Shem Oirere discusses a new road connecting with a wind farm development in Kenya The African Development Bank will provide 45% of the funding needed for the rehabilitation and rebuilding of a new 200km road which leads to Africa's largest wind farm project, located in northern Kenya. The bank said the $13.5 million grant for rehabilitation of the existing Laisamis – Ngurunit – llaut - South Horr – Loyangalani road- will be provided by the Government of the Netherlands. The bank says works on the road will
February 20, 2014
Read time: 4 mins
Shem Oirere discusses a new road connecting with a wind farm development in Kenya
The African Development Bank will provide 45% of the funding needed for the rehabilitation and rebuilding of a new 200km road which leads to Africa's largest wind farm project, located in northern Kenya. The bank said the $13.5 million grant for rehabilitation of the existing Laisamis – Ngurunit – llaut - South Horr – Loyangalani road- will be provided by the Government of the Netherlands. The bank says works on the road will cost a Total of $30.4 million and entails, “…light and heavy excavation, gravelling, reconstruction of some sections, light grading and improvement of drainage structures.”
The remaining $16.9 million will be provided by Lake Turkana Wind Power (LTWP), the consortium developing the 300MW wind farm at Loiyangalani in Marsabit County. The consortium comprise of KP&P BV Africa, Aldwych International Limited, Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Norwegian Investment Fund for Developing Countries (Norfund), Industrial Fund for Developing Countries (IFU) Denmark.
LTWP will construct the road jointly with two road agencies- Kenya Rural Roads Authority (KeRRA) and the2639 Kenya National Highways Authority (KeNHA)- starting in the first quarter of 2014. A contract has been awarded to Civicon Kenya, a subsidiary of TransCentury, a Kenyan investor in infrastructure projects. KeRRA operates the 131km Laisamis-South Horr (D371) section while KeNHA operates the 64km South Horr-Loiyangalani stretch.
“The upgrading of the road is primarily to support this unique project and to allow for the wind turbines to reach site,” said Lilianne Ploumen, Minister for Foreign Trade and Development Corporation of the Netherlands. “However, the road will open the entire area for further development and improve accessibility to all the local communities,” she added.
LTWP says the construction works would entail realignment, levelling and grading, construction of culverts and general repairs of the section between Laisamis – Illaut – Kargi Junction (D371) and Kargi Junction – Loyangalani Road (C77). The road will be 6m wide with a 5m road reserve to each side.
