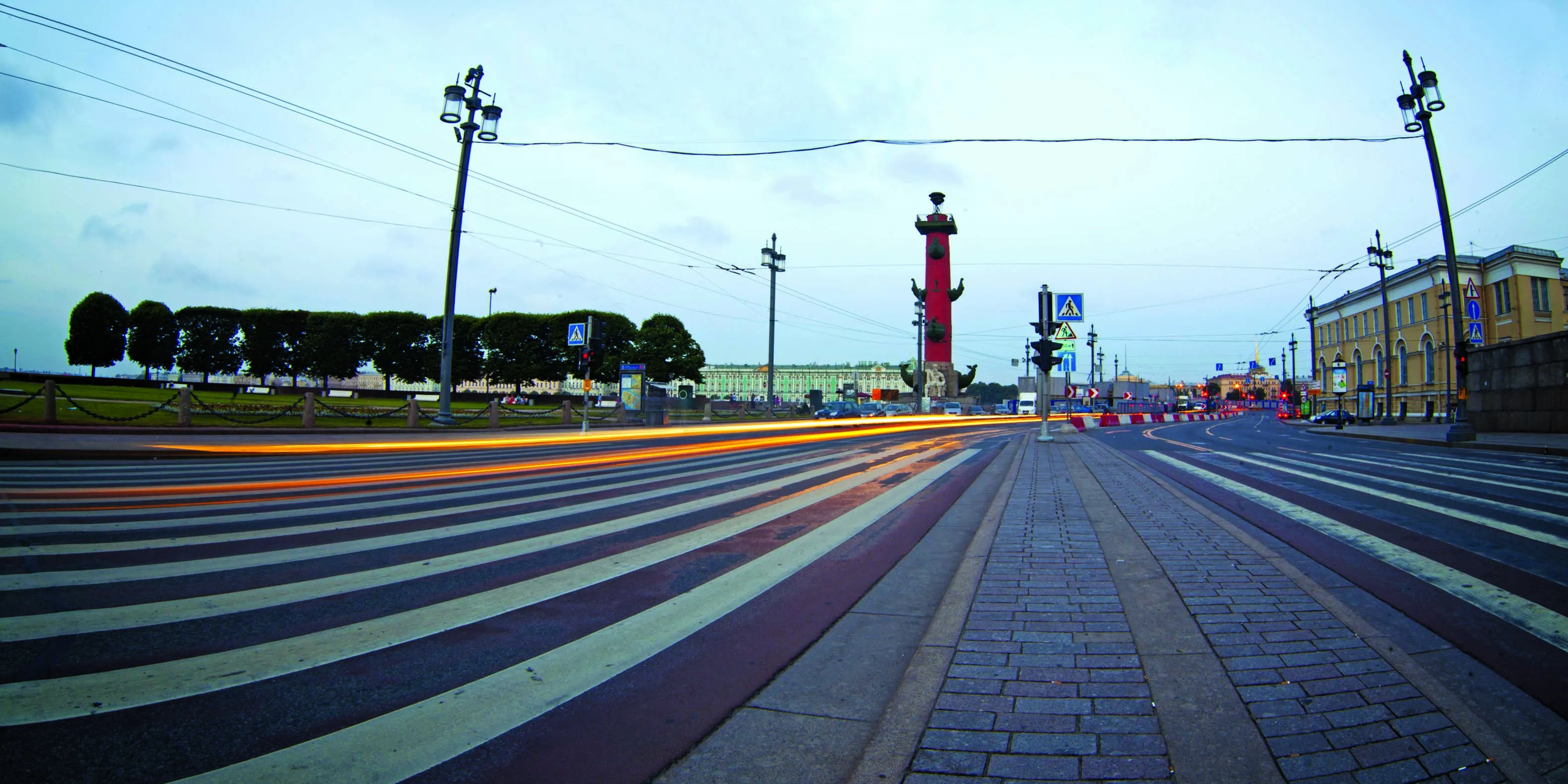
The UK’s capital London suffers from some of the worst traffic congestion in Europe, with only Moscow registering far worse conditions on a regular basis. Traffic speeds along key routes in the centre of the city have long had a reputation for being low but recent research shows that they have fallen yet again. According to Transport for London (TfL), average traffic speeds in the centre of the city are just 12.5km/h, roughly the same as they were in the 19th century when the majority of road traffic was ho
March 8, 2017
Read time: 3 mins

The UK’s capital London suffers from some of the worst traffic congestion in Europe, with only Moscow registering far worse conditions on a regular basis. Traffic speeds along key routes in the centre of the city have long had a reputation for being low but recent research shows that they have fallen yet again. According to Transport for London (TfL), average traffic speeds in the centre of the city are just 12.5km/h, roughly the same as they were in the 19th century when the majority of road traffic was horsedrawn. London’s traffic ills are similar to those of many large cities in both developed and developing nations. And common solutions will have to be found.
