At the core of the amo/Debus Gruppe’s success is its longstanding expertise in asphalt production—a journey that began in 1964 with the launch of its first asphalt plant. Over the decades, the company has continued to invest in innovation and efficiency and nowhere is this commitment more evident than at its state-of-the-art facility in Hof.
Cutting-Edge Technology at the Hof Plant
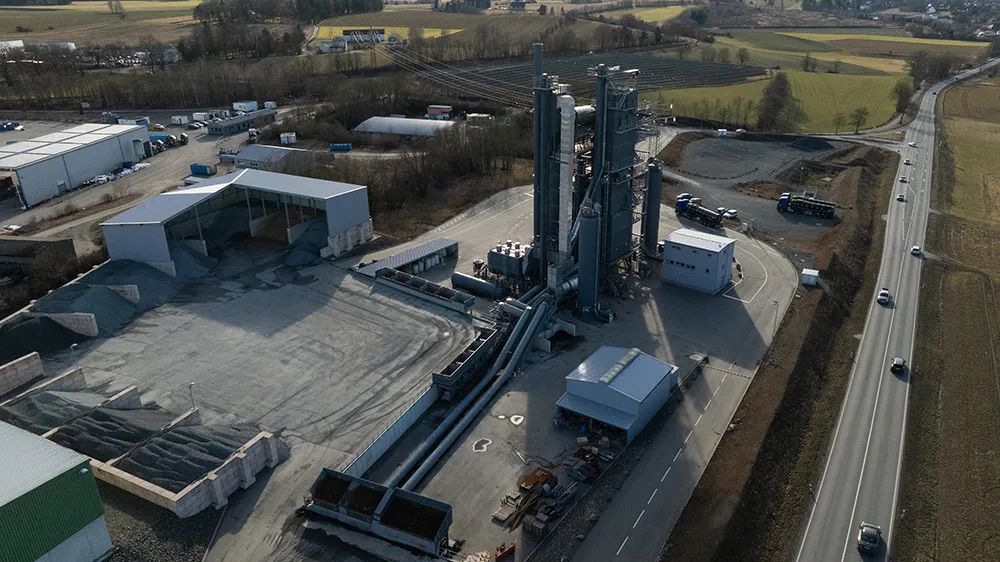
The Hof asphalt plant is a modern marvel in materials engineering. It houses the Ammann HRT 320, a high-performance plant that stands at the forefront of recycling and mixing technology. Designed for both hot and cold recycling, the plant is equipped with a twin-line recycling system capable of efficiently integrating reclaimed materials into the production process. To support this, the system includes four cold feeders dedicated to recycling material and ten cold feeders for new material, allowing for precise dosing and flexibility when incorporating recycled und fresh components into the asphalt mixes.
A standout feature of the Hof facility is its use of the RAH100 system—an advanced warm recycling technology. Powered by a patented hot gas generator system that reuses chimney air, this system allows the plant to produce high-quality asphalt while significantly reducing its environmental footprint. Importantly, the RAH100 system is capable of handling small production runs, making it possible to fulfill small-scale, customized orders using high percentages of recycled material without compromising quality or efficiency.
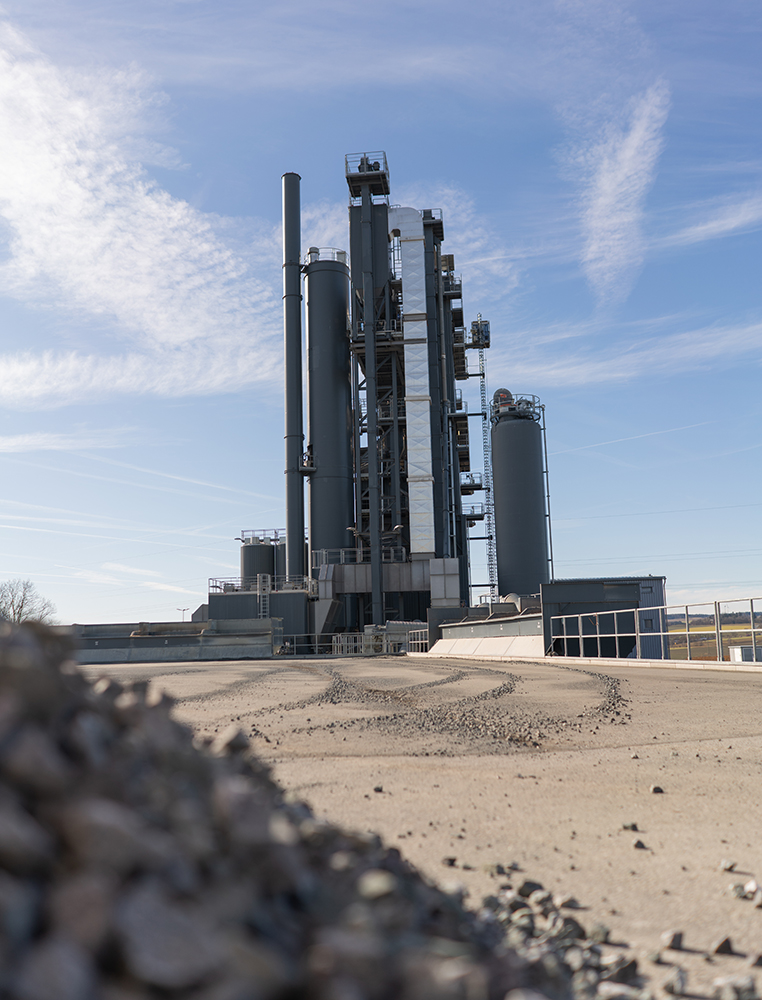 Flexibility is further emphasized through the mixing tower’s six-selection screen, which enables precise sorting of mineral aggregates for tailored mixes. The tower includes a 200-ton hot mineral silo, divided into two rows with a total of 12 chambers, allowing for the storage of multiple aggregate fractions. Two bypass chambers also ensure uninterrupted material flow and rapid changeover between production cycles.