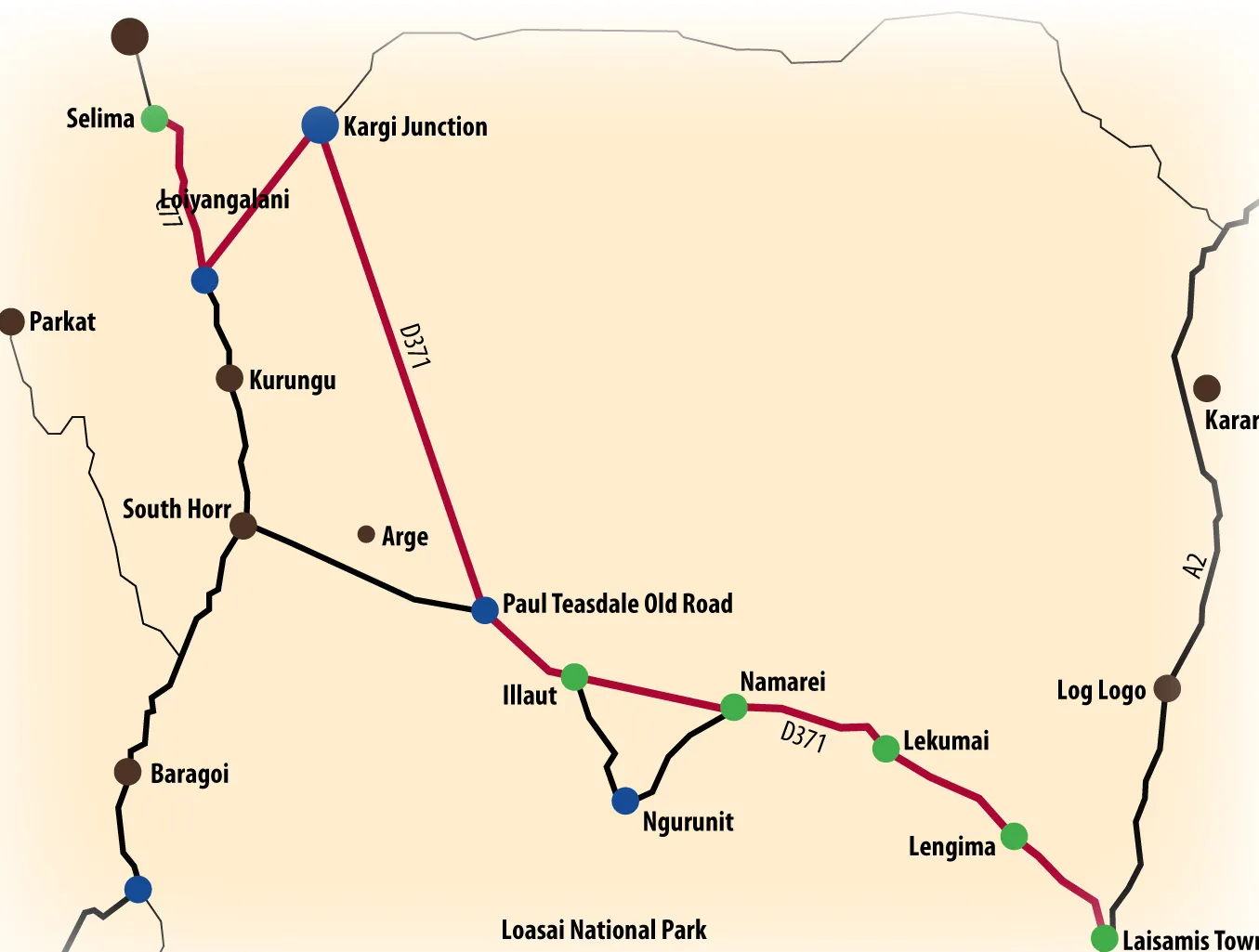
The road branches off from the main A2 Isiolo-Moyale road at Laisamis as D371 in a northerly direction and passes through various centres which include Namarei and Illaut.
From Kargi Junction the road becomes C77 after joining the main road from South Horr and continues all the way to Loyangalani town, the site of the $820 million wind farm project. LTWP says the entire stretch “is a murram road that is marked by low lying terrain lying between numerous hills and dry sand riverbeds.”
“The main output of the work is a drivable standard engineered gravel road with a gravel running surface, road Cross drain comprising of culverts and perforated drifts.”
LTWP abandoned an earlier option of pursuing a 281km route of Marsabit – Kargi – Loyangalani which branches off from the main Isiolo – Marsabit road.
Although the road has what a project environmental impact assessment report said, “…is reasonable horizontal geometrics with long straight sections and curves with large radii,” the route was found unsuitable because it, “…has unfavourable vertical curves, is poorly drained although in most sections the alignment is free draining.”
LTWP says the route was also abandoned because, “There was no guarantee for the availability of adequate construction materials since the alignment soils are mostly loamy sands.”
“Strengthening of the route will be more expensive than the proposed Laisamis – South Horr – Loyangalani road. The Kargi route would also lengthen the haulage distance of the wind farm equipment by an additional 50km, the distance to the takeoff point from Isiolo on the Isiolo - Marsabit road.”
The consortium said the option also did not show evidence of availability of adequate water needed during construction work
LWTP instead opted for an alternative route of Laisamis – Ngurunit – llaut - South Horr – Loyangalani. The route was supported by Kenya’s environmental regulator, National Environmental Management Authority.
The road branches off from the main Isiolo - Marsabit road at Laisamis town and runs 196km in a northerly direction.
Because the route passes through the settlements of Ngurunit, South Horr and Kurungu, it was agreed between LTWP and the communities that it be modified to avoid the settlements and ease transportation of the heavy wind farm development equipment.
The road will, therefore, have two diversions. The first diversion is the 19.6km Namarei to Illaut section, which avoids the Ngurunit settlement area, and has flat and rolling terrain, making it a viable route to use.
