As a key engineering project on the Changsha-Chongqing Expressway in Southwest China, the Aizhai Bridge, constructed by the Hunan Road & Bridge Construction Group, was opened to traffic in March 2012. The Aizhai Bridge crosses the 1000m-wide scenic Dehang Canyon at an elevation of 355m. It has a main span of 1,176m, making it the world’s longest canyon-crossing bridge in the world.
The erection of the main girder (the stiffening girder) of the Aizhai Bridge encountered serious challenges, including a la
January 5, 2016
Read time: 3 mins
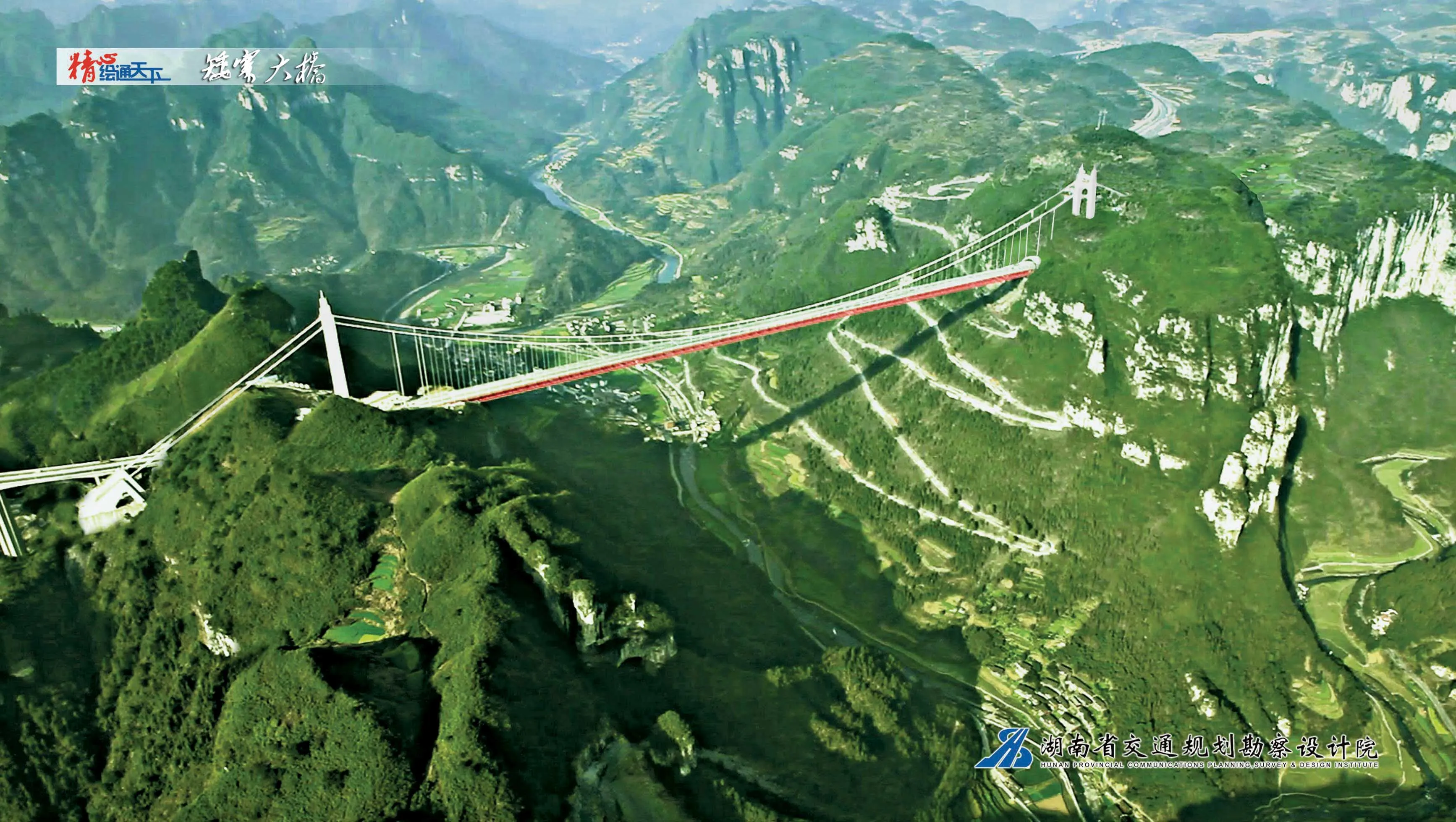

RSSAs a key engineering project on the Changsha-Chongqing Expressway in Southwest China, the Aizhai Bridge, constructed by the Hunan Road & Bridge Construction Group, was opened to traffic in March 2012. The Aizhai Bridge crosses the 1000m-wide scenic Dehang Canyon at an elevation of 355m. It has a main span of 1,176m, making it the world’s longest canyon-crossing bridge in the world.
