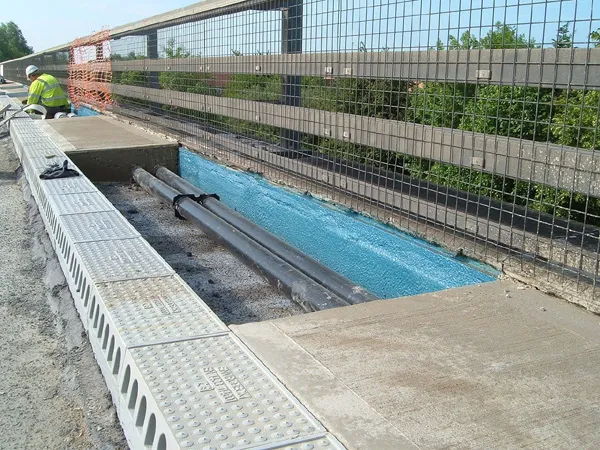
The ongoing Highways Agency A66 Carkin Moor to Scotch Corner project involves upgrading the original single carriageway to address safety concerns, particularly at junctions and crossings. Where differential settlement is threatening a remodelled junction, Tensar International's new TriAx geogrid provides an additional dimension of stability, saving design and build contractors Balfour Beatty Regional Civil Engineering Limited (BBRCEL) the heavy time and costs inherent in conventional remedial solutions and
March 14, 2012
Read time: 3 mins
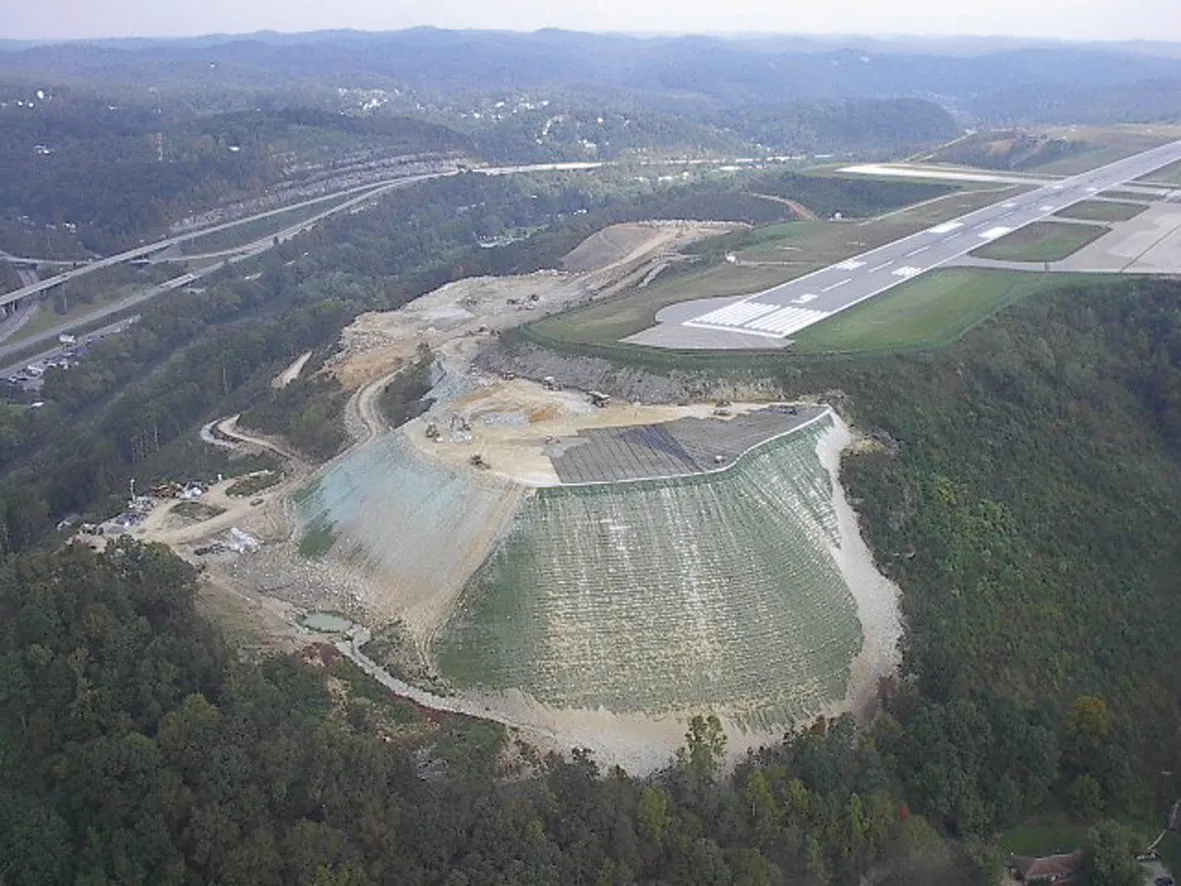

The ongoing Highways Agency A66 Carkin Moor to Scotch Corner project involves upgrading the original single carriageway to address safety concerns, particularly at junctions and crossings.
Where differential settlement is threatening a remodelled junction,The widened junction incorporates radiused corners on 'turn in' and 'turn out', and overlies part of a 7m deep old quarry variably infilled with very poor quality mixed domestic waste. The original proposals by BBRCEL's design partner
With the encouragement of the HA to look at innovative solutions to manage costs more effectively and reduce environmental impact, BBCREL and Atkins consulted Tensar about geogrid solutions.
A specific concern of the project was that one leg of the junction runs over the irregular edge of the quarry, with very variable direction of potential instability while, at the same point, vehicle wheel loadings are also going to be variable in direction.
To meet this problem, Tensar proposed use of its new TriAx geogrid, as a composite structure including granular fill and heavy duty bi-axial geogrid at the base to create a reinforced granular mattress.
Says Sean McCready, site project manager for BBRCEL: "The innovative TriAx solution offers excellent cost benefits of at least 75% savings to the project against very acceptable risk levels. This approach also fulfilled the HA's objective of looking at innovative proven solutions to drive down cost. We talked this through with
Inbitex development
In a recent partnership between Terram and Formpave, the specialist geotextile Inbitex has been developed to enhance the performance of Formpave's Aquaflow permeable paving system.Research conducted by Coventry University in the UK identified the need for an improved geotextile during the installation of the sub-base of the paving system.
Inbitex was the new geotextile developed in conjunction with Terram, creating a product of greater quality and strength: importantly the fibres of the geotextile encourage the growth of a microbic biofilm habitat. These microbes biodegrade any organic matter found in the run-off, with a capacity to consume 400g of hydrocarbon/year. Also, any non-degradable matter such as heavy metals and silts are trapped in the laying course, so optimising the cleansing of water entering the Aquaflow paving system.
A typical infiltration system in the Aquaflow paving system installation uses two permeable Inbitex geotextiles, one beneath the base of the paving and the other beneath the sub-base or lower sub-base