The Eyiste Viaduct will be part of a route between Central Anatolia and Turkey’s Mediterranean region, shortening travel time between the cities of Konya and Alanya. Cantilever forming travellers and
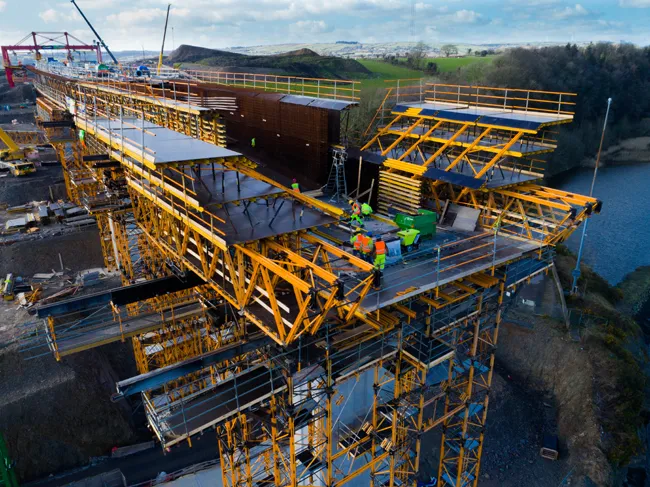
The viaduct is nearly 1.4km long and carried by two abutments and eight piers, stretching across the Göksu River near the city of Konya. The superstructure of the balanced cantilever bridge has nine spans, the longest being 170m. The piers vary from 31-155m high.
Work started in March 2017 and the structure is scheduled to be opened for traffic in June 2020. The bridge’s superstructure is being constructed by the balanced cantilever method, which is ideal for long spans and has established itself as the method of choice for bridge-building projects in Turkey. A total of 130,000m³ of concrete and 28,000tonnes of steel - excluding prestressing cables - will eventually be used.
Differing pier heights and the long deck cause differences in the way external influences affect the structure. The CSiBridge software was used to model the viaduct in 3D. This was to assess the bridge’s ability to handle vertical and lateral forces and the results incorporated into planning.
The simulations indicated that the shortest pier of 31m would be most affected by seismic forces. The long bridge deck and the tallest pier at155m, by contrast, would be more susceptible to creep, shrinkage and temperature effects (CST) and to wind loads.
Based on these results, only the four tallest piers are being cast monolithically with the deck sections. The deck remains supported on longitudinally sliding bearings, providing flexibility and reducing seismic effects.
The balanced cantilevering superstructure sections of the new Eyiste Viaduct are constructed toward each other from pier head to pier head. The four cantilever forming travellers work in pairs, so that the horizontal forces acting on the bridge piers are always in equilibrium.
The travellers can handle varying section lengths from 3-5m and concrete weights up to 250tonnes. The forming carriages speed up progress on the build and allow for variations in segment geometry. Slide bearings secure the travellers against unwanted travelling on longitudinal gradients.
Fully enclosed working platforms on all levels and hydraulic test loading of the rear carriage anchorages prior to each pouring operation help ensure safety at work.
The bridge piers were formed using six paired sets of Doka’s automatic climbing formwork Xclimb 60. The system climbs hydraulically, anchored to the structure at all times by guiding shoes. Because it is guided on the structure at all times, the system can still be climbed even in windy conditions.