M62 eastbound are integrated to make best use of the available road capacity. These are set in response to prevailing traffic conditions, with information displayed on overhead gantries, using advanced motorway indicators and variable message signs. Mott MacDonald developed the algorithms which coordinate the separate systems. Where no mandatory speed restriction is displayed the national speed limit will apply.
Stuart Scott, Mott MacDonald’s project principal, said, “Highways England is committed to building upon the success of its existing smart motorway programme. The M2M scheme increases the resilience of the overall network, with the benefit to the road user of smoother traffic flows, improved journey times and increased quality of information provided.”
“By utilising the latest technologies and making use of the existing capacity of the link roads, the M2M scheme is a lower cost solution than conventional widening programmes. Additionally, it does not require additional road-space, leading to a low environmental impact during construction while delivering a positive impact during operation,” Scott added.