Braunstein + Berndt has released a new SoundPLAN version, SoundPLAN 7.0, and a main feature of this is the new calculation core employing the Dynamic Search scanning method. This, according to the company, makes it possible to calculate anything, no matter how complex the geometry and no matter what size the project.
March 1, 2012
Read time: 2 mins
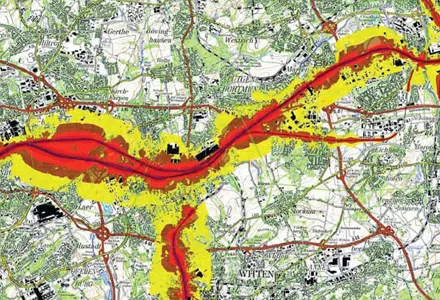
Braunstein + Berndt has released a new 334 SoundPLAN version, SoundPLAN 7.0, and a main feature of this is the new calculation core employing the Dynamic Search scanning method.
This, according to the company, makes it possible to calculate anything, no matter how complex the geometry and no matter what size the project.
"It is a real breakthrough in noise control software. It was used to map Germany's railroads and would be equally useful to map all the roads in any country," says Braunstein + Berndt.
Noise modelling software is required to model noise from source to receiver and to accurately and concisely document the findings.
Dynamic Search estimates the contribution for each receiver and ranks the influence of all sources. Only the sources important to the final result of a receiver are calculated: the rest are estimated. By dynamically selecting the sources that need to be calculated versus estimated, more data can be calculated more quickly than was ever thought possible.
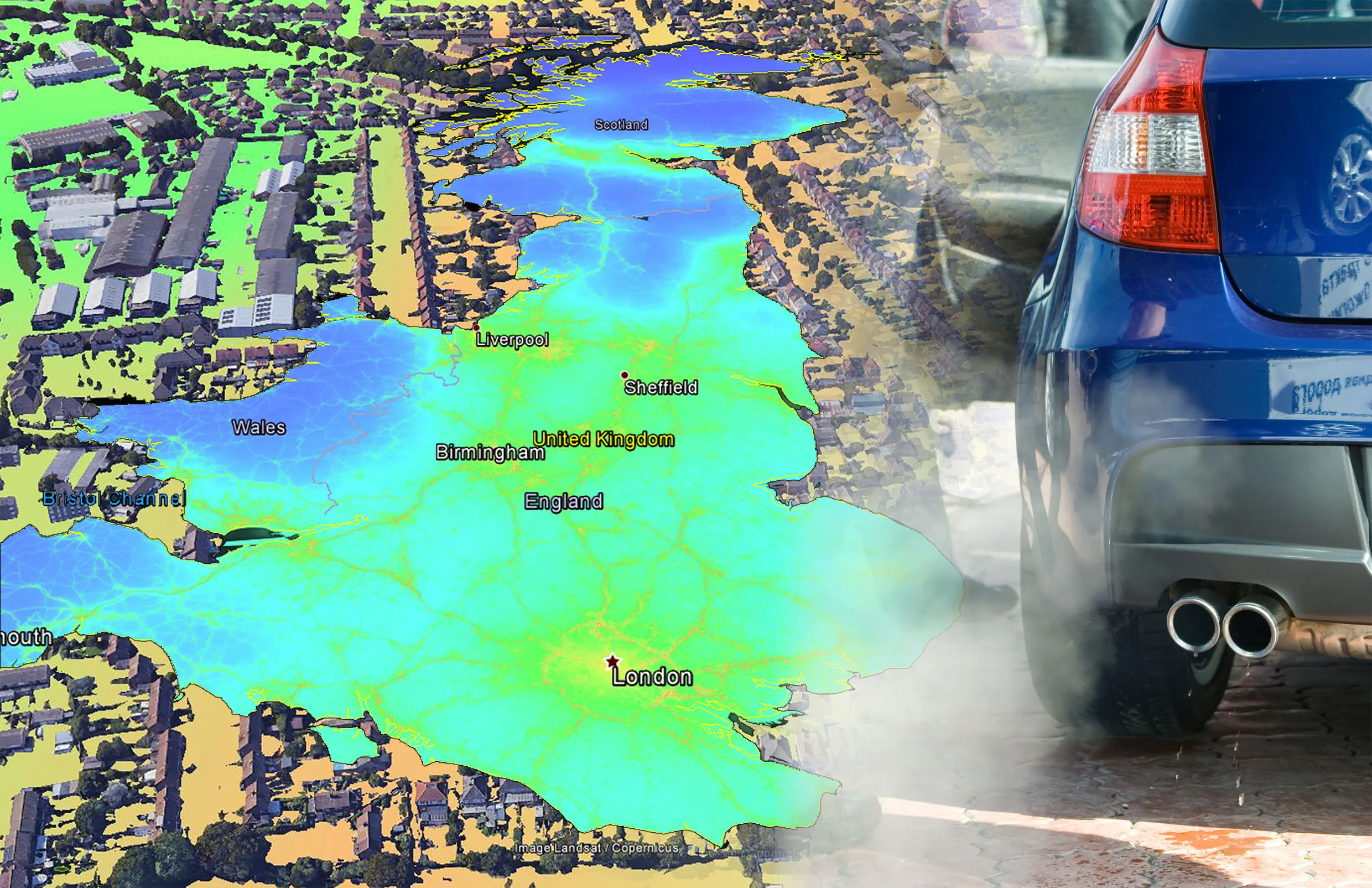
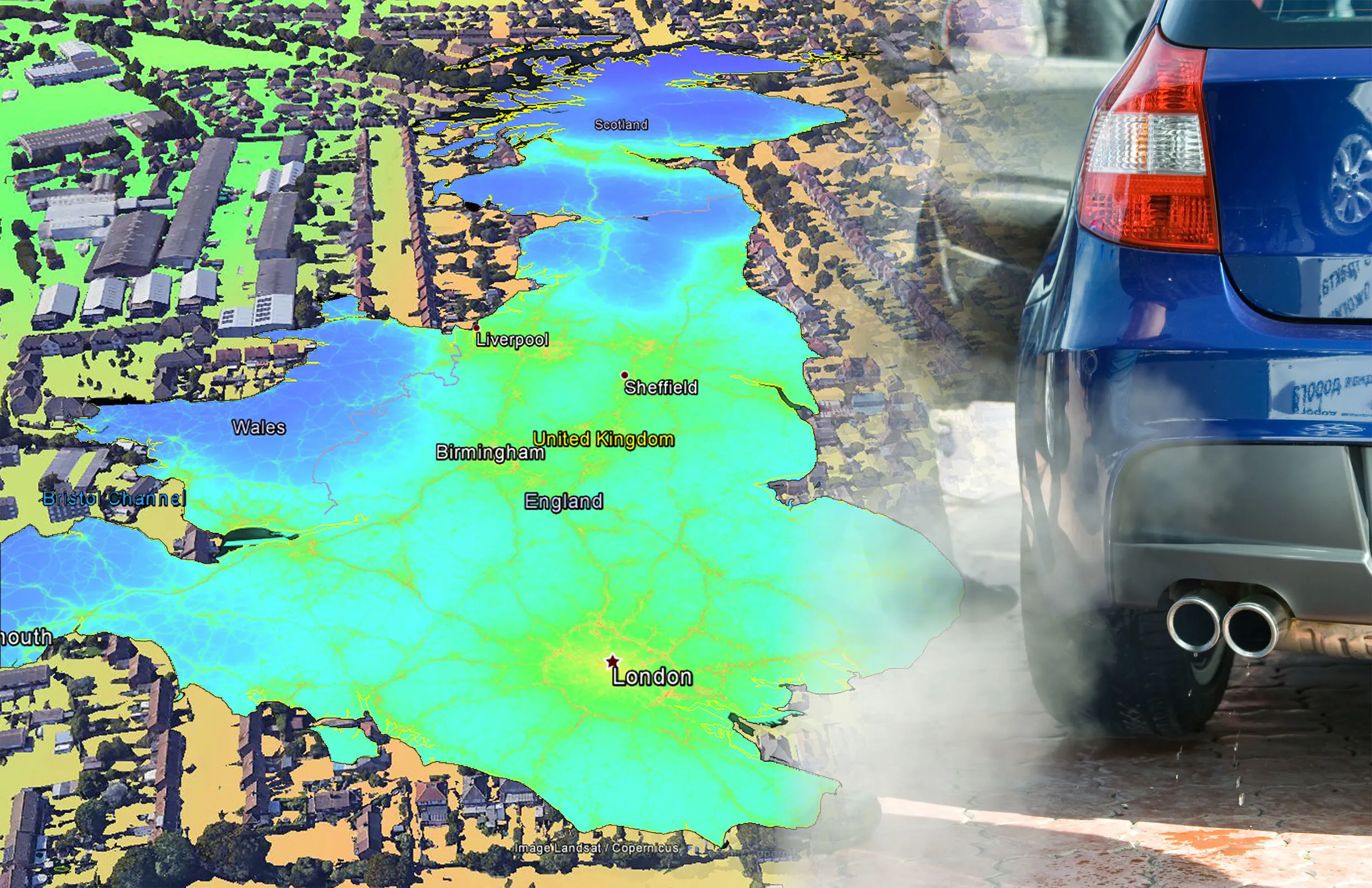
