IRF chairman and mayor of Riyadh, Eng Abdullah A Almogbel, discusses the city’s massive infrastructure investment and the pressing need for this development work
Saudi Arabian capital Riyadh is fast growing with a pressing need for additional transport infrastructure resulting in a massive investment programme. The oil industry has fuelled Riyadh’s rapid expansion from being a medium sized town just 100 years ago, to its status as a major city today. With the explosion in vehicle use during the 20th ce
August 29, 2013
Read time: 4 mins
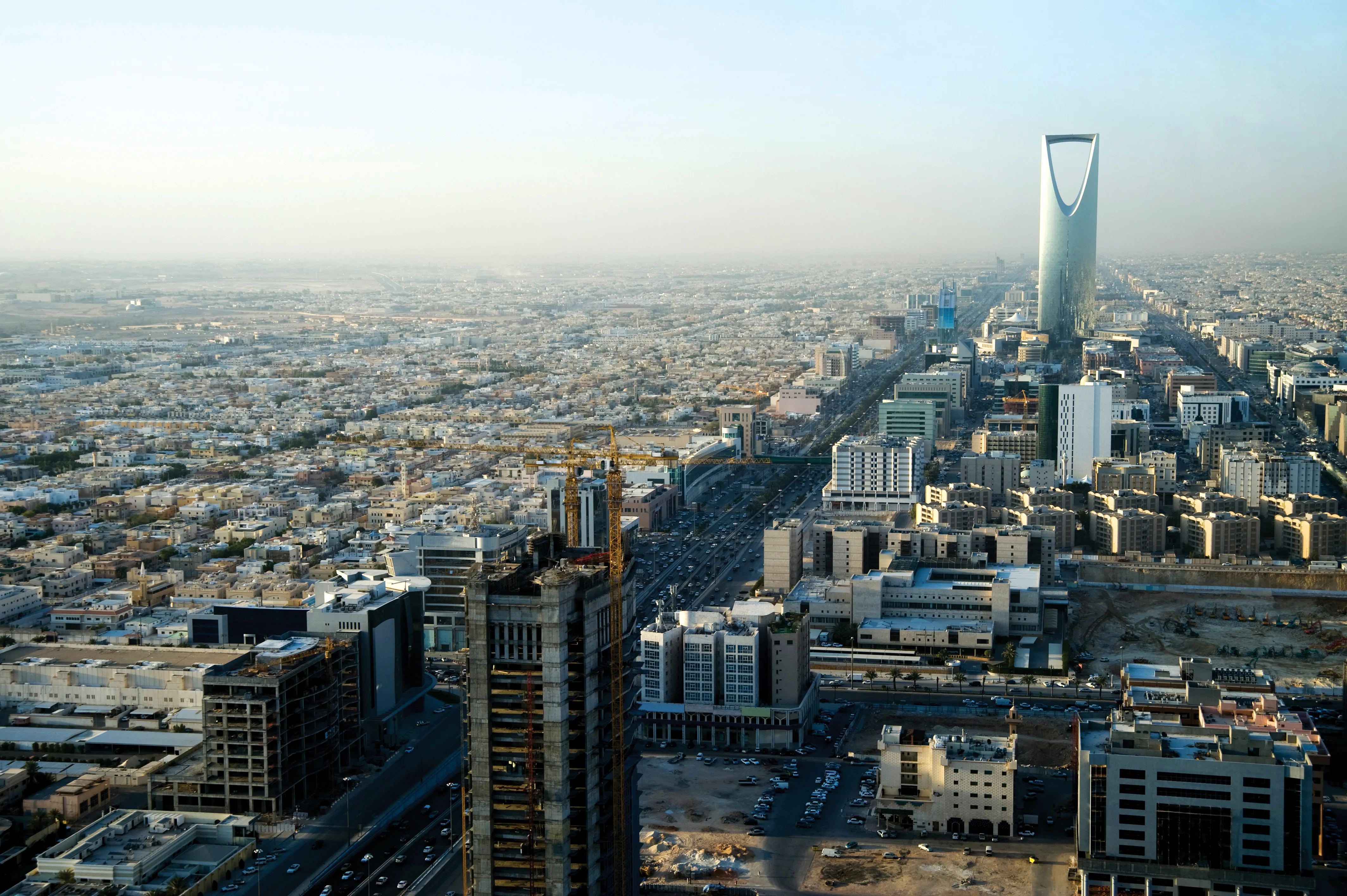

Riyadh’s urban area has spread out from its original centre and the current road network is becoming unable to cope with the traffic volumes, leading to congestion at peak periods. To address the shortcomings of the current road network, a strategy has been established for developing the system and this will be carried out in several stages. At present Riyadh’s 1st ring road runs around the city, while King Fahd Road runs through the centre of the city from north to south, and Makah Road runs east-west across the centre and connects eastern parts of the city with the city's main business district and the diplomatic quarters. However, there is an inconsistency in the corridors crossing the city and the existing freeways are discontinuous without sufficient on and off ramps. The existing layout also suffers traffic safety related issues while there is a shortage of parking spaces and insuf¬ficient facilities for pedestrians or the disabled.
Action points have been drawn up to address these issues such as the construction of tunnels and bridges at various intersections, the completion of traffic corridors across the city and the standardisation of the roadway design. These action points also include reviewing the exit and entry points between service roads and main carriageways along freeways, the proper separation of parking areas and carriageways and the improvement of sidewalks and road furniture. Other priorities are implementing traffic safety requirements and the application of intelligent transport systems (ITS) to improve traffic management.
Due to the huge construction work needed and which will require a huge budget, the implementation of the upgrade has been divided into four stages. The first stage includes completing work on the 2nd and 3rd ring roads, construction of a total of 38 tunnels, building 15 bridges, upgrading 100km of existing roads and constructing 244km of new roads. And all in all, this enormous programme has a projected cost of close to US$2.74 billion.
The second stage includes completing 11 key roads, building 30 tunnels, constructing 50 bridges, upgrading 199km of existing roads and the construction of 71km of new roads and this is expected to cost $2.96 billion. The third stage envisages completing work on 14 key roads, building 40 tunnels, 29 bridges, 58km of new roads and upgrading 158km of existing roads, all of which will cost $2.74 billion. For the fourth stage 41 roads will be completed with 322km of roads being upgraded, 118km of new roads being built and the construction of 46 tunnels and 86 bridges, at a total cost of $4.9 billion.
This massive programme of works is an ambitious project that will revitalise Riyadh and provide the city with the road network it requires, cutting congestion, reducing journey times and improving safety for all road users.