The erection of the main girder (the stiffening girder) of the Aizhai Bridge encountered serious challenges, including a large bridge span length, a deep valley, dangerous mountain roads, a narrow construction site, and complex weather conditions — among others. All the three conventional girder-erecting techniques at the time failed to address the needs in constructing the Aizhai Bridge. After five years of hard and persistent exploration, the team at HNRB proposed an innovative technique, called the “Girder-Conveying Track Cable” technique, which overcame the constraints of conventional methods. This new technique enables a safe, highly efficient, and economical solution for girder erection and has now been widely accepted around the world as the fourth method for the construction of suspension bridges.
The basic principle of the GCTC technique is to install horizontal wire ropes under the suspenders as temporary traveling rails (track cables), which are used to carry and transport segments of the main girder from both banks to their mounting positions, where they are then raised by lifting devices and connected to the suspenders. The erection of the main girder starts from the mid-span and proceeds from there to both banks until all the segments are completed.
This technique creatively uses the main cable, suspenders and temporary track cables to form a safe and stable supporting system. It also significantly increases the installation capacity and enables the transportation and installation of large-size girder segments (up to 200tonnes). In addition, it significantly speeds up the construction, and with a construction speed six times faster than the conventional methods, this technique has become the fastest technique for erecting the main girder of suspension bridges. The technology is especially applicable for the construction of long-span suspension bridges when the horizontal or vertical transportation of the girder segments is restricted. It is also applicable for the installation of the main girder of half-through and through arch bridges, and is expected to be a promising technique for wide use.
The application of the GCTC Technique has shown great success at the Aizhai Bridge. It took only 80 days to complete the erection of all 69 girder segments and shortened the construction period by 10 months, as compared to conventional methods. Meanwhile, the new technology has reduced the use of structural steel by about 2000 tonnes, creating a direct economic benefit of US $20.5 million (CNY 124 million).
3918 IRF Washington.
The erection of the main girder (the stiffening girder) of the Aizhai Bridge encountered serious challenges, including a large bridge span length, a deep valley, dangerous mountain roads, a narrow construction site, and complex weather conditions — among others. All the three conventional girder-erecting techniques at the time failed to address the needs in constructing the Aizhai Bridge. After five years of hard and persistent exploration, the team at HNRB proposed an innovative technique, called the “Girder-Conveying Track Cable” technique, which overcame the constraints of conventional methods. This new technique enables a safe, highly efficient, and economical solution for girder erection and has now been widely accepted around the world as the fourth method for the construction of suspension bridges.
The basic principle of the GCTC technique is to install horizontal wire ropes under the suspenders as temporary traveling rails (track cables), which are used to carry and transport segments of the main girder from both banks to their mounting positions, where they are then raised by lifting devices and connected to the suspenders. The erection of the main girder starts from the mid-span and proceeds from there to both banks until all the segments are completed.
This technique creatively uses the main cable, suspenders and temporary track cables to form a safe and stable supporting system. It also significantly increases the installation capacity and enables the transportation and installation of large-size girder segments (up to 200tonnes). In addition, it significantly speeds up the construction, and with a construction speed six times faster than the conventional methods, this technique has become the fastest technique for erecting the main girder of suspension bridges. The technology is especially applicable for the construction of long-span suspension bridges when the horizontal or vertical transportation of the girder segments is restricted. It is also applicable for the installation of the main girder of half-through and through arch bridges, and is expected to be a promising technique for wide use.
The application of the GCTC Technique has shown great success at the Aizhai Bridge. It took only 80 days to complete the erection of all 69 girder segments and shortened the construction period by 10 months, as compared to conventional methods. Meanwhile, the new technology has reduced the use of structural steel by about 2000 tonnes, creating a direct economic benefit of US $20.5 million (CNY 124 million).