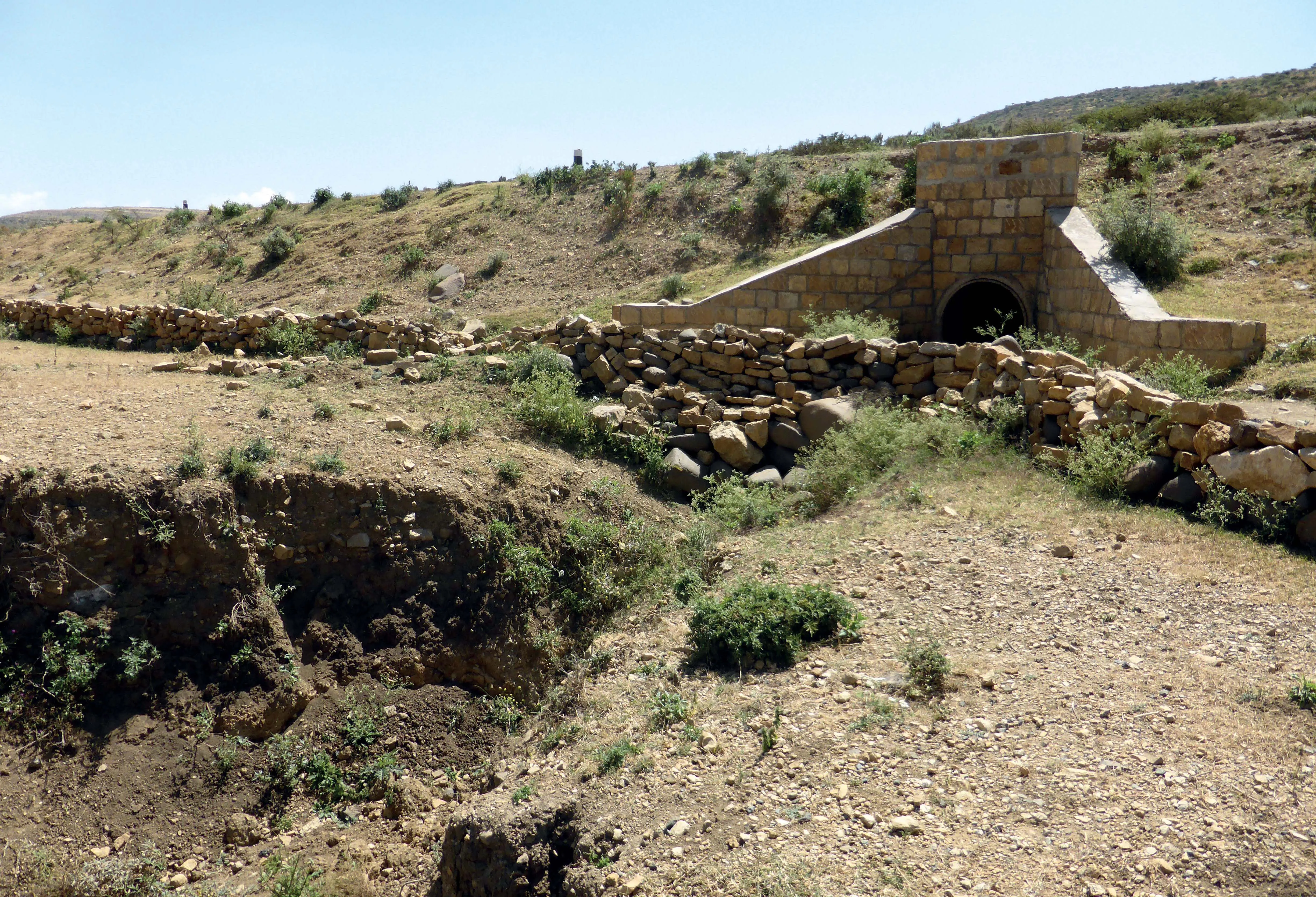
A highly innovative solution for road embankment stabilisation has helped save costs by up to 30% over conventional techniques. Balfour Beatty Mott MacDonald has used electrical current to stabilise embankments on a busy UK dual carriageway, avoiding disruption to motorists, cutting carbon by 40% and costs by 30%, and producing zero waste
When slope failure was detected on embankments carrying the popular A21 dual carriageway, Balfour Beatty Mott MacDonald pioneered a novel technique to tackle the prob
August 28, 2013
Read time: 3 mins

A highly innovative solution for road embankment stabilisation has helped save costs by up to 30% over conventional techniques. Balfour Beatty Mott MacDonald has used electrical current to stabilise embankments on a busy UK dual carriageway, avoiding disruption to motorists, cutting carbon by 40% and costs by 30%, and producing zero waste
When slope failure was detected on embankments carrying the popular A21 dual carriageway,The earth embankment had been constructed with sides that were too steep and combined with poor drainage, this was causing the slopes to shear and slump. “Progressive failure would have undermined the safety barrier,” said Michael Tandy, Balfour Beatty Mott MacDonald geotechnical engineer.
Slope failure is normally tackled by replacing earth with granular material that is freer draining and better withstands loading, mixing lime into the embankment to stiffen and strengthen it, installing soil nails, or building retaining walls. All involve removing vegetation and closing traffic lanes. “The A21 is a major commuter route, so restricting the width of the road would have resulted in major congestion,” Tandy said.
