Geosynthetic materials are increasing its significance in many applications in the civil and underground engineering. One of such application is in foundation stabilization for roads. A life cycle assessment (LCA) study on behalf of the European Association for Geosynthetic Manufacturers (EAGM)1 has re-vealed that the use of geosynthetic materials will contribute for sustainable highways.
In road construction the sub-base needs to meet defined requirements for compaction and bearing ca-pacity. Improveme
June 29, 2015
Read time: 3 mins
Geosynthetic materials are increasing its significance in many applications in the civil and underground engineering. One of such application is in foundation stabilization for roads. A life cycle assessment (LCA) study on behalf of the European Association for Geosynthetic Manufacturers (EAGM)1 has re-vealed that the use of geosynthetic materials will contribute for sustainable highways.
In road construction the sub-base needs to meet defined requirements for compaction and bearing ca-pacity. Improvements of some soil characteristics may be necessary while building on weak soils. Geo-synthetics materials is one approach to support such weak soils.
Today, there are 3 types of different geosynthetics that can be used for stabilization. Those 3 types are, extruded stretched grids, layed grids, and woven / knitted grids. For the LCA study, the average of the three is used to represent its performance. Polypropylene granulates are used as basic material to manufac-ture geogrids or wovens used in the study.
The environmental friendliness of the use of geosynthetic materials were found by carrying out a cradle-to-grave LCA2 study with data from numerous participating EAGM member companies which compared 3 cases. Those cases are conventional road (2A), a road reinforced with geosynthetics (2B) and a ce-ment/lime stabilised road (2C). Besides the construction of a conventional road with a non-frost sensitive gravel/sand layer (case A), soil improvement can be done with geosynthetic (case B) or by adding lime, cement or hydraulic binder (case C). Both cases B and C lead to a reduced thickness of the gravel/sand layer. Figure 1 illustrates the cross section of the road profile of the roads for all three alternatives.
The considered road is class III with the same finished surface level in all cases with lifetime of 30 years. The road is built on frost-sensitive soil class F3. In regions where the frost penetration depth does not reach the frost-sensitive soil, this soil needs not being removed. This is considered the standard case 2B.
The environmental performance is assessed with the following impact category indicators:
• Cumulative Energy Demand (Primary Energy Consumption, split into non-renewable and renewa-ble fractions),
• Climate Change (Global Warming Potential, GWP100),
• Photochemical Ozone Formation,
• Particulate Formation,
• Acidification,
• Eutrophication,
• Land competition, and
• Water use.
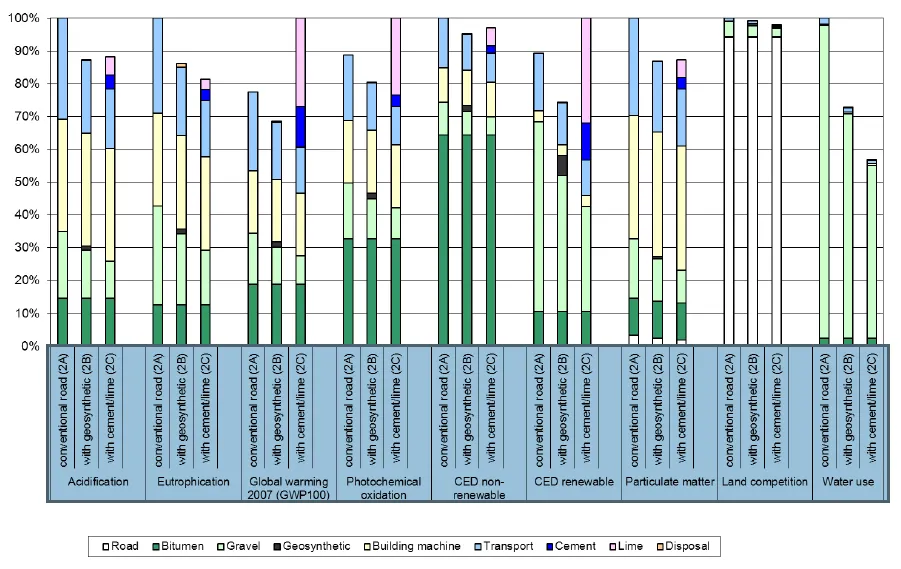
In Figure 2 the environmental impacts over the full life cycle of a road in class III with a length of 1 meter, a width of 12 meters are shown.
Compared to a conventional road (case 2A), the use of geosynthetics leads to lower environmental im-pacts concerning all indicators investigated (case 2B). At least a layer of 25 cm of gravel in a conventional road must be replaced by geosynthetics used in road foundation in order to cause the same or lower envi-ronmental impacts regarding all indicators. The comparison between a road stabilised with geosynthetics (case 2B) and a road stabilised with cement/lime (case 2C) is less clear-cut. However, among the 8 envi-ronmental performance assessed, the use of geosynthetics materials (case 2B) turned out to be the best op-tion among the 3 cases. The fact illustrates the potential contribution of geosynthetic materials towards sustainable highways. For the details of the study, please refer to the document available on EAGM homepage3.
In road construction the sub-base needs to meet defined requirements for compaction and bearing ca-pacity. Improvements of some soil characteristics may be necessary while building on weak soils. Geo-synthetics materials is one approach to support such weak soils.
Today, there are 3 types of different geosynthetics that can be used for stabilization. Those 3 types are, extruded stretched grids, layed grids, and woven / knitted grids. For the LCA study, the average of the three is used to represent its performance. Polypropylene granulates are used as basic material to manufac-ture geogrids or wovens used in the study.
The environmental friendliness of the use of geosynthetic materials were found by carrying out a cradle-to-grave LCA2 study with data from numerous participating EAGM member companies which compared 3 cases. Those cases are conventional road (2A), a road reinforced with geosynthetics (2B) and a ce-ment/lime stabilised road (2C). Besides the construction of a conventional road with a non-frost sensitive gravel/sand layer (case A), soil improvement can be done with geosynthetic (case B) or by adding lime, cement or hydraulic binder (case C). Both cases B and C lead to a reduced thickness of the gravel/sand layer. Figure 1 illustrates the cross section of the road profile of the roads for all three alternatives.
The considered road is class III with the same finished surface level in all cases with lifetime of 30 years. The road is built on frost-sensitive soil class F3. In regions where the frost penetration depth does not reach the frost-sensitive soil, this soil needs not being removed. This is considered the standard case 2B.
The environmental performance is assessed with the following impact category indicators:
• Cumulative Energy Demand (Primary Energy Consumption, split into non-renewable and renewa-ble fractions),
• Climate Change (Global Warming Potential, GWP100),
• Photochemical Ozone Formation,
• Particulate Formation,
• Acidification,
• Eutrophication,
• Land competition, and
• Water use.
In Figure 2 the environmental impacts over the full life cycle of a road in class III with a length of 1 meter, a width of 12 meters are shown.
Compared to a conventional road (case 2A), the use of geosynthetics leads to lower environmental im-pacts concerning all indicators investigated (case 2B). At least a layer of 25 cm of gravel in a conventional road must be replaced by geosynthetics used in road foundation in order to cause the same or lower envi-ronmental impacts regarding all indicators. The comparison between a road stabilised with geosynthetics (case 2B) and a road stabilised with cement/lime (case 2C) is less clear-cut. However, among the 8 envi-ronmental performance assessed, the use of geosynthetics materials (case 2B) turned out to be the best op-tion among the 3 cases. The fact illustrates the potential contribution of geosynthetic materials towards sustainable highways. For the details of the study, please refer to the document available on EAGM homepage3.









