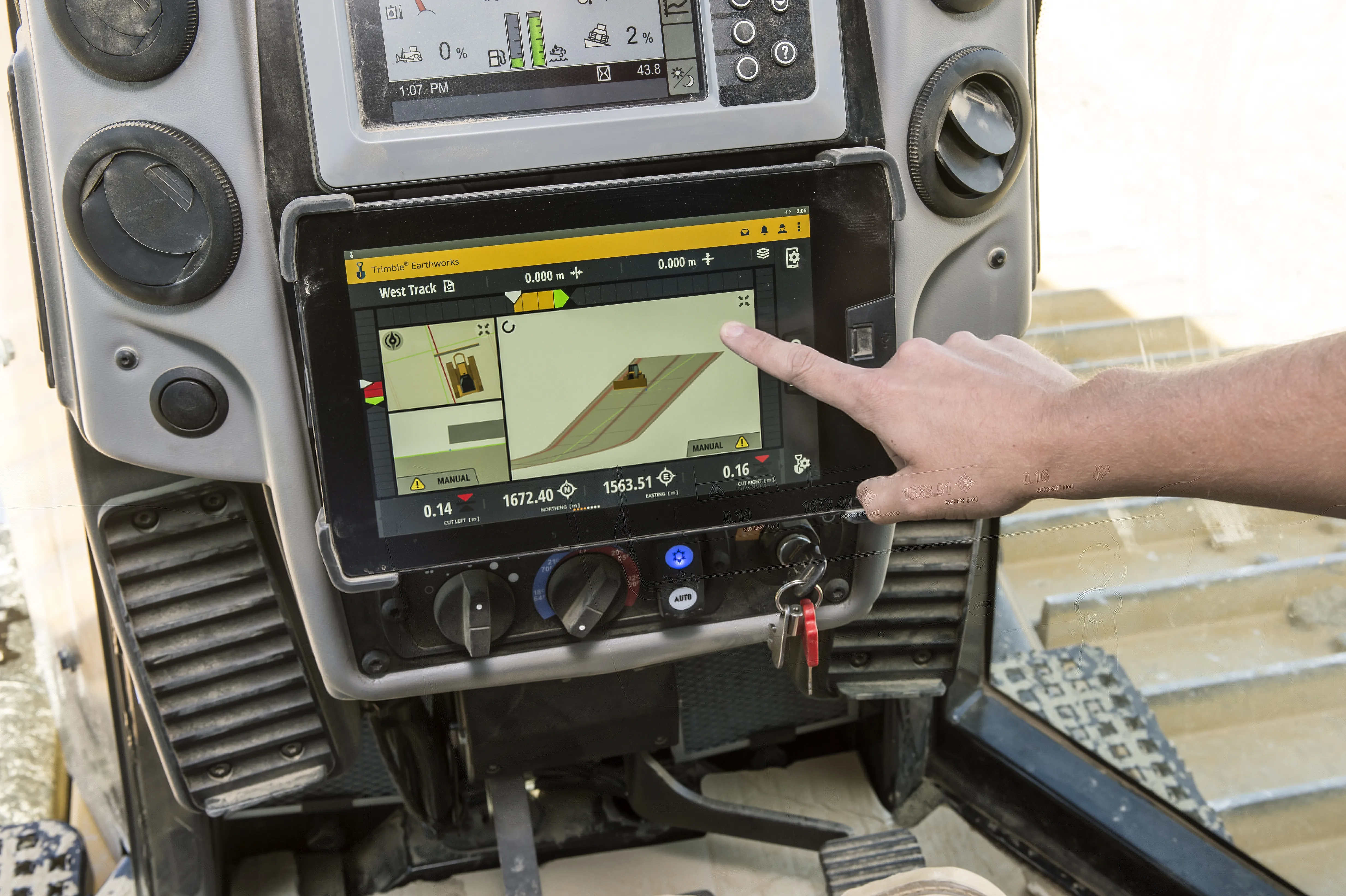
2122 Trimble is now introducing its Earthworks for Dozers package, following on from the Earthworks for Excavators system unveiled last year. The Earthworks Grade Control System for Dozers uses the same inertial motion sensors (IMUs) as the excavator package and mounts its dual GNSS receivers on top of the cab to eliminate masts and cables conventionally located on the blade. The dual GNSS receivers suit steep slope work and complex designs with tight tolerances. The new configuration keeps valuable receivers safer and also saves contractors time by reducing the time needed to remove and reinstall them each day. Putting the receivers on the cab means that safety is improved too, as there is no need to clamber over the blade to retrieve the units. Mounting the units on the top of the cab means that the system has to be calibrated with the distance to the blade tip. However the system is more accurate and provides more data than previous generation packages. Martin Wagener of the firm said, “It measures so fast we can monitor the whole machine. Before, the old system just measured the blade. But this takes 100 measurements/second and not just slope like the old sensor. We really know exactly where the blade is.”
The system is said to be highly rugged and durable and the IMU units are waterproof, with special salt-protection packages also available for use where seawater spray would otherwise cause corrosion isuses.
The Trimble Earthworks grade control application is built on the Android operating system and runs on a Trimble TD520 touch-screen display. The package has graphics and self-discovery features that are said to make the software intuitive and easy to learn. Earthworks also allows data files to be transferred to or from the office wirelessly and automatically so that the operator is always using the latest design. The software runs on an Android operating system and is said to be state-of-the-art, along with the hardware. According to Trimble, the package allows operators of all skill levels the ability to work faster and more productively than before.