"This new method was used to successfully complete the world's largest noise map, the END noise mapping of the railways throughout Germany in which 12,000km of railway were mapped, and this included 11GB of terrain information, 8 million buildings and 36 million receiver points. All of this was calculated on four personal computers in less than 30 days running time using 32?bit WindowsXP," says Braunstein + Berndt.
The mapping was conducted by PÖYRY and the database and viewer were supplied by Intergraph.
This, according to the company, makes it possible to calculate anything, no matter how complex the geometry and no matter what size the project.
"It is a real breakthrough in noise control software. It was used to map Germany's railroads and would be equally useful to map all the roads in any country," says Braunstein + Berndt.
Noise modelling software is required to model noise from source to receiver and to accurately and concisely document the findings.
Dynamic Search estimates the contribution for each receiver and ranks the influence of all sources. Only the sources important to the final result of a receiver are calculated: the rest are estimated. By dynamically selecting the sources that need to be calculated versus estimated, more data can be calculated more quickly than was ever thought possible.
"This new method was used to successfully complete the world's largest noise map, the END noise mapping of the railways throughout Germany in which 12,000km of railway were mapped, and this included 11GB of terrain information, 8 million buildings and 36 million receiver points. All of this was calculated on four personal computers in less than 30 days running time using 32?bit WindowsXP," says Braunstein + Berndt.
The mapping was conducted by PÖYRY and the database and viewer were supplied by Intergraph.









