A new study highlights the increased risk of road crash fatality facing the morbidly obese. The report, by the Transportation Research and Education Center of the University of California, said that those who are significantly overweight may have an 80% higher risk of being killed if involved in a car crash. The research suggests that vehicles tend to be designed to give protection for those with a BMI in the optimal 21-25 range. And vehicle testing generally involves the use of crash test dummies that repl
January 28, 2013
Read time: 2 mins
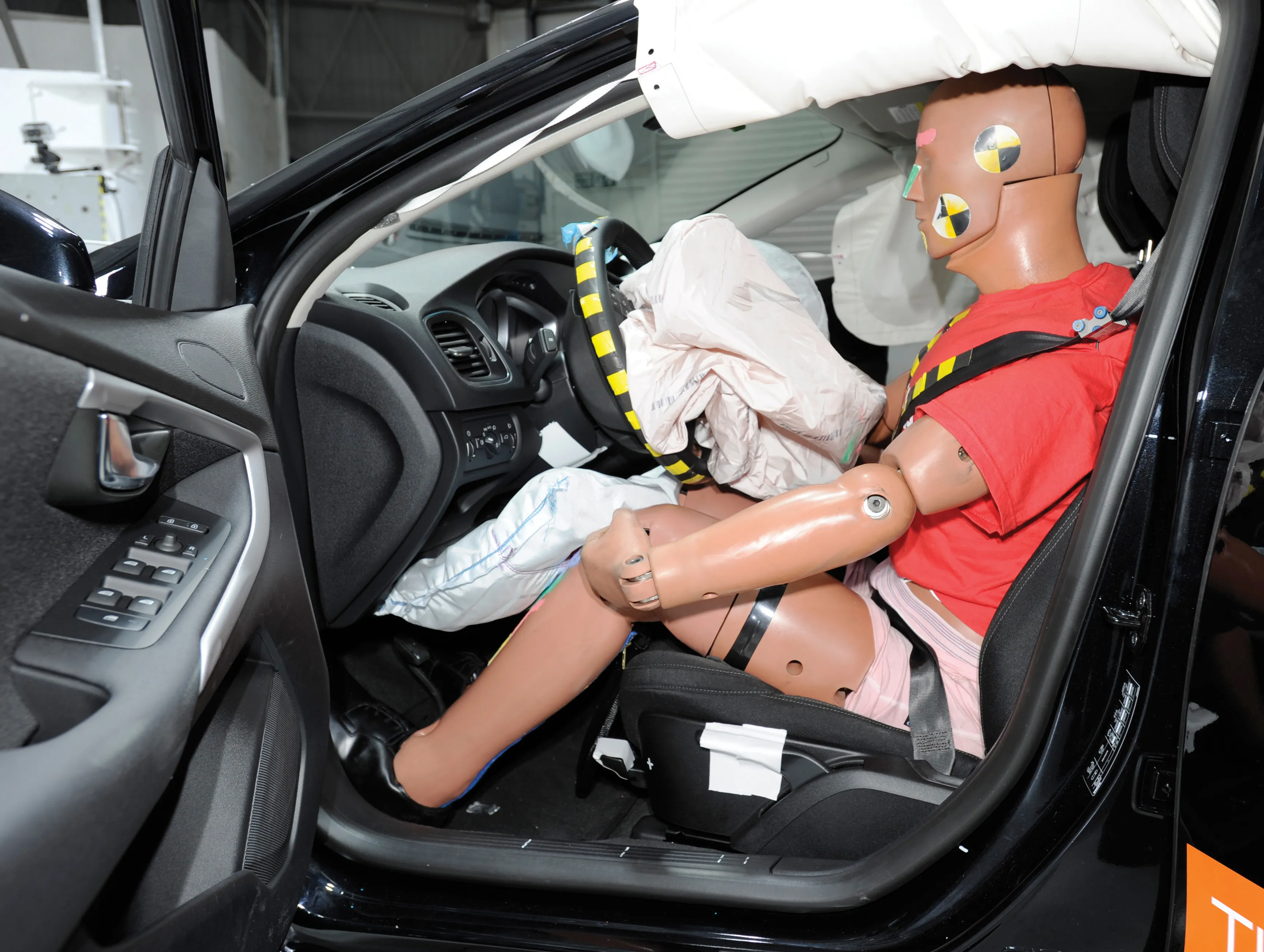
A new study highlights the increased risk of road crash fatality facing the morbidly obese. The report, by the Transportation Research and Education Center of the University of California, said that those who are significantly overweight may have an 80% higher risk of being killed if involved in a car crash. The research suggests that vehicles tend to be designed to give protection for those with a BMI in the optimal 21-25 range. And vehicle testing generally involves the use of crash test dummies that replicate the BMI of 21-25.
As part of the research data from some 57,491 road crashes that occurred in the US from 1996-2008 was analysed. Around 33% of those killed were not wearing seatbelts at the time of impact and these fatalities were not compared. But once those non seatbelt wearers were removed from the figures, the study revealed that those with a BMI of 30-34.9 were 21% more likely to die in a car crash than those with a BMI in the optimal 21-25 range. Those with a BMI of 35-39.9 were 51% more likely to be killed in the event of a crash than those with a BMI of 21-25. But drivers with a BMI of 40 or more were 80% more likely to be killed in a car crash than those with a BMI of 21-25. Obese women were at an even greater risk of dying from a crash than men. However the study also showed that men with a BMI of less than 21-25 also had a higher risk of being killed in a crash.
As part of the research data from some 57,491 road crashes that occurred in the US from 1996-2008 was analysed. Around 33% of those killed were not wearing seatbelts at the time of impact and these fatalities were not compared. But once those non seatbelt wearers were removed from the figures, the study revealed that those with a BMI of 30-34.9 were 21% more likely to die in a car crash than those with a BMI in the optimal 21-25 range. Those with a BMI of 35-39.9 were 51% more likely to be killed in the event of a crash than those with a BMI of 21-25. But drivers with a BMI of 40 or more were 80% more likely to be killed in a car crash than those with a BMI of 21-25. Obese women were at an even greater risk of dying from a crash than men. However the study also showed that men with a BMI of less than 21-25 also had a higher risk of being killed in a crash.