The diversion avoids the 34km stretch through Ngurunit market (saving 14.4km), and transportation over a hilly undulating terrain “which have acute bends and rocky terrain.”
This route is an old disused road which will require drainage to be improved and be rehabilitated.
The African Development Bank will provide 45% of the funding needed for the rehabilitation and rebuilding of a new 200km road which leads to Africa's largest wind farm project, located in northern Kenya. The bank said the $13.5 million grant for rehabilitation of the existing Laisamis – Ngurunit – llaut - South Horr – Loyangalani road- will be provided by the Government of the Netherlands. The bank says works on the road will cost a Total of $30.4 million and entails, “…light and heavy excavation, gravelling, reconstruction of some sections, light grading and improvement of drainage structures.”
The remaining $16.9 million will be provided by Lake Turkana Wind Power (LTWP), the consortium developing the 300MW wind farm at Loiyangalani in Marsabit County. The consortium comprise of KP&P BV Africa, Aldwych International Limited, Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Norwegian Investment Fund for Developing Countries (Norfund), Industrial Fund for Developing Countries (IFU) Denmark.
LTWP will construct the road jointly with two road agencies- Kenya Rural Roads Authority (KeRRA) and the
“The upgrading of the road is primarily to support this unique project and to allow for the wind turbines to reach site,” said Lilianne Ploumen, Minister for Foreign Trade and Development Corporation of the Netherlands. “However, the road will open the entire area for further development and improve accessibility to all the local communities,” she added.
LTWP says the construction works would entail realignment, levelling and grading, construction of culverts and general repairs of the section between Laisamis – Illaut – Kargi Junction (D371) and Kargi Junction – Loyangalani Road (C77). The road will be 6m wide with a 5m road reserve to each side.
The road branches off from the main A2 Isiolo-Moyale road at Laisamis as D371 in a northerly direction and passes through various centres which include Namarei and Illaut.
From Kargi Junction the road becomes C77 after joining the main road from South Horr and continues all the way to Loyangalani town, the site of the $820 million wind farm project. LTWP says the entire stretch “is a murram road that is marked by low lying terrain lying between numerous hills and dry sand riverbeds.”
“The main output of the work is a drivable standard engineered gravel road with a gravel running surface, road Cross drain comprising of culverts and perforated drifts.”
LTWP abandoned an earlier option of pursuing a 281km route of Marsabit – Kargi – Loyangalani which branches off from the main Isiolo – Marsabit road.
Although the road has what a project environmental impact assessment report said, “…is reasonable horizontal geometrics with long straight sections and curves with large radii,” the route was found unsuitable because it, “…has unfavourable vertical curves, is poorly drained although in most sections the alignment is free draining.”
LTWP says the route was also abandoned because, “There was no guarantee for the availability of adequate construction materials since the alignment soils are mostly loamy sands.”
“Strengthening of the route will be more expensive than the proposed Laisamis – South Horr – Loyangalani road. The Kargi route would also lengthen the haulage distance of the wind farm equipment by an additional 50km, the distance to the takeoff point from Isiolo on the Isiolo - Marsabit road.”
The consortium said the option also did not show evidence of availability of adequate water needed during construction work
LWTP instead opted for an alternative route of Laisamis – Ngurunit – llaut - South Horr – Loyangalani. The route was supported by Kenya’s environmental regulator, National Environmental Management Authority.
The road branches off from the main Isiolo - Marsabit road at Laisamis town and runs 196km in a northerly direction.
Because the route passes through the settlements of Ngurunit, South Horr and Kurungu, it was agreed between LTWP and the communities that it be modified to avoid the settlements and ease transportation of the heavy wind farm development equipment.
The road will, therefore, have two diversions. The first diversion is the 19.6km Namarei to Illaut section, which avoids the Ngurunit settlement area, and has flat and rolling terrain, making it a viable route to use.
The diversion avoids the 34km stretch through Ngurunit market (saving 14.4km), and transportation over a hilly undulating terrain “which have acute bends and rocky terrain.”
This route is an old disused road which will require drainage to be improved and be rehabilitated.