Flexibility is further emphasized through the mixing tower’s six-selection screen, which enables precise sorting of mineral aggregates for tailored mixes. The tower includes a 200-ton hot mineral silo, divided into two rows with a total of 12 chambers, allowing for the storage of multiple aggregate fractions. Two bypass chambers also ensure uninterrupted material flow and rapid changeover between production cycles.
To support binder operations, the plant features four electric heated bitumen tanks, ensuring both storage flexibility and thermal consistency across multiple binder types. The vapors that arise during loading of the tanks or collected in a water lock to avoid odour nuisance on the site.
Additionally, a filler tower silo is installed, including a large chamber for coarse dust and three imported filler silos—one of which is dedicated to hydrated lime. This setup supports precise filler management and allows for the formulation of highly specialized asphalt mixes, enhancing the plant’s overall production range and quality control.
Integrated Storage and Fuel Flexibility
A significant infrastructural part of the plant is the 600-ton ready-mix silo, which is fully integrated into the central mixing tower. Divided into six chambers, this high-capacity silo allows for the simultaneous storage and dispatch of multiple asphalt types, supporting a wide range of production requirements. The system includes two dedicated truck lanes for the main silo, optimizing loading efficiency and minimizing downtime during high-demand periods.
In addition to the main silo, the facility features a direct load silo specifically designed for mastic asphalt. This setup ensures fast and reliable loading of specialized asphalt mixtures, making the plant highly versatile and well-suited to niche or demanding applications such as bridge decks and city street refurbishments.
Fuel flexibility is another key feature of the Hof plant’s operation. The burners are primarily powered by lignite powder—a cost-effective and regionally available energy source. Light oil serves as a secondary fuel, and the system is fully prepared for conversion to natural gas as well as liquid gas (LPG). This multi-fuel capability enhances both environmental adaptability and supply resilience in fluctuating energy markets.
Flexibility and Customisation
Versatility is another key strength of the Hof plant. It boasts three dedicated lines for the addition of solid additives, one of which is specifically configured for rubber granulate. This flexibility enables the production of customized asphalt mixes tailored to a variety of construction requirements, further emphasizing the plant’s commitment to innovation and sustainability.
Smart Operations with as1 Control System
Behind the scenes, the entire operation is orchestrated by the Ammann as1 control system—regarded as the most sophisticated plant control solutions on the market. This intelligent system ensures seamless operation, precise dosing, and consistent quality across every batch of asphalt produced.
The Hof plant also benefits from advanced software modules such as:
- as1 EcoView, which provides real-time monitoring of energy and emissions data, enabling operators to continuously optimize environmental performance.
- as1 Dynamic RAP Addition, a module that automatically adjusts the feed of reclaimed asphalt based on real-time plant conditions and mix specifications, enhancing both flexibility and precision when using recycled materials.
- as1 Solar Module, the latest innovation, designed to manage and optimize energy derived from the plant’s solar panels. It allows the system to dynamically decide whether to consume solar energy immediately or store it for later use, maximizing energy efficiency and contributing further to the plant’s sustainability goals.
A Model for the Future
With its Hof facility, the amo/Debus Gruppe is not just producing asphalt—it is setting new standards for sustainability, technological innovation, and operational excellence in the construction industry. Through advanced recycling technologies, integrated logistics infrastructure, multi-fuel systems, and intelligent automation, the plant embodies a forward-thinking approach that positions it as a model for the future of sustainable infrastructure.
Content produced in association with Ammann Group









