The
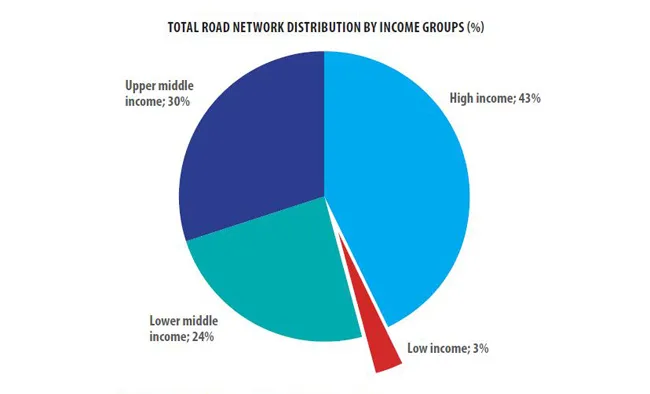
An analysis of the road network data reveals that low income countries account for just 3% of global road networks. With such a small percentage of road networks, low income countries have limited economic growth potential.
A reliable road network is vital to any country, and is especially important for low income countries, because a strong road network can lead to massive economic development benefits. Roads help economies grow by linking markets and allowing the flow of goods, people and services.
Available data provided by the WRS 2018 include the total length of road networks (in km) for each country. This total is broken down into smaller subsections that include: motorways, highways (main or national), secondary (or regional), and other roads. The WRS also categorises countries by geographic region and income group. The analysis of the road network data relating to a country's income group highlights a stark contrast in road network percentages:
• High income countries account for 43% of global road networks while low income countries account for only 3% of them.
The pie chart below above shows the total road network distribution by income group for the latest year of available data.
Source: IRF WRS 2018, latest year of available data for countries
The highest income group has the largest percentage of road networks followed by the upper middle income group, the lower middle income group and finally the low income group with the lowest percentage. The lack of funding and resources for new road networks combined with the absence of maintenance for roads that do exist in low income countries have led to infrastructure deficits and little economic growth. These deficits are partially responsible for preventing low income countries from moving into higher income groups. It is also important to look at the road network distribution by geographic region because the geographic regions of the world that are underdeveloped are usually those of low incomes. The pie chart below shows the total road network distribution by geographic regions of the world.
The key statistic to take away from this chart is Sub-Saharan Africa’s low percentage of road networks; it is just 6% in stark comparison to representing 17% of global land mass. Poor roads and infrastructure in this region make delivering goods and services a difficult task for businesses and individuals. According to data available, annual public spending on infrastructure was only 2% of GDP in 2009–15. Sub-Saharan Africa needs to invest billions of US dollars into its infrastructure. Until Sub-Saharan Africa is able to fund significantly higher road infrastructure construction and maintenance, the isolation caused by lack of well-developed and well-maintained road networks will continue to pose a key constraint to achieving the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals.
The new WRS 2018 encompass updated data on over 200 countries: Country Profile, Road Networks, Road Traffic, Multimodal Traffic Comparisons, Vehicles in Use, Road Accidents, Vehicles Industry (Production, Imports, Exports and First Registrations), Road Expenditures & Revenues, and Fuel Energy Prices.








