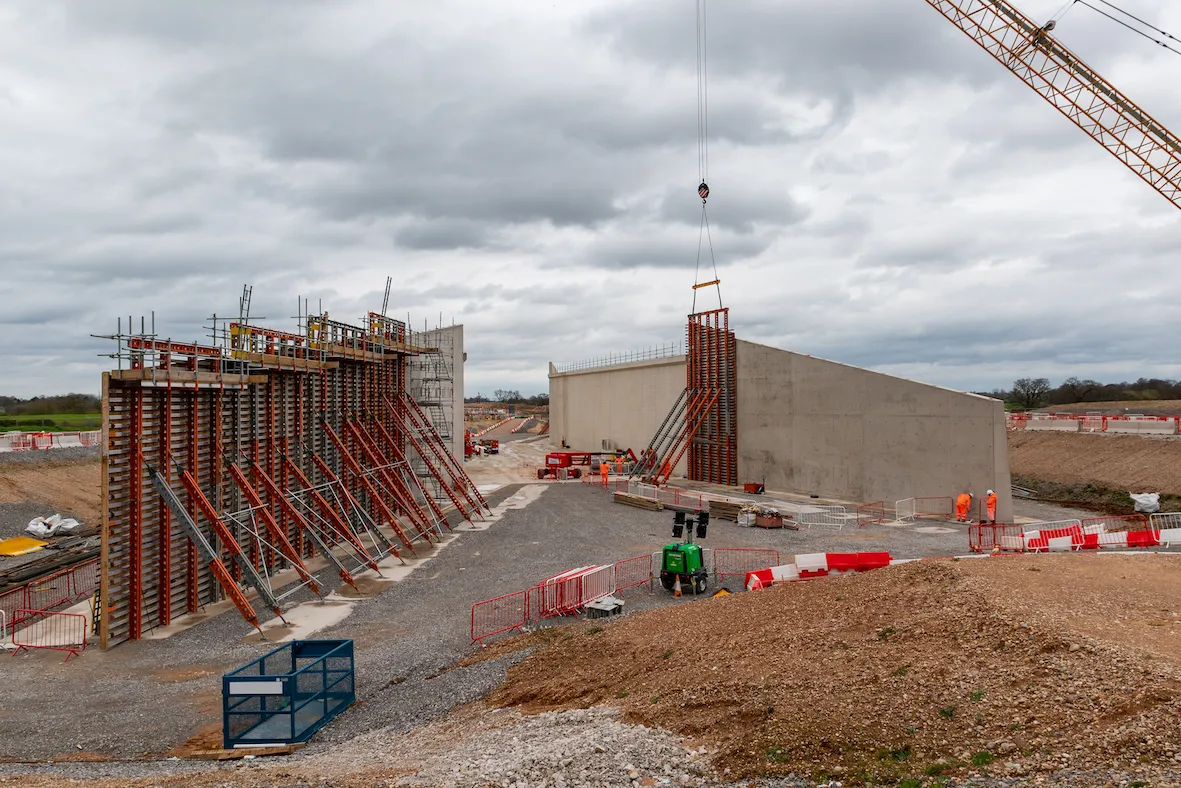
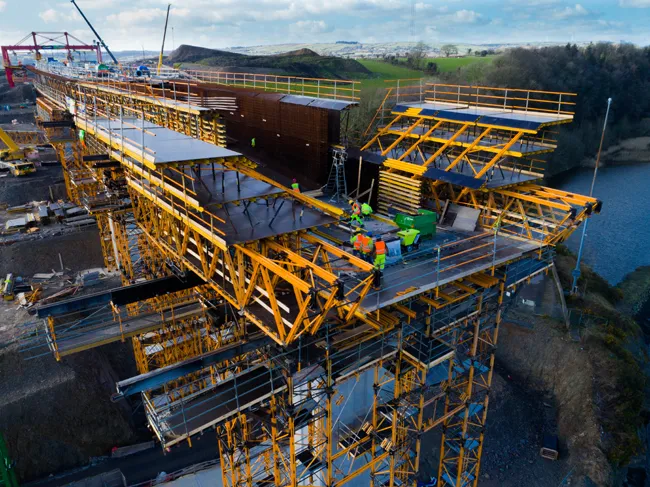
The structure was one of the highest concrete pours undertaken by Altrad RMDK in Europe to date with a pouring height of 13.5m to one of the main wingwalls. The project’s success was critical in maintaining the momentum of the HS2 timeline, highlighting the collaborative efforts of all involved.
The project presented a multitude of challenges due to the complex shape and weight of the bridge. One of the main challenges was overcoming the complex geometric patterns used for the wingwalls. These wingwalls tapered in height along their length and also along their width across the base. Not only this, but the external shutters lean into the internal face to taper in width across the height.
Where the wingwalls met the abutment walls, there was a complex movement joint that was required to allow for the expansion of the respective elements while still retaining the backfill that would eventually encapsulate the structure. The project demanded meticulous planning, coordination, and execution, with the additional pressure of adhering to a tight schedule.
Altrad RMDK and Galldris worked in partnership, bringing together expertise and resources from both organisations, which proved instrumental in overcoming the complex challenges posed by the project’s scope.
The contractor needed a solution that could be configured into various shapes and sizes. The solution was a custom specification to be engineered using Superslim Soldiers and Alform Aluminium Beams to meet the complex requirements.
Superslim Soldiers are designed to handle high loads, making them an ideal solution for a pour of this stature; they ensured that the formwork would remain stable under the pressure of the concrete. The beams helped maintain the structure’s shape and integrity during the entire pouring process, which was crucial in order to prevent deformities and ensure the accurate formation.
The Alform Beams provided a quick, durable and lightweight solution, allowing for simple installation, which was particularly advantageous on this high pour as moving and positioning formwork can be time and labour intensive.
Despite being lightweight, Alform Beams withstood the substantial pressure from the concrete. They worked alongside Superslim Soliders to ensure that formwork remained intact and stable throughout the pour. This was important as it was essential that the solutions maintained the tapering shapes and dimensions of the wingwalls throughout the pouring process.
“The A452 Kenilworth Overbridge project highlights Altrad RMD Kwikform’s engineering capabilities and innovative solutions,” said Stuart Grant, senior sales representative at Altrad RMD Kwikform. “Through partnerships, careful planning and the use of advanced equipment, the project demonstrated the effective collaboration needed for this infrastructure development.”
Altrad RMD Kwikform provides of formwork, falsework/shoring, heavy-duty support, ground shoring and safety and access systems, specialising in temporary structure needed to deliver major infrastructure and building projects. The company designs, hires and sells formwork, falsework/shoring, heavy-duty support, ground shoring as well as safety and access systems.
Key sectors include civil engineering and infrastructure, ground works, energy and industrial, commercial and multi-storey residential buildings. The company works in 3D designs and BIM (building information modelling)-compliant models through its visualisation software LocusEye.