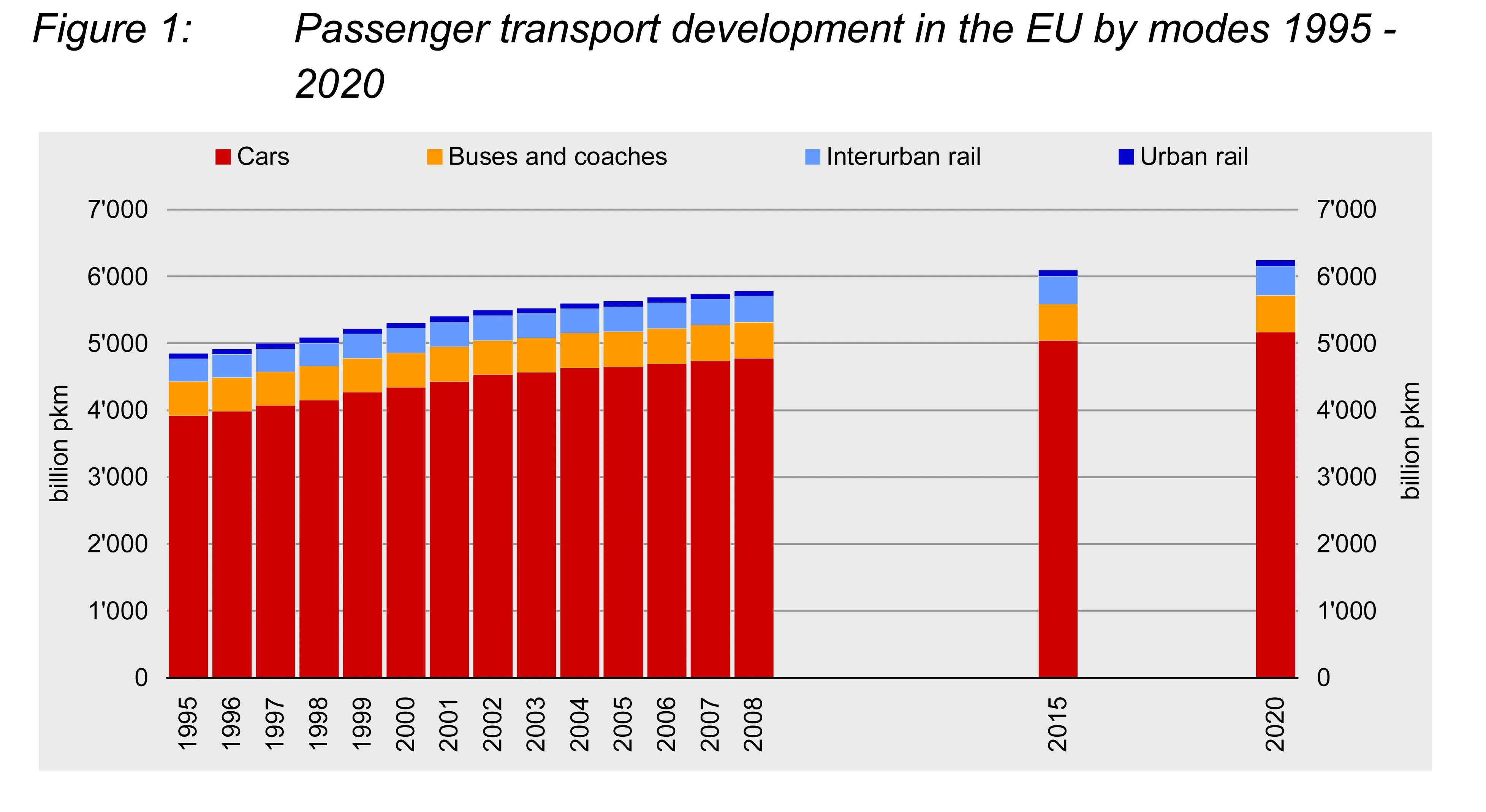
No country in the EU is without a growing transport market. This is the main message of the European Transport Report 2007/08 prepared by ProgTrans of Basel, Switzerland.
In the 27
Interestingly, overall passenger traffic demand is less dependent on population forecasts than on economic development. Although the overall population in the new EU countries will diminish by nine million persons until 2020, the total passenger mileage (cars, buses/coaches and rail) will go up by 25% from 2006 to 2020. While the market share in the old EU countries is expected to remain stable over time, the mode share for roads in the new EU Member States will grow form 72% to 77% at the cost of coaches and railway.
On the other hand, old EU countries can expect a rise of 14 million inhabitants compared to 2006 (+3.5%) and roughly 8% more pkm. This indicates that passenger transport demand in the old EU world has already reached a relatively high level of saturation but still offers some room for further modest growth.
The report says that if the EU is targeting continuous economic growth in Europe there needs to be an efficient transport system meeting changing transport requirements in both qualitative and quantitative terms.
With a view to the different modes of transport recent policy and market trends underline that there will be few dynamism: road absorbed in all EU countries 76.4% of the total transport performance in 2006 and is expected to push its market share to 77.3% within the next 14 years. Railway plays a less important role with a share of above 17% which is expected to not change considerably until 2020.
Tonnes-kilometres in old EU countries account for 86% of total EU goods transport performance in 2006. This underlines the strength of the Western EU countries, compared to the new members. However, the transport market in the new EU will show stronger growth rates in relative terms (+44% in the new, +31% in the old EU countries), but starting from a much lower level. As the EU enlargement is aiming at facilitating international trade, more imports and exports of goods will be generated. In those countries with a low level of international trade and low average salaries the highest growth rates are expected. It is, according to the long term forecasts of this study, not very likely that these framework conditions will change in a short period of time.
The main difference between both parties of the EU is that railways in the new EU will still lose market shares but they are coming from a stronger position than in the old EU. There, the rail mode share will decrease from 45% in 2006 to 40% in 2020 whereas road will go up from 52% to 57%. Railways still had a market share of 60% in 2000.
Old EU countries will not face further changes in mode share as road has already reached a level of more than 80% in 2006, says the report. Forthcoming economic activities in the old EU countries will call for road rather than for railway transport services, quoted in quantitative terms.







