Siemens wins BRT order A major contract order was placed with Siemens by DIMTS (Delhi Integrated Multi-Modal Transit System Limited) on behalf of the local Transport Department for the development of the city's Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) system.
February 9, 2012
Read time: 2 mins
A major contract order was placed with 1134 Siemens by DIMTS (2519 Delhi Integrated Multi-Modal Transit System Limited) on behalf of the local Transport Department for the development of the city's Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) system.
The order is for the supply of design services and the installation of a significant range of intelligent traffic signalling equipment including extra low voltage controllers and associated technology for 20 junctions.
Additional equipment and services being supplied includes the provision of a new Central Control Room with Urban Traffic Control (UTC) and SCOOT, over 600 traffic and pedestrian signals, around 350 above-ground detectors, a supply of nearside push-button units for pedestrian crossings and a long-term maintenance contract.
On behalf of the company responsible for placing the contract, AmiChand Srivastava, principal (Transport Planning) for DIMTS, confirmed that Siemens had won the contract order for the first BRT corridor from Ambedkar Nagar to Delhi Gate (length 14.5km.).
"In addition to offering a highly comprehensive and technically robust capability, Siemens provides a reliable range of innovative and sustainable products and services. This gives us great confidence as we develop the next stages of the BRT to meet the increasing needs for mobility with economic growth and for the benefit of the growing volume of people travelling in and around our city," he said.
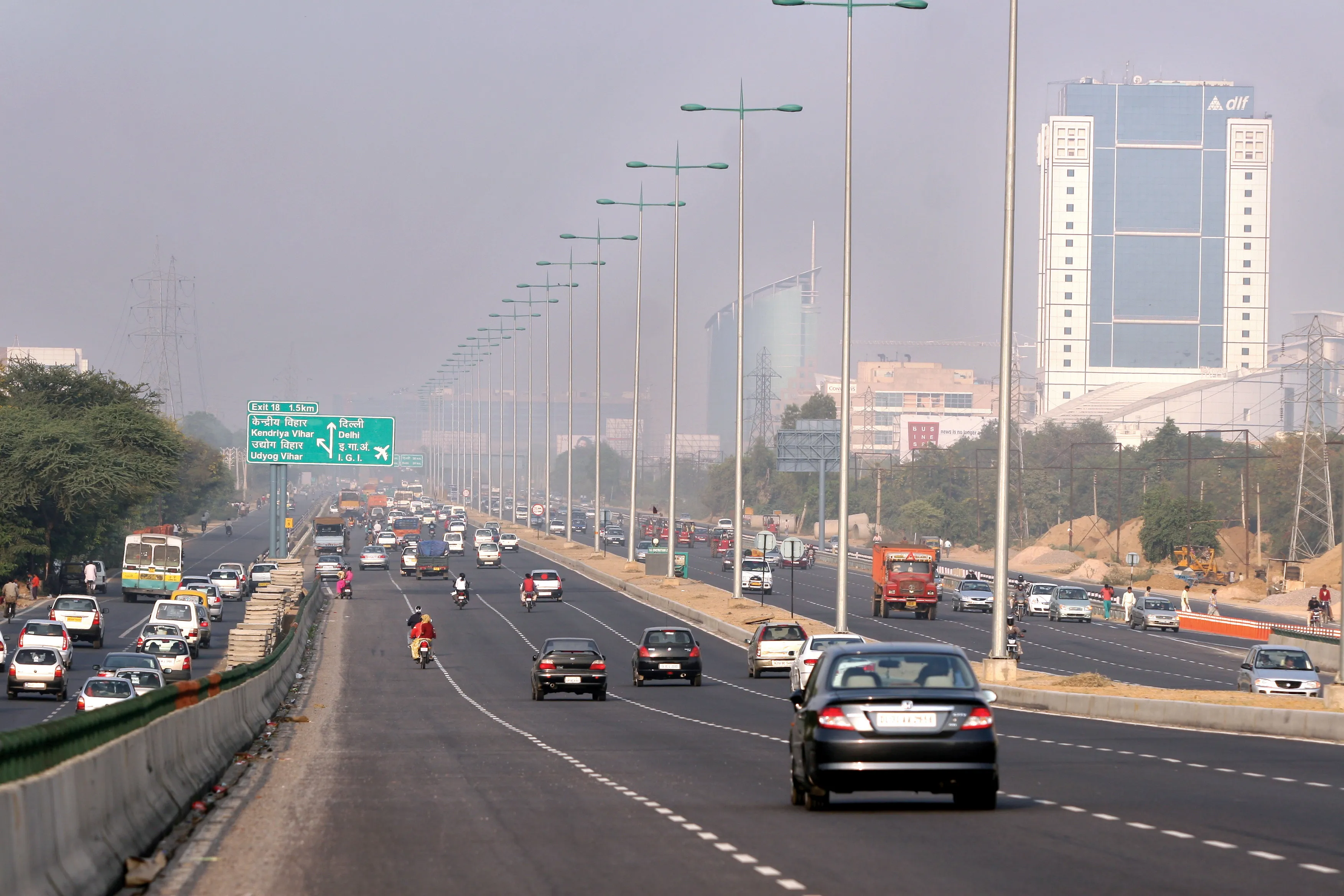
Delhi is emerging as a hub for all kinds of commercial activities. According to a recent study, it is projected that Delhi and its satellite towns will be among the most densely populated cities in the world by 2020. The transportation network in Delhi is predominantly road based and the number of private vehicles on Delhi's road is increasing at a phenomenal rate.
Around 46% of total personal trips in Delhi were completed by using the public transport system (bus and metro) in 2007-08.
To attract a larger number of bus passengers, the BRT system is designed to play an important role. A reliable and good quality public transportation system offers better mobility, besides other social advantages such as reducing congestion and air pollution. In total, Delhi Government plans to build 26 BRT corridors, covering a total length of 310km by 2020. It has planned to build seven of these in phase one by 2010.
The order is for the supply of design services and the installation of a significant range of intelligent traffic signalling equipment including extra low voltage controllers and associated technology for 20 junctions.
Additional equipment and services being supplied includes the provision of a new Central Control Room with Urban Traffic Control (UTC) and SCOOT, over 600 traffic and pedestrian signals, around 350 above-ground detectors, a supply of nearside push-button units for pedestrian crossings and a long-term maintenance contract.
On behalf of the company responsible for placing the contract, AmiChand Srivastava, principal (Transport Planning) for DIMTS, confirmed that Siemens had won the contract order for the first BRT corridor from Ambedkar Nagar to Delhi Gate (length 14.5km.).
"In addition to offering a highly comprehensive and technically robust capability, Siemens provides a reliable range of innovative and sustainable products and services. This gives us great confidence as we develop the next stages of the BRT to meet the increasing needs for mobility with economic growth and for the benefit of the growing volume of people travelling in and around our city," he said.
Delhi is emerging as a hub for all kinds of commercial activities. According to a recent study, it is projected that Delhi and its satellite towns will be among the most densely populated cities in the world by 2020. The transportation network in Delhi is predominantly road based and the number of private vehicles on Delhi's road is increasing at a phenomenal rate.
Around 46% of total personal trips in Delhi were completed by using the public transport system (bus and metro) in 2007-08.
To attract a larger number of bus passengers, the BRT system is designed to play an important role. A reliable and good quality public transportation system offers better mobility, besides other social advantages such as reducing congestion and air pollution. In total, Delhi Government plans to build 26 BRT corridors, covering a total length of 310km by 2020. It has planned to build seven of these in phase one by 2010.