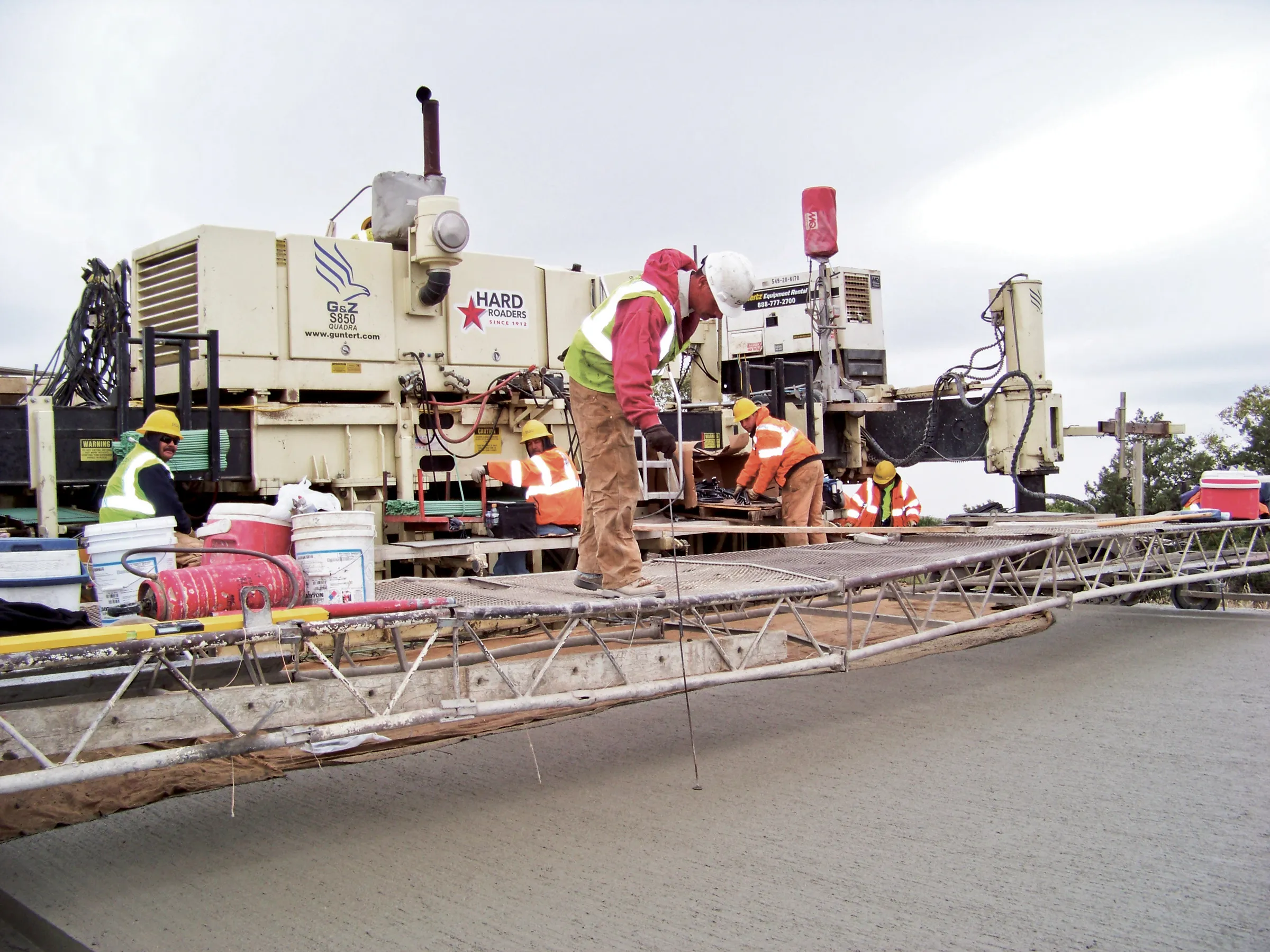
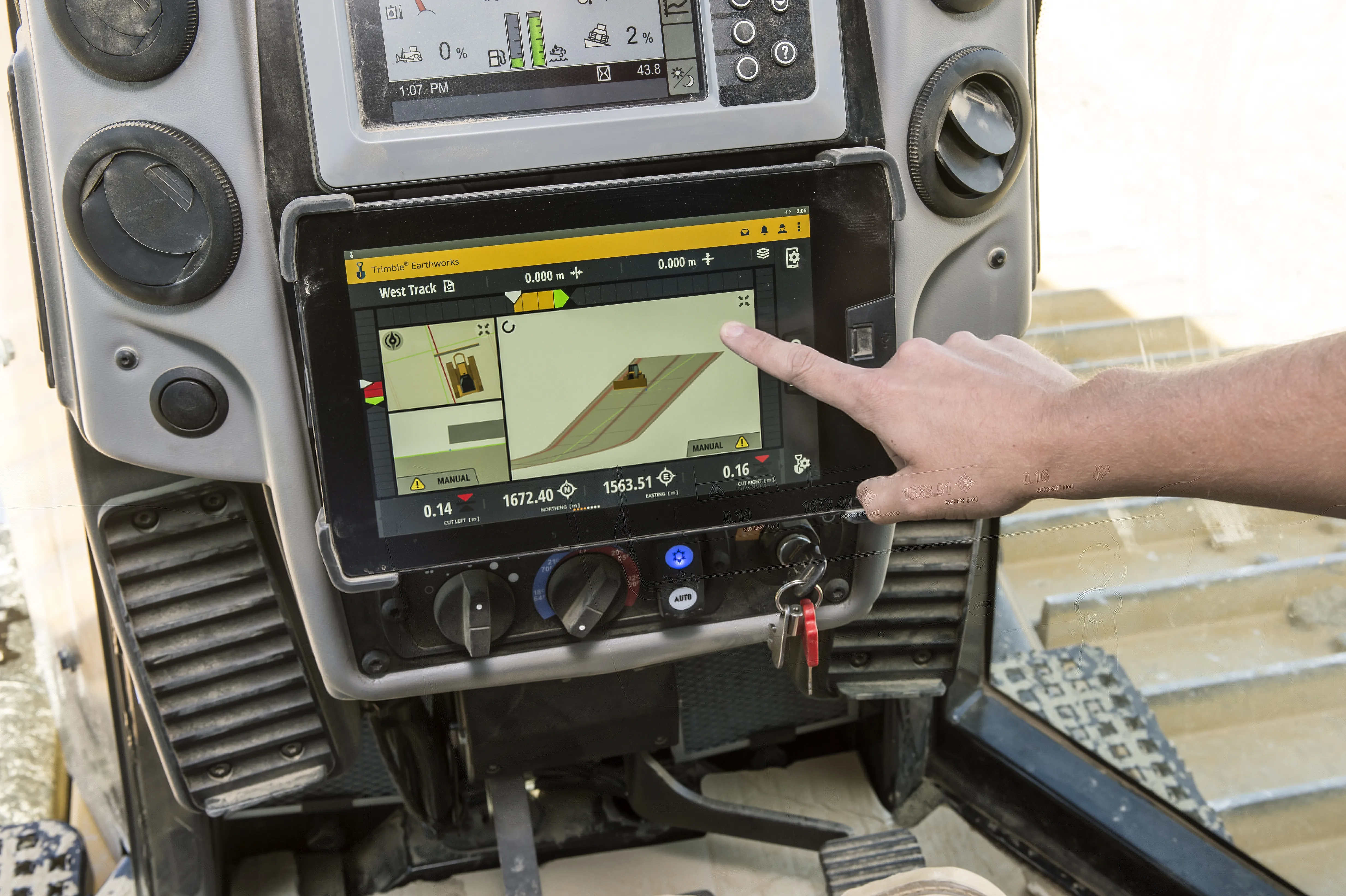
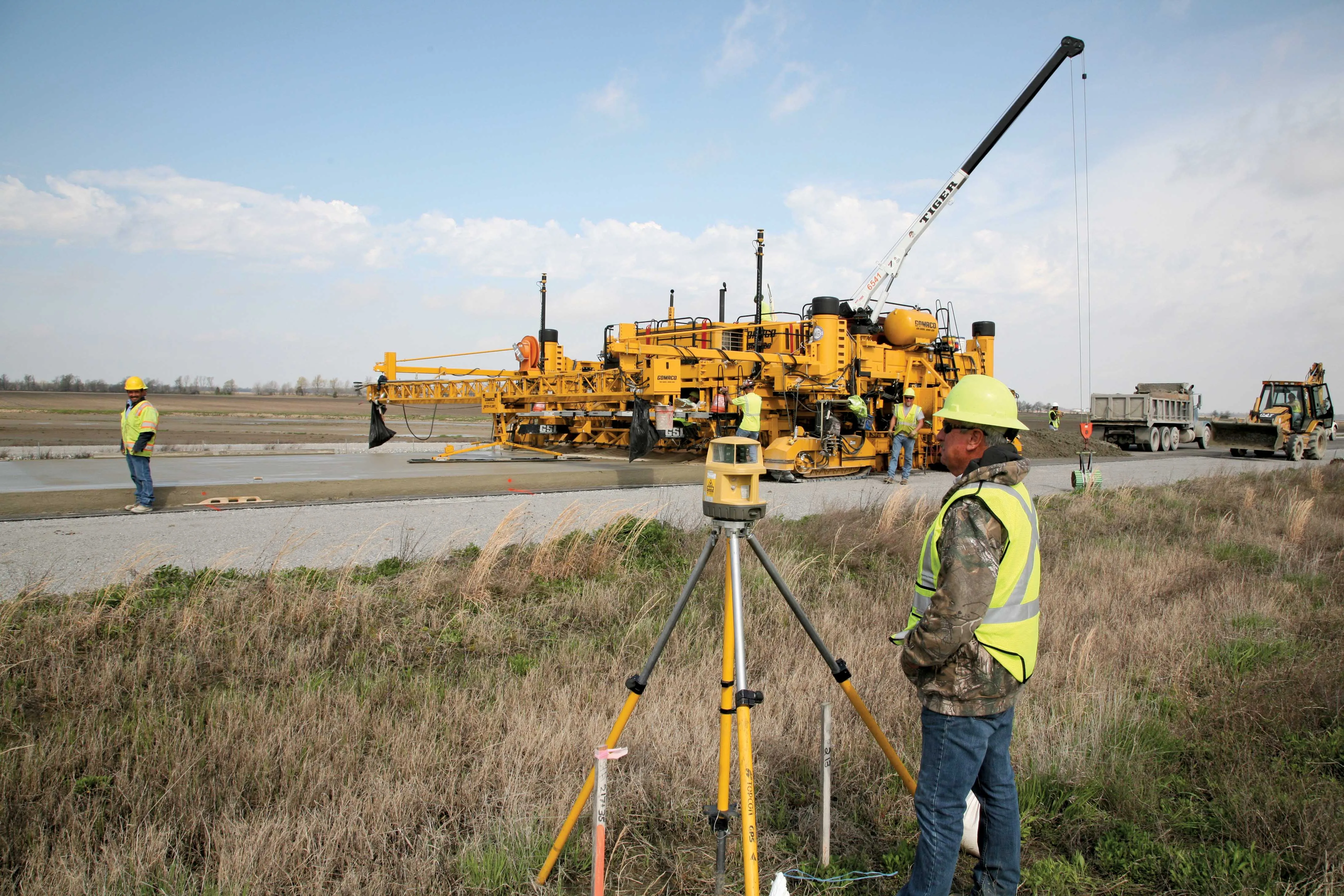
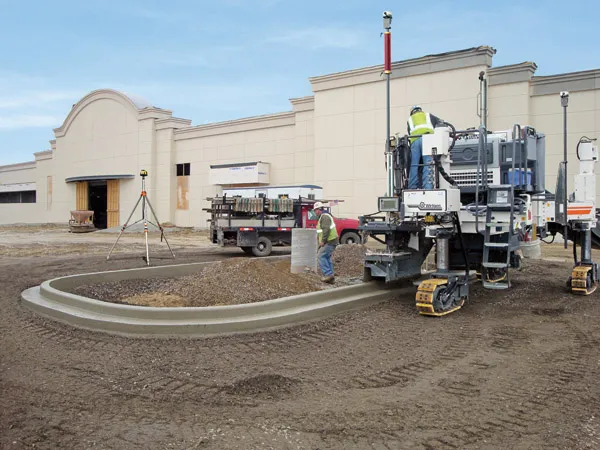
Wirtgen has developed a novel control system for use on its concrete paving equipment. Matthias Fritz is the product engineer at Wirtgen tasked with developing the system. The new AutoControlpackage uses GPS technology to provide guidance for the machine's steering functions. Fritz added, "It has an augmentation centre for vertical control because it requires millimetre accuracy for height." This 3D control system is for use with the firm's SP15 and SP25 slipform pavers and is said to be a user-friendly, co
February 14, 2012
Read time: 4 mins

Wirtgen has developed a novel control system for use on its concrete paving equipment.
Matthias Fritz is the product engineer atFritz said, "Handling data on the job-site is a big deal. That was the basic trigger and we thought that there is a way to change this." There is no need to use a digital terrain model as programming of the profile path or profile configuration is completed on site. Fritz said, "...the data is generated in the field and the operator tells the machine what to do." The AutoPilot system can be used