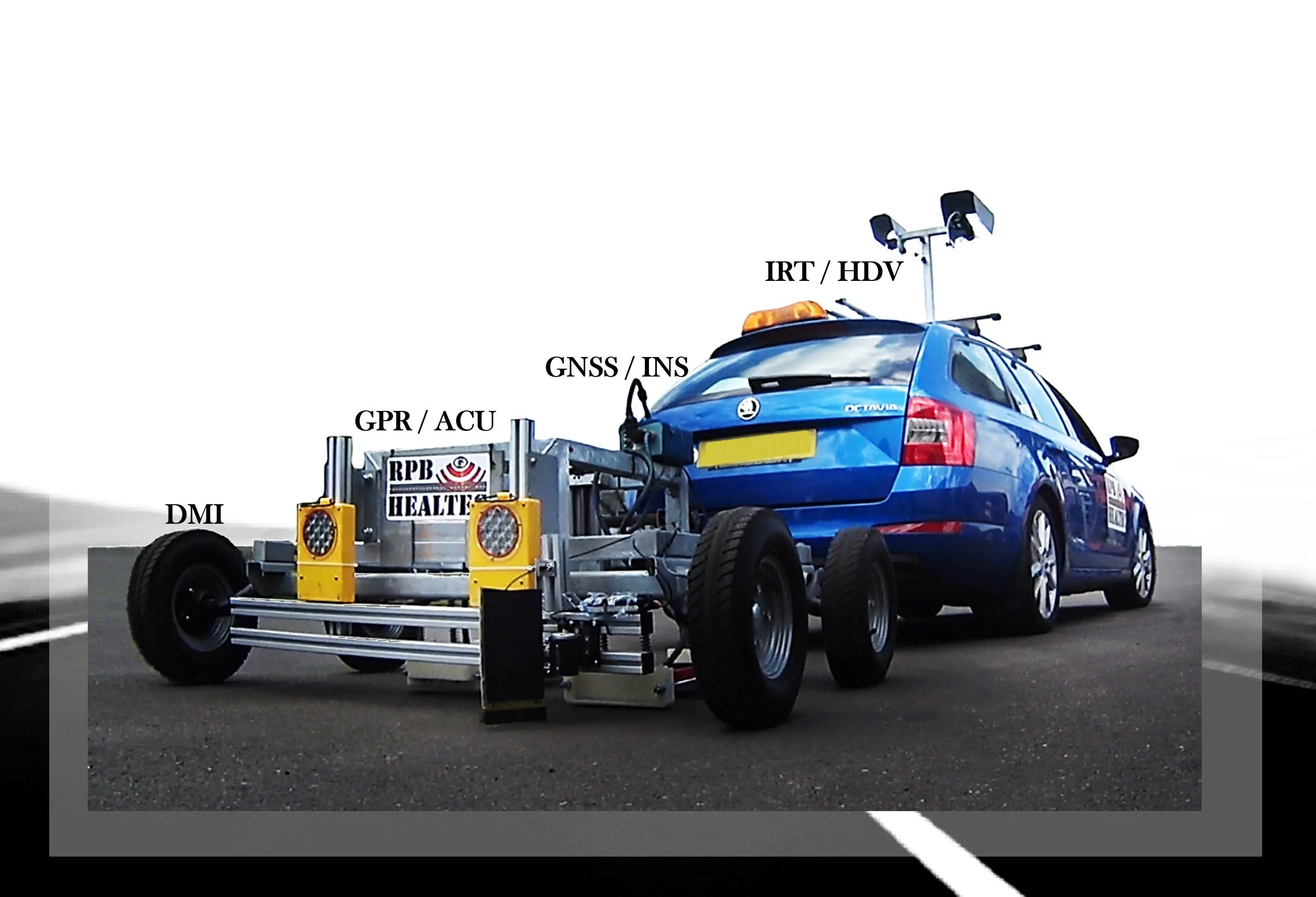
An innovative technology developed for the nuclear industry can be used to assess the structural conditions of tunnels and bridges. Deep-tech company GScan uses cosmic rays combined with AI/ML to provide precise assessments of the structural integrity and chemical composition of infrastructure, ensuring ongoing safety and longevity.
Decay, cracks and corrosion can compromise the structural integrity of transport systems, risking public safety. A pilot project on a nuclear reactor scanning proved this innovative technology for use on a broad range of engineering applications.
The firm can deliver infrastructure assessments for assets like bridges and tunnels. The company will conclude a project with National Highways, scanning for steel components in a post-tensioned concrete bridge next month.
The Estonian deep tech GScan uses muon flux scanning and this technology has the capability to penetrate over 1m of concrete and imaging steel, allowing non-invasive assessments across various industries.
GScan uses naturally occurring cosmic rays known as muons to ‘reveal’ items that may be hidden within tens of metres of a structure. Around 10,000 muons/m2 pass harmlessly through individuals, buildings and structures every minute, changing direction and speed based on the chemical composition of the objects they encounter. GScan’s scanners detect changes to the flow of muons (muon flux); it then uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse this information, creating 3D models of the structure accurate to 1cm.
Muon flux scanning shows significant promise in industries where traditional assessment methods fall short due to extreme conditions or access limitations. “GScan’s technology isn’t just a tool for decommissioning plants; it can be used to optimise the ongoing maintenance of facilities in challenging or difficult-to-access environments. Our method allows for a detailed and non-invasive analysis of almost any structure, helping to identify degradation and structural weaknesses before they become critical,” added Andi Hektor.