Instead the firm opted to try a technique combining electro-osmosis with soil nailing and drainage, patented by its supply chain partner Electrokinetic. More than 200 years ago, it was observed that when an electrical current was passed through fine-grained material, it drew water along with it. Electrokinetic has harnessed this principle, known as, electrokinetic geosynthetics (EKG).
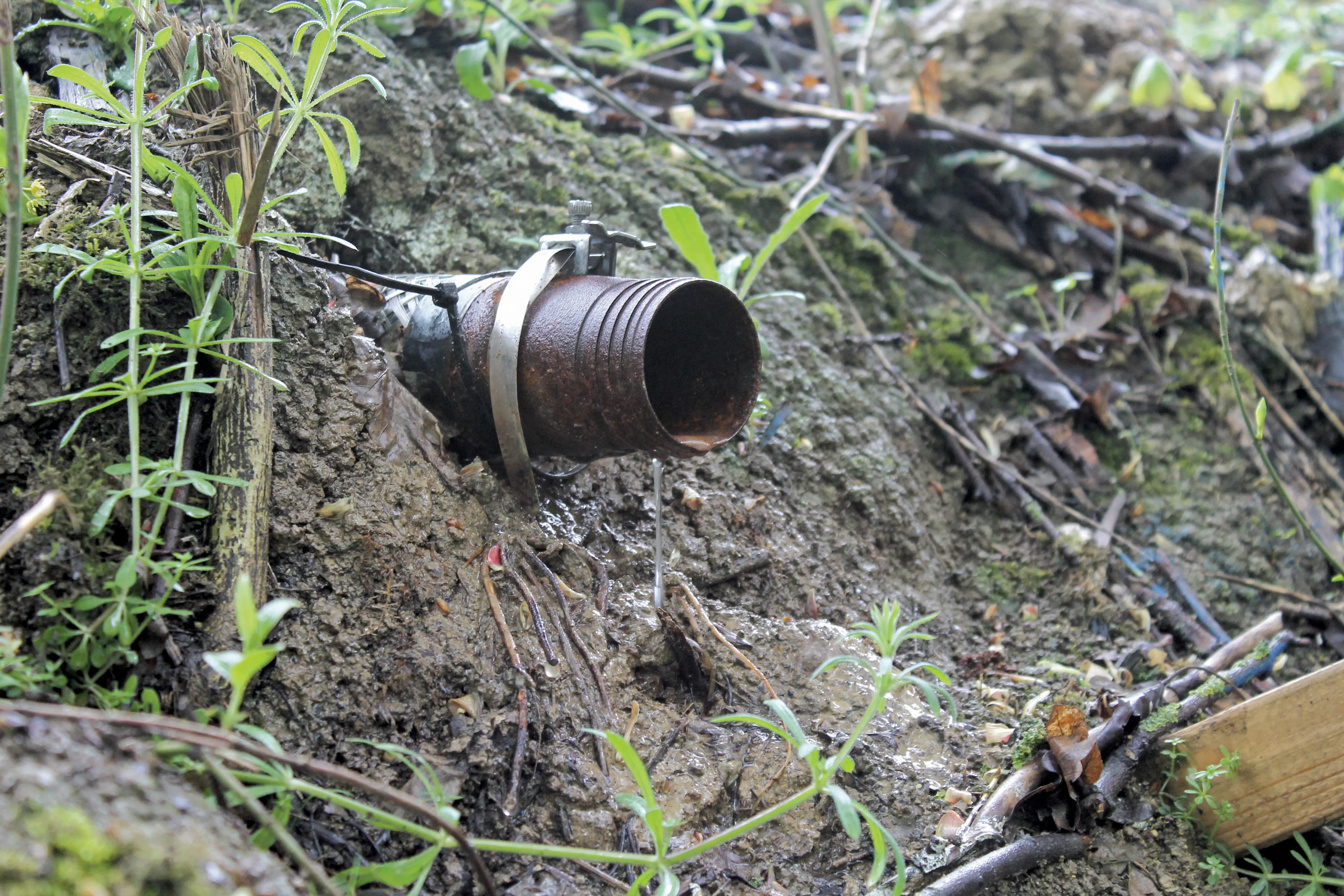
The company has developed a lightweight, mobile, track-mounted drilling and nailing rig, which was used to install 195 perforated steel tubes into the ground. Driven anodes were angled downward, acting like nails to hold material in place, while cathodes were inserted into pre-bored holes, sloping upward to act as drains to bring water from deep within the embankment to the surface.
Using a mobile generator, current was passed from anodes to cathodes to draw water out of the soil structure, consolidating it. “This method has been used in mining, in construction of dams and docks and on the
After six weeks the drainage phase was complete and the electricity shut off. To convert the anodes into permanent soil nails, grout was injected down the tubes and forced out, through the perforations, into the surrounding ground, locking the nails firmly into the soil matrix. The drains remain permanently in place.
Work was carried out from the foot of the embankment, meaning no lane closures were required. “The approach taken by Balfour Beatty Mott MacDonald meant personnel weren’t exposed to risk from passing vehicles,” Tandy said.
The scheme has won two industry awards for innovation and sustainability. “The technology worked so well that the