Cummins has taken a major leap forward with engine design as it ditches cooled exhaust gas recirculation for its newest heavy-duty six-cylinder engine platform launched at bauma – the 12-litre QSM12. As its Tier 4 Final/Stage 4 engine solution in the 250-383kW sector, the QSM12 benefits from higher efficiency air handling and an advanced in-cylinder combustion process, allowing a return to using a straightforward wastegated turbocharger.
April 15, 2013
Read time: 2 mins
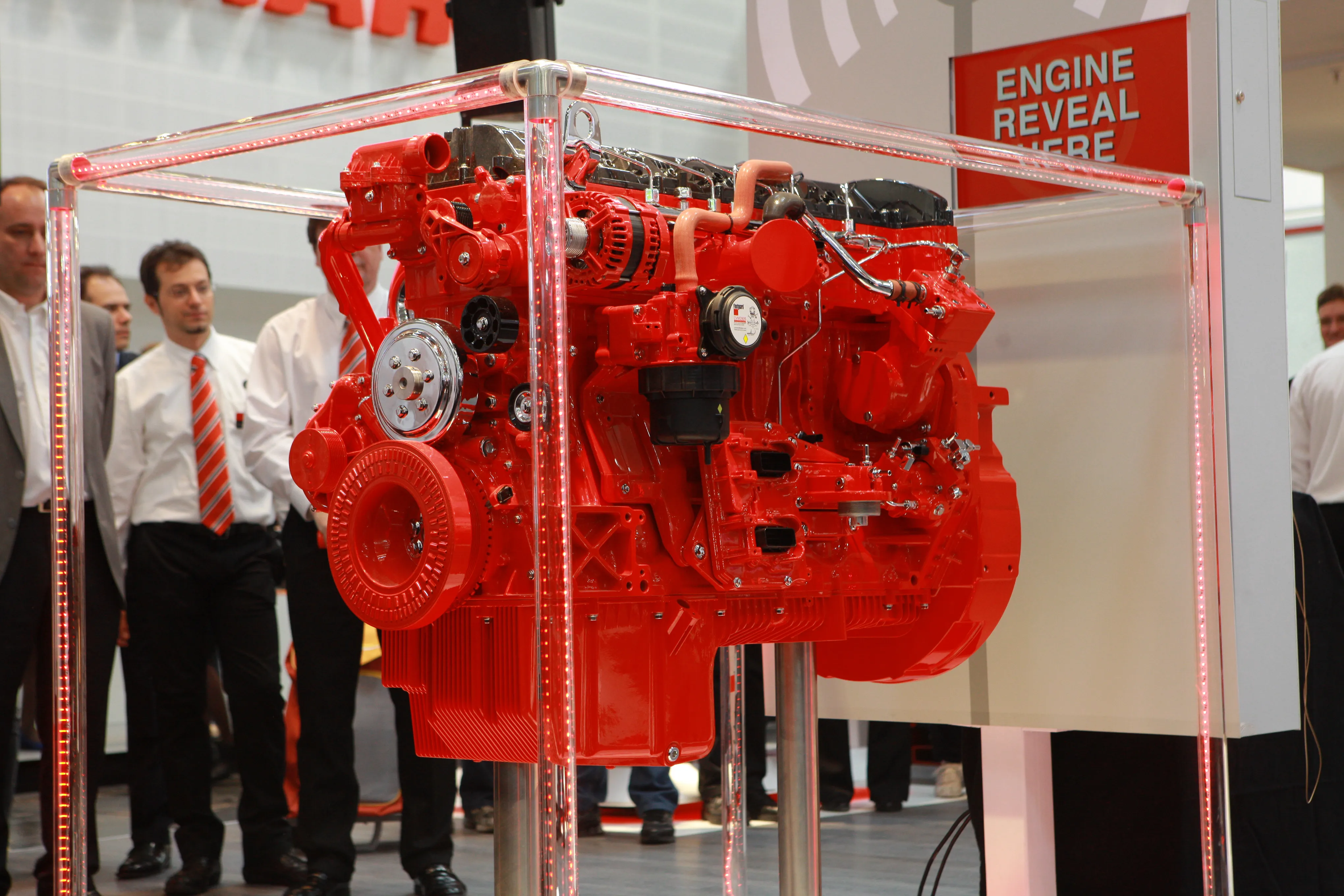
As its Tier 4 Final/Stage 4 engine solution in the 250-383kW sector, the QSM12 benefits from higher efficiency air handling and an advanced in-cylinder combustion process, allowing a return to using a straightforward wastegated turbocharger.
This latest engine design affords extra power potential, while dramatically reducing heat rejection by as much as 40% compared to engines using cooled EGR, resulting in the need for a much smaller cooling pack.
Achieving near-zero emissions levels without cooled EGR does, however, still require a form of exhaust after-treatment. For the QSM12, that treatment comes from a combined SCR and DPF system – the latter operates as a near passive device with automatic regeneration that occurs during less than 1% of engine running time.
“The QSM12 has simpler architecture, is no larger and no heavier than the QSX11.9 it replaces, and offers an impressive power to weight ratio,” said Tom Linebarger, Cummins chairman and CEO. “It provides OEMs with an ideal opportunity to downsize.”
Fuel injection comes from Cummins’ XPI system derived from the larger and more powerful 15litre QSX15. With multiple injection sequences and electronic management, the QSM12 can produce a torque peak of 2305Nm. Cummins said that a torque rise of up to 60% is available.
“When the cost of DEF is combined with the cost of fuel consumed, the overall fluid operating cost of the QSM12 for Tier 4 Final/Stage 4 is lower than that of the previous QSX11.9 at Tier 4i/Stage 3b,” he said.
Stand: A4/315
View more videosView more stories