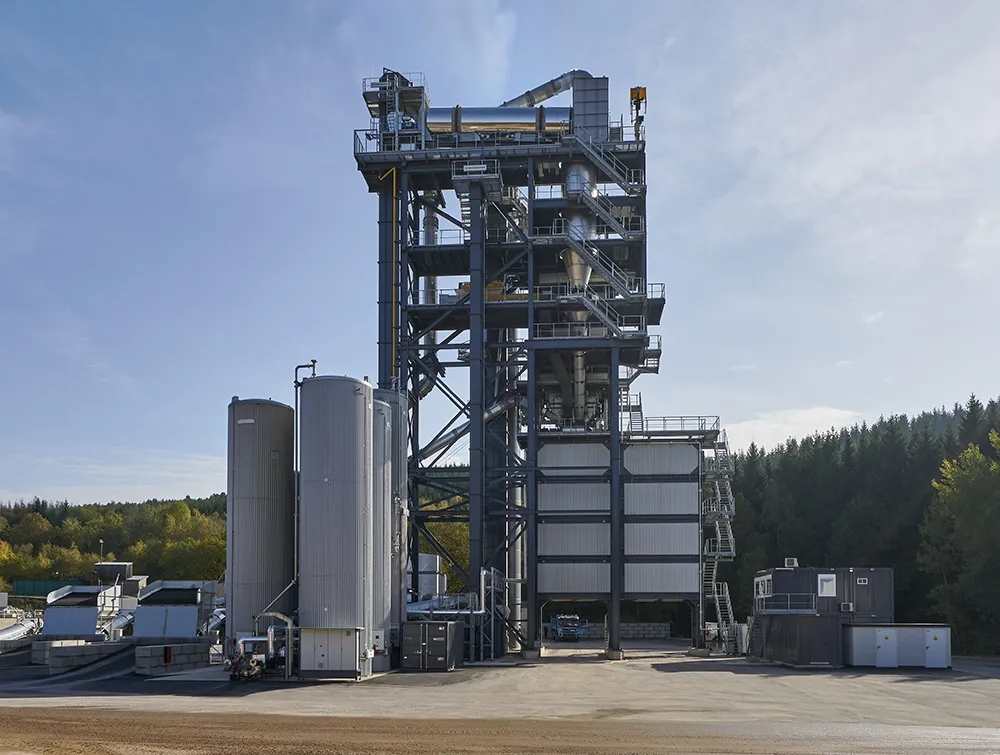
The production of reduced-temperature asphalt, which is also known as low-temperature asphalt, warm asphalt or warm mix, is nothing new. The process was already tested back in the 1990s. But now that road construction authorities are also focusing on issues such as CO2 balance, protecting resources and reducing the energy input, reduced-temperature asphalt has once again come to the fore.
According to Benninghoven, asphalt mixing plants from the firm are in use all over the world and are providing customers with high-quality mix and cost-effective operation as well as low emissions, and meeting stringent health and safety requirements.
Reduced-temperature asphalt is a mixture produced at temperatures between 110°C and 130°C. By comparison, hot asphalt is typically produced between 140°C and 180°C, usually with bitumen at 160°C as a binder. One advantage of the reduced-temperature mixtures is that they can be conveniently produced and processed in the conventional manner.
The bitumen requires a temperature of at least around 140°C to achieve good wetting and coating of the aggregates in the mixer. Below this temperature, it remains too viscous. To lower the temperature during asphalt production, the bitumen viscosity has to be reduced temporarily. This is achieved by adding water (foam bitumen) or additives. When the hot bitumen is mixed with water, the bitumen foams and the volume increases many times over. The increased surface area enables better wetting of the aggregates in the mixer. This means that the mineral is coated effectively even at a lower temperature.
According to the German Asphalt Association, a temperature reduction of just 30°C results in a saving of 0.9litre of heating oil (or a fuel equivalent)/tonne of finished asphalt.
For a plant delivering a daily production of 2,000tonnes of mixture, this corresponds to a saving of 1,800litres of oil or up to three quarters of the annual heating energy consumption of a home. The reduction in CO2 emissions is 6,000kg/day.
Given the current focus on reducing CO2 emissions, this switch to low temperature asphalt could help the construction sector meet its targets on sustainability and help address climate change.