Why anyone would actively choose to drive a private vehicle into the centre of London at peak travel periods is not clear. Yet some still persist with driving in the city, almost inevitably resulting in them sitting inside their cars, fuming as pedestrians saunter past on the pavement.
But much of the increase in road traffic can be explained by the increase in the number of private hire vehicles using the city’s streets, as well as the huge growth in the market for online door-to-door deliveries. A range of construction projects and road upgrades are also slowing traffic, with the £4.2 billion sewer project being one of the largest. There were 8,146 roadworks on key routes across Greater London during the July to September 2016 period. This is around 900 more than for the same period in 2015. Across Greater London, traffic speeds fell to 27.8km/h.
With more and more commuters becoming frustrated by the traffic delays, numbers of bus passengers also declined by 5% in the same period, according to TfL data.
There have been some surprising suggestions as to how to deal with the problem. One proposal by former mayor Boris Johnson was to build a new circular road tunnel underneath the city that would help redirect traffic away from congested surface routes. However this suggestion rather ignored the practical problems of constructing a road tunnel in poor soil conditions under many existing buildings without damaging their foundations, while also avoiding underground rail routes and many buried utilities. Nor were the problems of providing suitably located air vents to remove vehicle exhaust from the tunnel without polluting the area above ground adequately considered. To anyone with even a passing understanding of civil engineering, this concept would have been immediately recognised as being hugely expensive.
Even more outlandish and markedly less practical (not to say stratospherically costly) still has been a more recent suggestion by a team of architects to construct underground conveyor belts under the city to carry motor traffic. A user would simply drive onto the belt at a suitable on-ramp and be whisked to a suitable departure point.
Other more practical suggestions include variable congestion charge rates depending on the time of day and congestion levels.
Why anyone would actively choose to drive a private vehicle into the centre of London at peak travel periods is not clear. Yet some still persist with driving in the city, almost inevitably resulting in them sitting inside their cars, fuming as pedestrians saunter past on the pavement.
But much of the increase in road traffic can be explained by the increase in the number of private hire vehicles using the city’s streets, as well as the huge growth in the market for online door-to-door deliveries. A range of construction projects and road upgrades are also slowing traffic, with the £4.2 billion sewer project being one of the largest. There were 8,146 roadworks on key routes across Greater London during the July to September 2016 period. This is around 900 more than for the same period in 2015. Across Greater London, traffic speeds fell to 27.8km/h.
With more and more commuters becoming frustrated by the traffic delays, numbers of bus passengers also declined by 5% in the same period, according to TfL data.
There have been some surprising suggestions as to how to deal with the problem. One proposal by former mayor Boris Johnson was to build a new circular road tunnel underneath the city that would help redirect traffic away from congested surface routes. However this suggestion rather ignored the practical problems of constructing a road tunnel in poor soil conditions under many existing buildings without damaging their foundations, while also avoiding underground rail routes and many buried utilities. Nor were the problems of providing suitably located air vents to remove vehicle exhaust from the tunnel without polluting the area above ground adequately considered. To anyone with even a passing understanding of civil engineering, this concept would have been immediately recognised as being hugely expensive.
Even more outlandish and markedly less practical (not to say stratospherically costly) still has been a more recent suggestion by a team of architects to construct underground conveyor belts under the city to carry motor traffic. A user would simply drive onto the belt at a suitable on-ramp and be whisked to a suitable departure point.
Other more practical suggestions include variable congestion charge rates depending on the time of day and congestion levels.