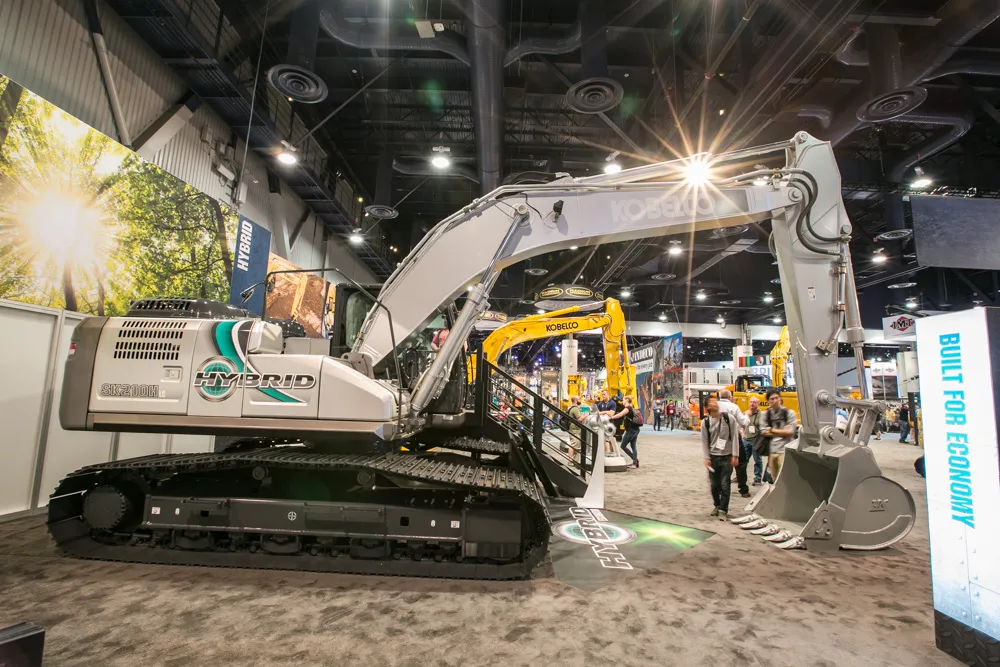
“We have been working on the prototype in Japan and it’s about a year since we went over there and ran it for the first time,” said Butch Hurst, field service representative for Kobelco. “I am an old guy and I am hard to impress but when I got out of the machine in Japan, I said ‘wow’.”
The difference between this machine and previous hybrids is that it offers greater productivity than conventional machines, according to Kobelco. And that’s why the manufacturer felt the time was right to launch it into the North American market.
“This hybrid gives savings on fuel without sacrificing performance. You take this machine and you can dig competitively, even more productively than a conventional machine and still get the fuel savings,” said Hurst.
Kobelco launched its first hybrid, an 8 tonne machine in 2011, and has worked with capacitor technology and nickel hydride batteries before it moved onto lithium-ion technology, which provides a denser energy source. “We have waited until the lithium-ion got to a position where it was reliable and dense enough to do this job,” said Hurst.
Kobelco’s new hybrid has a generator motor and a swing electric motor. During swing acceleration, the swing motor is powered by electricity accumulated in the lithium-ion battery. During swing deceleration, the braking energy generated is converted into electricity which is stored in the lithium-ion battery.
For high-load operation, the electricity accumulated in the lithium-ion battery allows the generator motor to assist the engine, reducing fuel consumption. During low-load operation, the engine power is used to generate electricity in the generator motor and electricity is accumulated in the lithium-ion battery.
Orders for the new machines have been received in Europe with the first due for delivery in April. North America can expect its first machines in the second half of this year.