SBG has set numerous engineering precedents with its hugely innovative Jamarat Bridge project in Saudi Arabia
February 17, 2012
Read time: 4 mins
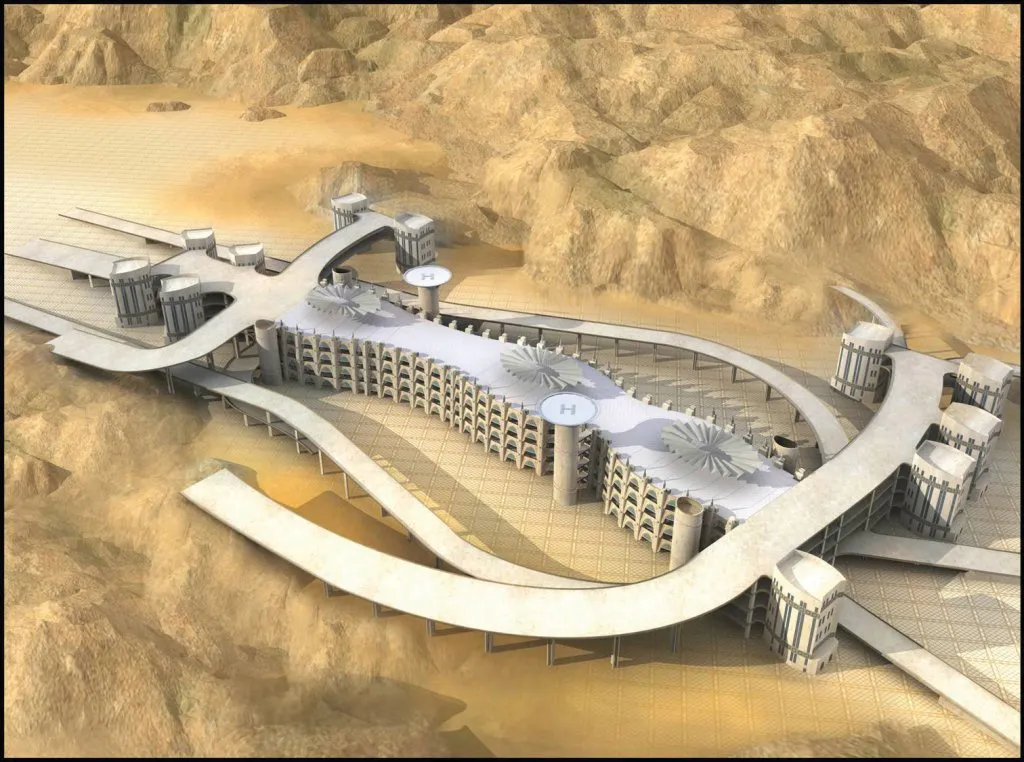
SBG has set numerous engineering precedents with its hugely innovative Jamarat Bridge project in Saudi Arabia
TheThe new structure has been designed, planned and built by SBG using cutting-edge technologies, many of which relate to highway construction. The project is run under a design-build process and managed by a dedicated executive committee. The client for the Project is the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and its representative the Ministry of Municipalities and Rural Affairs is supervising the work.
The religious pilgrimage to a number of sites in Saudi Arabia, of which this is one, forms an important part of the Islamic Faith. In the last month of every lunar (Hijrah) year millions of people travel to these sites as part of their religious beliefs. For over 1,400 years the stoning of the three Jamarat in Muna Valley near Makkah, has been one of the main rituals of Hajj (pilgrimage). The stoning of Jamarat by pilgrims is repeated daily, in part or in whole, over a short period of a few days. At the beginning, the Jamarat site was marked by three simple monuments on the ground, allowing the small number of pilgrims to perform the stoning. However, the number of pilgrims started to increase and mixed with vehicular traffic, resulted in congestion as well as safety issues. A single level bridge was erected in 1975 and this structure allowed access for two million pilgrims. This also was proving unequal to coping with the growing number of pilgrims and because of the religious importance of the site, the Saudi Arabian authorities instigated an intensive research programme into a better solution. All feasible designs were considered and the authorities then brought in SBG to deliver a new structure capable of handling both current and anticipated numbers.
A key step in the project has been the site-specific research based on data collected over more than four decades. This research included reviews of past studies on pedestrian flow and crowd dynamics as well as actual data collection and analysis.
The designers used flow modelling techniques to simulate the way people move through the site. Using sophisticated algorithms has allowed the design team to predict how people walk through the structure, a similar technology as used in determining how vehicle 'wave' effects occur on busy, multi-lane highways. Advanced design software has been used which has allowed SBG to examine a range of options and factors and select the optimum layout. Because of the depth of research used the project stood out, a major factor in it winning an IRF award for this category.
Work commenced in 2006, with a large fleet of hydraulic excavators fitted with hydraulic breakers and other tools being used to demolish the previous structure. Once this was broken up and hauled away, site clearance could be carried out and the area prepared for the new structure. All the construction work has to be scheduled in set phases, with personnel and equipment cleared away from the site prior to the pilgrimage. Construction work has had to be carried out within a strict time schedule and using an enormous workforce of up to 11,000, requiring SBG to manage the project very precisely indeed.
The Jamarat Bridge is massive, measuring 550m long, having a maximum width of 100m and with six levels in all, while the total area of the structure is 217,417 m². The design is complex and in effect each level comprises a series of interlinked bridges that offer a maximum clear span of 97m. Each floor is 12m high while to provide ingress and exit there are 19 ramps in all, which measure a total of nearly 7.7km and vary in width from 24-42m. In additions the structure features the Souk Al-Arab Tunnel, which is 1.85km long by 34m wide and the King Faisal Tunnel, which is 2.25km long by 16m wide. Also providing ingress and exit are 11 escalator buildings with a total of 308 escalators, as well as six service buildings and two helipads.
The sheer scale of the work required has been enormous, especially given the time-frame. Some 9,040,000m³ of rock has been cut while 180,000m² of shotcreting and rock anchoring has been carried out. There has also been 5,000m³ of rock injection and 825,000m³ of backfilling.
The structure is built from precast concrete sections made at a special yard set-up specifically for the project around 30 km from the construction site. In all there is 1,170,000m³ of cast-in-place concrete and 1,550,000m³ of precast concrete, not to mention 477,400tonnes of reinforcement steel and 20,000tonnes of post-tensioning. The 5,028 precast, post-tensioned concrete segments have been precision manufactured at the purpose-built yard along with the 4,214 precast, pre-stressed concrete beams, with some of the latter units measuring up to 38m long. In addition there are 590,000m² of concrete paving tiles while the structure has required 160,000m³ of asphalt and because of the desert location, the structure also features an extensive water supply network.