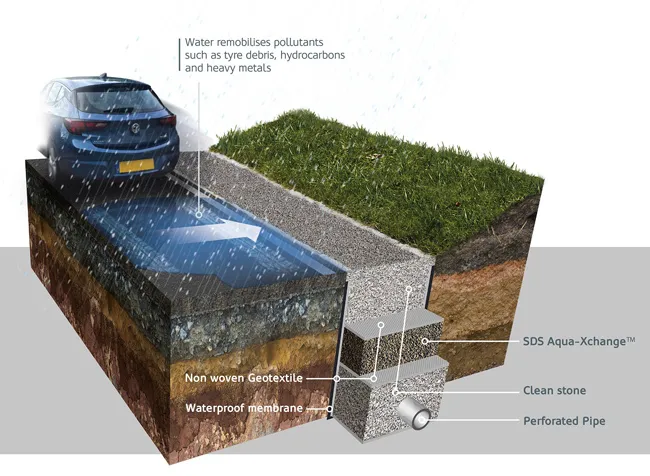
Methods of ensuring ecological and sustainable drainage in an urban environment are discussed in a new guide being published as part of Hydro International's Engineering Nature's Way initiative. Co-authored by Professor Richard Ashley, of EcoFutures , Sue Illman, of Illman Young Landscape architects, and Alex Stephenson, Stormwater Director of Hydro International and chair of the British Water SuDS focus group, Sustainable Drainage Systems (SuDS) in the Urban Landscape looks at Ecosystems Services, Green In
April 16, 2012
Read time: 2 mins

Methods of ensuring ecological and sustainable drainage in an urban environment are discussed in a new guide being published as part of Hydro International's Engineering Nature's Way initiative
Co-authored by Professor Richard Ashley, of EcoFutures , Sue Illman, of Illman Young Landscape architects, and Alex Stephenson, Stormwater Director ofMr Stephenson said: "A creative approach to planning for water above ground - in which stormwater is seen as a resource providing multiple bene ts - can help make the urban landscape a more balanced, healthy and enjoyable place to live.
"The Guide demonstrates that a correct interpretation of SuDS is one that can be applied to every development. It's simply no longer acceptable to have an 'either or' choice between SuDS or 'not possible'. A range of techniques, natural, manufactured or combined are available to recreate (or improve on) natural drainage paths." SuDS in the Urban Landscape is free to download at www.engineringnaturesway.co.uk.