for diverse profile shapes, such as kerbs, kerb and gutter profiles, safety barriers or narrow paths and can produce radii of 600mm without the use of stringlines. This dispenses with timeconsuming surveying and with the installation and removal of stringlines, saving money and time. The Wirtgen AutoPilot automatically negotiates obstacles on-site, such as manhole covers. The system comprises a computer integrated in the machine as well as a control panel, while two GPS receivers mounted on masts communicate with a GPS reference station positioned on site.
Certain slipforming applications can be straightforward to carry out and yet can be comparatively complex to programme into available control systems. Fritz said, "One of the main functions is doing island shapes for parking lots. The beauty of the system is you can define the shape on the computer and then recall it and do a repeat at a different site." He also said that it is a relatively simple task to use the original plan either as stored or to adapt it with different measurements, for example increasing the dimensions of an island form for a parking lot. The memory can store an indefinite number of designs as it has substantial memory capacity according to Fritz. He added, "For kerb and gutter work this combination function is very useful." The system can also be used to define a profile to suit the jobsite and Fritz added, "You can do a cross-slope with the system." He added that the key to this package is that the information used for machine guidance is loaded on-site from the machine location and he said, "This avoids data being generated in the office that doesn't match the site." The firm says that the system has been designed to be easy to use, even by inexperienced operators. After positioning the total station and laser on the construction site, the slipform paver is taken to the specified starting position and heading. Parameters are entered into the system, while graphics display the various profiles and profile configurations.
Programming is simple and the machine operator selects a profile configuration and enters length, width and radius of the configuration to set the steering path. The starting point is determined next, followed by machine level and elevation profile and the machine operator then sets the cross slope. A laser sensor or ultrasonic sensor mounted on the slipform paver scans the ground surface to ensure precise level control and automatic paving starts.