Gantries first appeared over highways in the late 1960s and are now of increased importance, thanks to the emergence of Smart Motorways, writes Simon Benfield*
The motorway network exhibits a timeline of innovation; lane control signals on highways appeared in the 1970s, with variable message signals following in the 1980s. By the late 1990s controlled motorways had been introduced on the M25. Managed Motorways were introduced in the 2000s and the past decade has seen the emergence of Smart Motorways that use technology and a regional traffic control centre to manage the traffic flow.
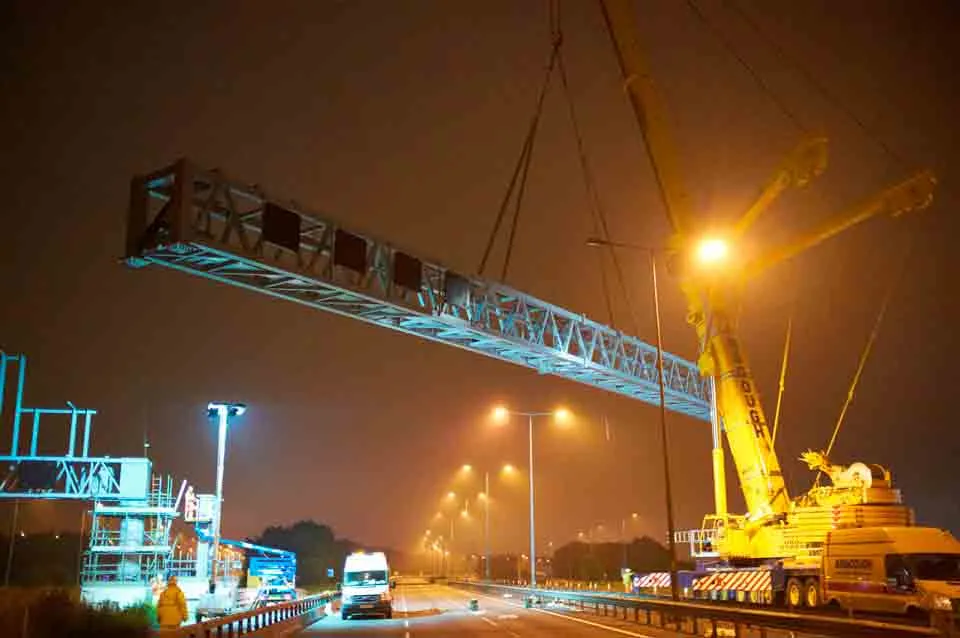
Gantries are now vital to the operation of Smart Motorways.
They help identify incidents and warn road users, give traffic flow advice and journey time information as well as mandate reduced speed limits. Smart Motorways can also increase a motorway’s capacity by 20 to 40% and at a fraction of the cost of conventional widening, depending on availability of land and constraints caused by existing structures. It is therefore imperative that construction, erection and commissioning of gantries is as rapid and efficient as possible to reduce disruption, costs and time.
Designs are developed through close collaboration between designers, fabricators and equipment suppliers. As well, equipment requires regular maintenance to ensure Smart Motorways operate safely and efficiently.
Time spent working onsite is costly. To reduce this, a product-based approach has been developed for gantry designs as well as for the tools to execute these designs.
Generic gantry types and subtypes are also now tailored to a range of requirements for specific highways: different equipment levels, varying provisions for fixed signage, different spans and wind speeds. In fact, wind loading is usually the primary design driver for gantries.
Using automated design processes, subtypes can be generated very quickly - in less than a day sometimes - as a new requirement is identified. Standard parts and arrangements help streamline a production-line approach to gantry manufacture. Structures can be outfitted offsite, which reduces hazardous on-site work.
To save yet more time, the design of the main structural connections has been simplified to speed up on-site erection of a gantry. If an experienced fabricator or erector is involved, erection time can be less than 10 minutes, as was recently seen on the UK’s M60 and M62 during part of the Manchester Smart Motorway project.
Unsurprisingly, the biggest focus will be on driverless vehicles - not only on how they will impact driver experience and congestion, but how roads will accommodate them. With road and traffic information beamed directly into the vehicle via satellite, signs and signals can be discarded and vehicle sensors will “see in the dark”, negating the need for road lighting, on motorways at least. The removal of human error means that barriers are no longer needed. As vehicles can talk to one another, traffic flows can “zip” together, dramatically changing the appearance of junctions.
But do gantries have a limited lifespan? This is not likely because of their central role in physically supporting telecommunications systems that in turn reduce the reliance on satellites. They will continue to carry sensing equipment required to manage the feed into individual vehicles.
They may also even earn their keep by supporting valuable advertising that can be tailored to a captive audience in driverless cars beneath them.
*Simon Benfield is a team director at